What is Platform as a Service (PaaS)? A Comprehensive Guide
In the ever-evolving landscape of cloud computing, understanding the various service models is crucial for businesses of all sizes. One such model, Platform as a Service (PaaS), offers a compelling solution for developers and organizations seeking to streamline their application development and deployment processes. But what is Platform as a Service exactly? This comprehensive guide will delve into the intricacies of PaaS, exploring its benefits, use cases, and how it compares to other cloud service models.
Defining Platform as a Service (PaaS)
Platform as a Service (PaaS) is a cloud computing model that delivers a complete platform – including hardware, software, and infrastructure – for developing, running, and managing applications. Unlike Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), which provides raw computing resources, PaaS offers a higher-level abstraction, allowing developers to focus on building and deploying applications without the burden of managing the underlying infrastructure. Think of it as renting a fully equipped kitchen instead of just the ingredients and appliances; you can start cooking immediately without worrying about setting up the oven or plumbing.
Key Components of a PaaS Solution
A typical PaaS solution comprises several key components that work together to provide a comprehensive development and deployment environment:
- Operating Systems: The foundation upon which applications run.
- Programming Languages Execution Environment: Support for various programming languages and frameworks.
- Databases: Storage and management of application data.
- Web Servers: Handling incoming requests and serving application content.
- Development Tools: Integrated Development Environments (IDEs), debuggers, and other tools to aid in application development.
- Deployment Tools: Tools for deploying and managing applications.
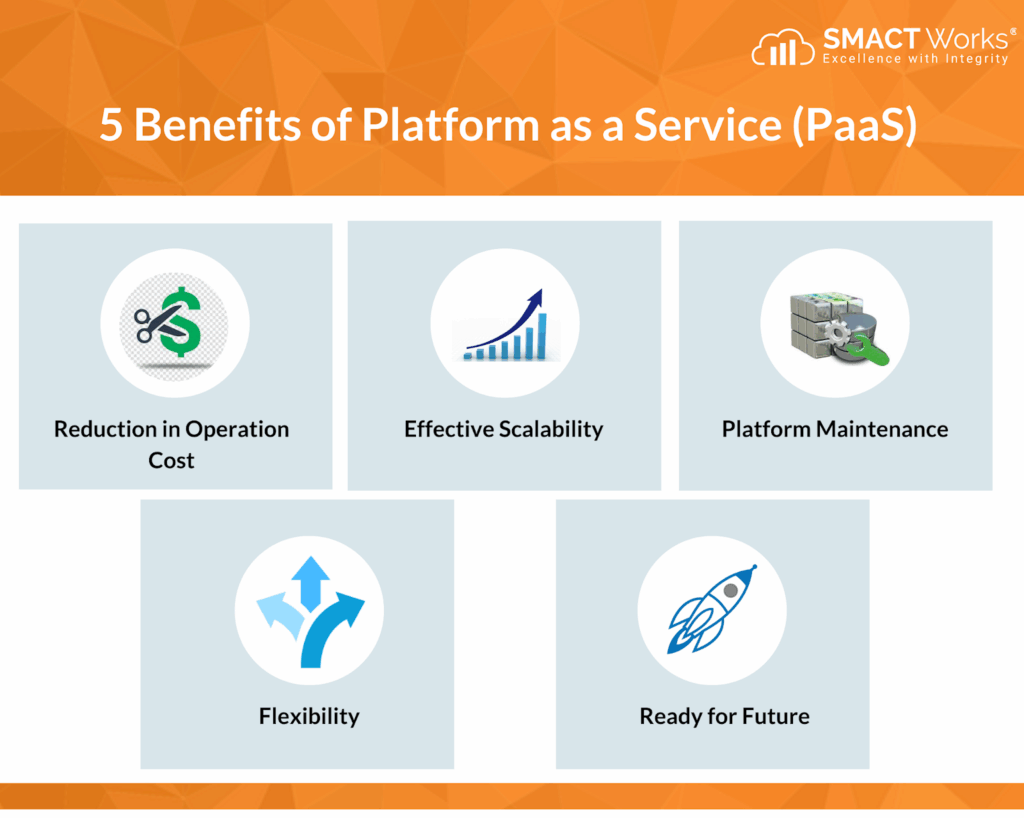
Benefits of Using Platform as a Service
Adopting a PaaS solution offers numerous advantages for organizations and developers:
Reduced Operational Overhead
One of the primary benefits of PaaS is the significant reduction in operational overhead. By offloading infrastructure management tasks to the PaaS provider, developers can focus on what they do best: building and innovating. This frees up valuable time and resources that can be redirected towards core business objectives.
Faster Time to Market
PaaS accelerates the application development lifecycle by providing developers with pre-configured tools and environments. This eliminates the need to spend time setting up and configuring infrastructure, allowing developers to quickly prototype, test, and deploy applications. This rapid development cycle translates to faster time to market and a competitive edge.
Improved Collaboration
PaaS solutions often include collaboration features that facilitate teamwork and communication among developers. These features can include shared code repositories, version control systems, and integrated communication tools, enabling developers to work together more effectively and efficiently.
Scalability and Flexibility
PaaS provides inherent scalability and flexibility, allowing applications to easily scale up or down based on demand. This ensures that applications can handle peak loads without performance degradation and that resources are not wasted during periods of low activity. This scalability is crucial for businesses experiencing rapid growth or fluctuating demand.
Cost Savings
While there is a cost associated with using a PaaS solution, it can often result in significant cost savings compared to traditional on-premises infrastructure. By eliminating the need to purchase and maintain hardware, organizations can reduce capital expenditures and operational expenses. Furthermore, the pay-as-you-go pricing model of many PaaS providers allows organizations to only pay for the resources they consume, optimizing cost efficiency.
Support for Multiple Languages and Frameworks
Most PaaS offerings support a wide range of programming languages, frameworks, and databases. This allows developers to choose the tools that best suit their needs and expertise, without being constrained by the limitations of the underlying infrastructure. This flexibility is particularly beneficial for organizations with diverse development teams and application requirements.
Use Cases for Platform as a Service
PaaS is well-suited for a variety of use cases, including:
- Web Application Development: Building and deploying web applications quickly and easily.
- Mobile Application Development: Creating and deploying mobile applications with integrated backend services.
- API Development and Management: Developing and managing APIs for internal and external use.
- Business Analytics: Analyzing large datasets and generating insights for business decision-making.
- Internet of Things (IoT) Application Development: Building and deploying applications that connect to and manage IoT devices.
PaaS vs. IaaS vs. SaaS
It’s important to understand the differences between PaaS, Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), and Software as a Service (SaaS). These three cloud service models offer different levels of abstraction and control.
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
IaaS provides access to fundamental computing resources, such as virtual machines, storage, and networks. Users have full control over these resources but are also responsible for managing the operating system, middleware, and applications. IaaS offers the most flexibility but also requires the most technical expertise.
Platform as a Service (PaaS)
As discussed, PaaS provides a complete platform for developing, running, and managing applications. Users are responsible for developing and deploying applications but do not need to manage the underlying infrastructure. PaaS offers a balance between flexibility and ease of use.
Software as a Service (SaaS)
SaaS provides access to ready-to-use applications over the internet. Users do not need to manage any of the underlying infrastructure or software. SaaS offers the least flexibility but is the easiest to use. Examples of SaaS applications include Salesforce, Google Workspace, and Microsoft Office 365.
[See also: IaaS vs PaaS vs SaaS: Understanding the Cloud Service Models]
The choice between IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS depends on the specific needs and requirements of the organization. IaaS is best suited for organizations that need maximum control over their infrastructure. PaaS is ideal for organizations that want to focus on application development without managing infrastructure. SaaS is the best choice for organizations that need ready-to-use applications without any management overhead.
Examples of PaaS Providers
Several companies offer PaaS solutions, each with its own unique features and capabilities. Some popular PaaS providers include:
- AWS Elastic Beanstalk: A PaaS offering from Amazon Web Services that simplifies the deployment and management of web applications and services.
- Google App Engine: A PaaS offering from Google Cloud Platform that allows developers to build and deploy web applications and mobile backends.
- Microsoft Azure App Service: A PaaS offering from Microsoft Azure that provides a platform for building, deploying, and scaling web applications, mobile backends, and APIs.
- Heroku: A popular PaaS provider that offers a simple and intuitive platform for deploying and managing web applications.
- Red Hat OpenShift: A PaaS platform based on Kubernetes that provides a container-centric environment for developing and deploying applications.
Choosing the Right PaaS Solution
Selecting the right PaaS solution is a critical decision that can significantly impact the success of application development projects. When evaluating PaaS providers, consider the following factors:
- Supported Languages and Frameworks: Ensure that the PaaS supports the programming languages and frameworks that your development team is familiar with.
- Scalability and Performance: Evaluate the PaaS’s ability to scale applications to meet peak demand and maintain consistent performance.
- Security: Assess the PaaS’s security features and compliance certifications to ensure that your data is protected.
- Integration Capabilities: Determine how well the PaaS integrates with other tools and services that your organization uses.
- Pricing: Compare the pricing models of different PaaS providers and choose the one that offers the best value for your needs.
- Support and Documentation: Evaluate the quality of the PaaS provider’s support and documentation.
The Future of Platform as a Service
Platform as a Service continues to evolve and adapt to the changing needs of the cloud computing landscape. Emerging trends in PaaS include:
- Serverless Computing: PaaS offerings are increasingly incorporating serverless computing capabilities, allowing developers to build and deploy applications without managing servers.
- Containerization: Container technologies like Docker and Kubernetes are becoming increasingly prevalent in PaaS environments, providing a more flexible and portable way to package and deploy applications.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML): PaaS providers are integrating AI and ML capabilities into their platforms, allowing developers to easily build and deploy intelligent applications.
- Low-Code/No-Code Platforms: Some PaaS offerings are incorporating low-code/no-code development tools, enabling citizen developers to build applications without extensive coding knowledge.
Conclusion
Platform as a Service (PaaS) is a powerful cloud computing model that offers numerous benefits for developers and organizations. By providing a complete platform for developing, running, and managing applications, PaaS enables organizations to reduce operational overhead, accelerate time to market, improve collaboration, and achieve greater scalability and flexibility. As the cloud computing landscape continues to evolve, PaaS is poised to play an increasingly important role in helping organizations innovate and compete in the digital age. Understanding what is Platform as a Service and its potential is crucial for any organization looking to leverage the power of the cloud.
