What is Remote Monitoring? A Comprehensive Guide
In today’s interconnected world, businesses and individuals alike rely heavily on the smooth operation of various systems and devices. From critical infrastructure to everyday gadgets, ensuring optimal performance and preventing failures is paramount. This is where remote monitoring comes into play. But what is remote monitoring exactly? This comprehensive guide will delve into the intricacies of remote monitoring, exploring its definition, applications, benefits, and future trends.
Defining Remote Monitoring
At its core, remote monitoring involves observing and tracking the status and performance of equipment, systems, or processes from a distant location. This is typically achieved through the use of sensors, software, and communication networks that transmit data to a central monitoring station or dashboard. Think of it as having a virtual eye on your assets, constantly providing real-time insights without the need for physical presence.
The key components of a remote monitoring system generally include:
- Sensors: These devices collect data on various parameters such as temperature, pressure, humidity, vibration, voltage, and more.
- Communication Network: This network, which can be wired or wireless, transmits the data from the sensors to the central monitoring system. Common options include cellular, Wi-Fi, satellite, and LoRaWAN.
- Data Processing and Analysis: The central system receives the data, processes it, and analyzes it to identify trends, anomalies, and potential problems. This often involves sophisticated algorithms and machine learning techniques.
- Alerting and Notification: When a critical event or threshold is breached, the system automatically generates alerts and notifications to designated personnel, allowing them to take immediate action.
- User Interface: A user-friendly dashboard or interface provides a visual representation of the monitored data, allowing users to easily track performance and identify areas of concern.
Applications of Remote Monitoring
The applications of remote monitoring are vast and diverse, spanning across numerous industries and sectors. Here are some notable examples:
Healthcare
In healthcare, remote monitoring plays a crucial role in improving patient care and reducing costs. Wearable devices and sensors can track vital signs such as heart rate, blood pressure, and glucose levels, allowing doctors to monitor patients remotely and intervene proactively in case of emergencies. This is particularly beneficial for patients with chronic conditions or those recovering from surgery. [See also: Telehealth Solutions for Modern Healthcare]
Manufacturing
In manufacturing, remote monitoring is used to optimize production processes, prevent equipment failures, and improve overall efficiency. Sensors can track the performance of machinery, identify potential problems before they lead to downtime, and enable predictive maintenance. This can significantly reduce maintenance costs and improve productivity. Imagine monitoring the vibration of a critical pump to detect early signs of bearing failure.
Energy
The energy sector relies heavily on remote monitoring to ensure the reliability and efficiency of power grids, oil and gas pipelines, and renewable energy systems. Sensors can monitor the performance of wind turbines, solar panels, and other energy assets, allowing operators to optimize energy production and prevent outages. Furthermore, remote monitoring can help detect leaks in pipelines, preventing environmental damage and ensuring safety.
Transportation
In transportation, remote monitoring is used to track the location and condition of vehicles, optimize routes, and improve safety. GPS trackers can monitor the location of trucks, trains, and ships, while sensors can track parameters such as temperature, humidity, and pressure within cargo containers. This allows logistics companies to ensure the safe and efficient delivery of goods. Think about monitoring the temperature of refrigerated trucks transporting perishable goods to maintain quality.
Agriculture
Remote monitoring is transforming the agriculture industry by enabling farmers to optimize irrigation, fertilization, and pest control. Sensors can monitor soil moisture, temperature, and nutrient levels, allowing farmers to make data-driven decisions about when and how to irrigate and fertilize their crops. Drones equipped with cameras can also be used to monitor crop health and identify areas affected by pests or diseases. This leads to increased yields and reduced resource consumption.
Environmental Monitoring
Remote monitoring is essential for tracking environmental conditions and protecting natural resources. Sensors can monitor air and water quality, track wildlife populations, and detect pollution. This information is crucial for understanding environmental changes and developing effective conservation strategies. For example, monitoring water levels in reservoirs to manage water resources during droughts.
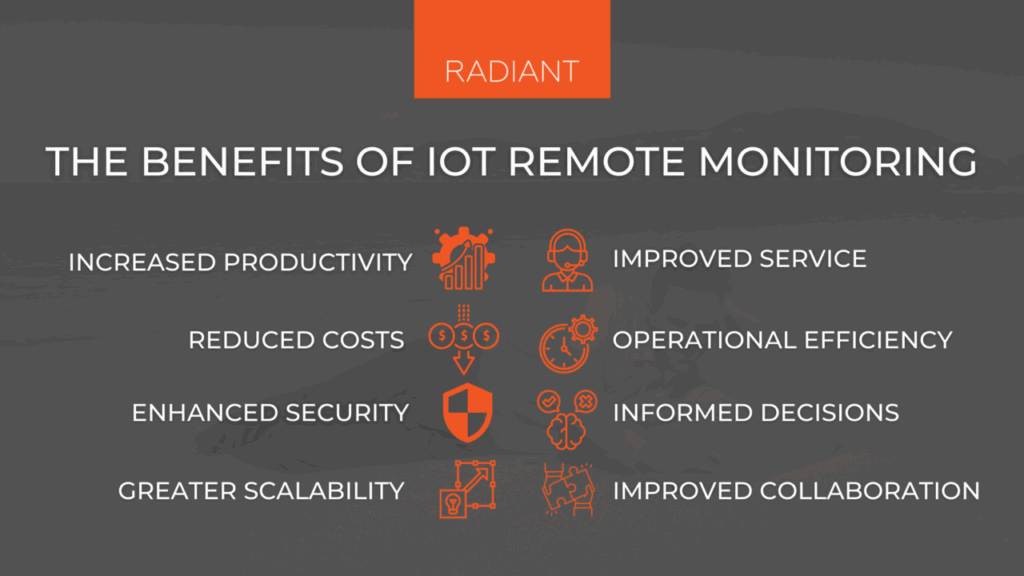
Benefits of Remote Monitoring
The benefits of remote monitoring are numerous and far-reaching. Some of the key advantages include:
- Reduced Downtime: By detecting potential problems early, remote monitoring can prevent equipment failures and minimize downtime.
- Improved Efficiency: By optimizing processes and resource utilization, remote monitoring can improve overall efficiency.
- Reduced Costs: By preventing failures, optimizing maintenance schedules, and reducing resource consumption, remote monitoring can significantly reduce costs.
- Enhanced Safety: By detecting potential hazards and alerting personnel to dangerous situations, remote monitoring can enhance safety.
- Better Decision-Making: By providing real-time data and insights, remote monitoring enables better decision-making.
- Increased Productivity: By automating tasks and providing employees with the information they need to do their jobs effectively, remote monitoring can increase productivity.
- Scalability: Remote monitoring solutions can be easily scaled to accommodate growing needs and expanding operations.
Challenges of Remote Monitoring
While remote monitoring offers numerous benefits, it also presents some challenges. These challenges include:
- Initial Investment: Implementing a remote monitoring system can require a significant initial investment in sensors, software, and infrastructure.
- Data Security: Transmitting and storing sensitive data over the internet raises concerns about data security. It’s essential to implement robust security measures to protect against cyber threats.
- Integration Complexity: Integrating remote monitoring systems with existing IT infrastructure can be complex and require specialized expertise.
- Data Overload: The sheer volume of data generated by remote monitoring systems can be overwhelming. It’s important to have the right tools and processes in place to analyze the data and extract meaningful insights.
- Connectivity Issues: Reliable connectivity is essential for remote monitoring. In areas with poor cellular coverage or limited access to internet, it can be challenging to maintain a stable connection.
Future Trends in Remote Monitoring
The field of remote monitoring is constantly evolving, driven by advancements in technology and changing business needs. Some of the key trends shaping the future of remote monitoring include:
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML): AI and ML are being increasingly used to analyze data from remote monitoring systems, identify patterns, and predict future events. This enables predictive maintenance and proactive problem-solving.
- Internet of Things (IoT): The proliferation of IoT devices is driving the growth of remote monitoring. IoT devices are becoming more affordable and easier to deploy, making it possible to monitor a wider range of assets and processes.
- Cloud Computing: Cloud computing provides a scalable and cost-effective platform for storing and processing data from remote monitoring systems. This makes it easier for businesses to deploy and manage remote monitoring solutions.
- Edge Computing: Edge computing involves processing data closer to the source, reducing latency and improving responsiveness. This is particularly important for applications that require real-time decision-making.
- 5G Technology: The rollout of 5G networks is enabling faster and more reliable connectivity for remote monitoring systems. This is particularly beneficial for applications that require high bandwidth and low latency.
Conclusion
Remote monitoring is a powerful tool that can help businesses and individuals improve efficiency, reduce costs, and enhance safety. By understanding the principles, applications, and benefits of remote monitoring, you can leverage this technology to gain a competitive advantage and achieve your goals. As technology continues to evolve, remote monitoring will become even more sophisticated and pervasive, transforming the way we manage our assets and operations. Embracing remote monitoring is no longer just a trend; it’s a necessity for staying ahead in today’s rapidly changing world. The insights gained from remote monitoring are invaluable for proactive decision-making and overall system optimization.
