Why is Google Racist? Examining Algorithmic Bias and Its Impact
The question, “Why is Google racist?” isn’t just provocative; it’s a reflection of growing concerns about algorithmic bias. While Google, as a company, vehemently denies intentional discrimination, evidence suggests its search algorithms and AI models can inadvertently perpetuate and amplify existing societal biases. This article delves into the complexities of algorithmic bias, explores how it manifests within Google’s products, and discusses the potential consequences and solutions.
Understanding Algorithmic Bias
Algorithmic bias arises when algorithms, designed to be objective, systematically produce unfair or discriminatory outcomes. This bias isn’t necessarily intentional; it often stems from the data used to train these algorithms. If the training data reflects existing societal biases, the algorithm will learn and replicate those biases. Think of it like teaching a child: if the information they receive is skewed, their understanding of the world will be skewed as well. [See also: Understanding AI Bias: A Comprehensive Guide]
Several factors contribute to algorithmic bias:
- Biased Training Data: The data used to train algorithms may contain historical biases, stereotypes, or underrepresentation of certain groups.
- Flawed Algorithm Design: The way an algorithm is designed can inadvertently introduce bias. For example, certain features might be given more weight than others, leading to discriminatory outcomes.
- Feedback Loops: Algorithms can reinforce existing biases by learning from user interactions. If users interact with biased content, the algorithm may promote similar content, perpetuating the bias.
- Lack of Diversity in Development Teams: If the teams developing these algorithms lack diversity, they may be less likely to identify and address potential biases.
Manifestations of Bias in Google Products
The impact of algorithmic bias can be seen across various Google products, from search results to image recognition and even translation services. Let’s examine some specific examples:
Search Results and Stereotypes
One of the most visible manifestations of bias is in Google’s search results. Studies have shown that searches for certain professions, like “CEO” or “engineer,” tend to return images predominantly featuring white men. Conversely, searches for terms like “unprofessional hairstyles” may disproportionately display images of Black women. This perpetuates harmful stereotypes and reinforces existing societal biases. This is why the question of “Why is Google racist?” arises.
Even seemingly innocuous searches can reveal underlying biases. For instance, searching for information about specific medical conditions may yield results that are more relevant to certain demographic groups than others, potentially disadvantaging those who don’t fit the typical profile. The core issue of “Why is Google racist?” boils down to representation and equitable outcomes.
Image Recognition
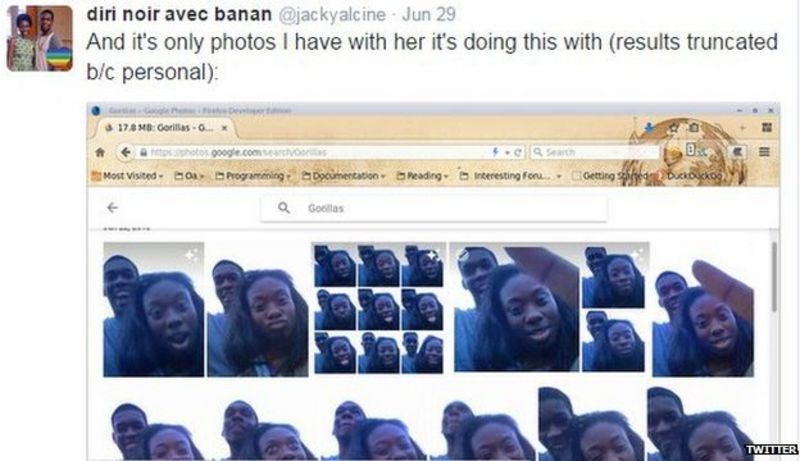
Google’s image recognition technology has also faced criticism for its biases. In the past, Google Photos misidentified Black people as gorillas, a deeply offensive and racially charged error. While Google has since implemented measures to prevent this specific error from recurring, it highlights the potential for AI to perpetuate harmful stereotypes.
Translation Services
Google Translate, while incredibly useful, has also been shown to exhibit gender bias. For example, when translating gender-neutral languages like Turkish into English, the system often defaults to assigning male pronouns to certain professions, such as “doctor” or “engineer,” and female pronouns to others, such as “nurse” or “teacher.” This reinforces traditional gender roles and stereotypes.
Advertising and Targeting
Google’s advertising platform, which relies heavily on algorithms to target users with relevant ads, can also contribute to discriminatory practices. Studies have shown that Google’s ad targeting algorithms can discriminate based on race, gender, and other protected characteristics, potentially limiting opportunities for certain groups. For instance, housing ads may be shown less frequently to users of color, perpetuating housing segregation. The question of “Why is Google racist?” extends to its advertising practices.
The Consequences of Algorithmic Bias
The consequences of algorithmic bias are far-reaching and can have a significant impact on individuals and society as a whole. These consequences include:
- Reinforcement of Stereotypes: Algorithmic bias can reinforce existing stereotypes and prejudice, making it harder for marginalized groups to overcome societal barriers.
- Discrimination in Opportunities: Biased algorithms can lead to discrimination in areas such as hiring, lending, and housing, limiting opportunities for certain groups.
- Erosion of Trust: When people perceive algorithms as unfair or biased, it can erode trust in technology and institutions.
- Perpetuation of Inequality: Algorithmic bias can exacerbate existing inequalities and contribute to a more divided society.
Addressing the underlying reasons behind “Why is Google racist?” is crucial for building a more equitable future.
Addressing Algorithmic Bias: Potential Solutions
Addressing algorithmic bias requires a multi-faceted approach involving researchers, developers, policymakers, and the public. Some potential solutions include:
Improving Data Diversity and Quality
Ensuring that training data is diverse and representative is crucial for mitigating bias. This involves actively seeking out and incorporating data from underrepresented groups. It also means carefully auditing existing datasets to identify and correct biases. Data quality is also paramount; inaccurate or incomplete data can exacerbate bias.
Developing Fairer Algorithms
Researchers are developing new techniques for designing fairer algorithms that are less susceptible to bias. These techniques include:
- Adversarial Debiasing: Training algorithms to actively identify and remove bias from data.
- Fairness Metrics: Using metrics to measure and track the fairness of algorithms.
- Explainable AI (XAI): Developing algorithms that are more transparent and explainable, allowing users to understand how decisions are made.
Promoting Diversity in Tech
Increasing diversity in the tech industry is essential for addressing algorithmic bias. Diverse teams are more likely to identify and address potential biases in algorithms. Companies should actively recruit and retain employees from underrepresented groups.
Regulation and Oversight
Some argue that regulation and oversight are necessary to ensure that algorithms are used fairly and responsibly. This could involve establishing independent bodies to audit algorithms and enforce fairness standards. The debate surrounding “Why is Google racist?” often leads to calls for greater accountability.
Raising Awareness
Raising public awareness about algorithmic bias is crucial for holding companies accountable and promoting change. This involves educating the public about the potential consequences of bias and empowering them to demand fairer algorithms. Understanding “Why is Google racist?” is the first step towards change.
Google’s Response and Efforts
Google has acknowledged the issue of algorithmic bias and has taken steps to address it. The company has invested in research on fairness in AI and has developed tools and resources to help developers build fairer algorithms. Google also publishes reports on its efforts to address bias in its products.
However, critics argue that Google’s efforts are not enough and that the company needs to do more to address the root causes of algorithmic bias. They argue that Google’s business model, which relies heavily on data collection and targeted advertising, can incentivize bias. The question of “Why is Google racist?” persists despite these efforts.
Conclusion: The Ongoing Challenge of Algorithmic Bias
The question of “Why is Google racist?” is a complex one with no easy answers. While Google, as a company, may not be intentionally discriminatory, its algorithms can perpetuate and amplify existing societal biases. Addressing this issue requires a multi-faceted approach involving researchers, developers, policymakers, and the public. By improving data diversity, developing fairer algorithms, promoting diversity in tech, and raising awareness, we can work towards a future where algorithms are used fairly and responsibly. The fight against algorithmic bias is an ongoing challenge, but it is a challenge worth fighting for a more equitable and just society. The persistence of the question “Why is Google racist?” underscores the importance of continued vigilance and action. [See also: The Future of AI Ethics: Navigating the Moral Landscape]
Ultimately, understanding and mitigating algorithmic bias is essential for ensuring that AI benefits all of humanity and does not perpetuate existing inequalities. The conversation about “Why is Google racist?” needs to continue to drive meaningful change.
