What is Data Centre Management: A Comprehensive Guide
In today’s digital age, data centres are the backbone of our interconnected world. They house the critical infrastructure that powers everything from social media to online banking. But what exactly is data centre management, and why is it so crucial? This comprehensive guide will delve into the intricacies of data centre management, exploring its key components, challenges, and best practices.
Understanding Data Centres
Before diving into management, let’s define what a data centre is. A data centre is a dedicated space, often a building or a portion of a building, that houses computer systems and associated components, such as telecommunications and storage systems. It typically includes redundant or backup power supplies, redundant data communications connections, environmental controls (e.g., air conditioning, fire suppression), and various security devices.
Data centres are essential for businesses of all sizes. They provide the infrastructure needed to store, process, and distribute data. Without data centres, many of the online services we rely on daily would simply not exist.
What is Data Centre Management?
Data centre management encompasses the processes and practices involved in maintaining the optimal operation of a data centre. It’s a multifaceted discipline that includes everything from infrastructure management and security to capacity planning and disaster recovery. Effective data centre management ensures that the data centre operates efficiently, securely, and reliably, minimizing downtime and maximizing performance.
Think of a data centre as a complex machine. Data centre management is like being the mechanic, electrician, and plumber all rolled into one, ensuring everything runs smoothly. It’s a proactive approach to prevent problems before they occur and to resolve issues quickly when they do arise.
Key Components of Data Centre Management
Data centre management comprises several critical components, each playing a vital role in the overall health and performance of the facility:
Infrastructure Management
This involves the physical infrastructure of the data centre, including:
- Power: Ensuring a reliable and redundant power supply is crucial. This includes uninterruptible power supplies (UPS), generators, and power distribution units (PDUs).
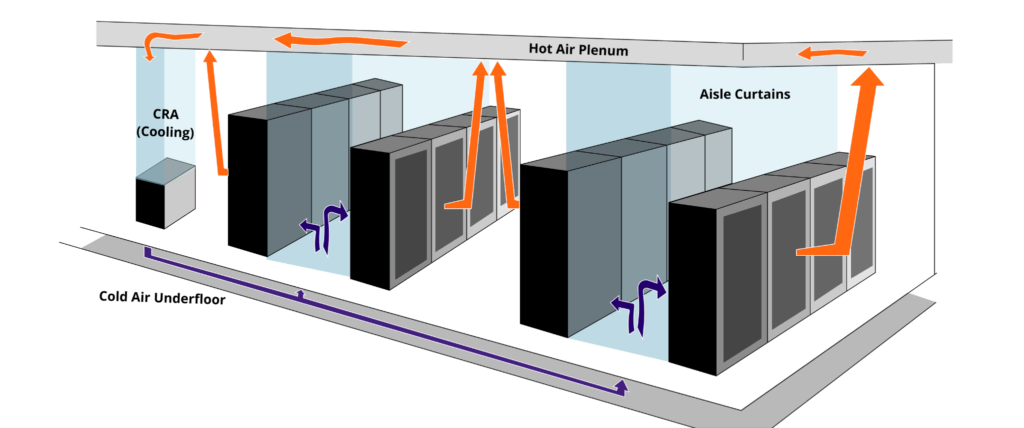
- Cooling: Maintaining optimal temperature and humidity levels to prevent equipment overheating. This involves cooling systems like CRAC (Computer Room Air Conditioning) units and liquid cooling solutions.
- Networking: Managing the network infrastructure, including routers, switches, and cabling, to ensure seamless data flow.
- Servers and Storage: Maintaining the physical servers and storage devices, including hardware maintenance, upgrades, and replacements.
Security Management
Protecting the data centre from physical and cyber threats is paramount. Security management includes:
- Physical Security: Implementing access control measures, surveillance systems, and security personnel to prevent unauthorized access.
- Cybersecurity: Protecting against cyberattacks, malware, and data breaches through firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and security audits.
- Data Security: Ensuring data integrity and confidentiality through encryption, access controls, and data loss prevention (DLP) measures.
Capacity Planning
Predicting future resource needs and ensuring the data centre has sufficient capacity to meet those needs. This involves:
- Monitoring Resource Utilization: Tracking CPU usage, memory consumption, storage capacity, and network bandwidth.
- Forecasting Demand: Predicting future growth based on historical data and business projections.
- Scaling Resources: Adding or upgrading hardware and software to meet increasing demand.
Disaster Recovery and Business Continuity
Developing and implementing plans to recover from disasters and ensure business continuity. This includes:
- Backup and Recovery: Regularly backing up data and testing recovery procedures.
- Redundancy and Failover: Implementing redundant systems and failover mechanisms to minimize downtime.
- Disaster Recovery Planning: Creating a comprehensive plan that outlines procedures for responding to various disaster scenarios.
Monitoring and Management Tools
Utilizing software and hardware tools to monitor the health and performance of the data centre. These tools provide real-time insights into system performance, identify potential problems, and automate routine tasks. Examples include:
- Data Centre Infrastructure Management (DCIM) Software: Provides a centralized view of the data centre infrastructure, including power, cooling, and networking.
- Network Monitoring Tools: Monitor network performance and identify bottlenecks.
- Server Monitoring Tools: Track server health and performance metrics.
Challenges in Data Centre Management
Data centre management is not without its challenges. Some of the most common challenges include:
- Complexity: Data centres are becoming increasingly complex, with a growing number of interconnected systems and technologies.
- Cost: Managing a data centre can be expensive, with significant costs associated with power, cooling, and maintenance.
- Security Threats: Data centres are constantly under attack from cybercriminals, making security a top priority.
- Downtime: Even a brief period of downtime can have significant financial and reputational consequences.
- Sustainability: Data centres consume a significant amount of energy, raising concerns about their environmental impact. [See also: Green Data Centre Practices]
Best Practices for Data Centre Management
To overcome these challenges and ensure the optimal operation of a data centre, it’s essential to follow best practices:
- Implement a DCIM Solution: A DCIM solution provides a centralized view of the data centre infrastructure, enabling better monitoring and management.
- Automate Routine Tasks: Automate tasks such as patching, configuration management, and monitoring to reduce manual effort and improve efficiency.
- Conduct Regular Security Audits: Regularly assess security vulnerabilities and implement measures to mitigate risks.
- Develop a Disaster Recovery Plan: Create a comprehensive disaster recovery plan and test it regularly to ensure its effectiveness.
- Optimize Power and Cooling: Implement energy-efficient technologies and practices to reduce power consumption and cooling costs. [See also: Data Centre Energy Efficiency]
- Implement Robust Monitoring: Use monitoring tools to track key performance indicators (KPIs) and identify potential problems before they escalate.
- Train Staff: Ensure that staff are properly trained on data centre management best practices.
- Regular Maintenance: Perform routine maintenance on all equipment to prevent failures and extend its lifespan.
The Future of Data Centre Management
The future of data centre management is being shaped by several emerging trends, including:
- Cloud Computing: The increasing adoption of cloud computing is changing the way data centres are managed. Many organizations are outsourcing their data centre operations to cloud providers.
- Edge Computing: Edge computing is bringing data processing closer to the source of data, reducing latency and improving performance. This requires a distributed approach to data centre management.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI is being used to automate tasks, optimize resource utilization, and improve security.
- Sustainability: There is growing pressure on data centres to reduce their environmental impact. This is driving innovation in energy-efficient technologies and practices.
Conclusion
Data centre management is a critical function that ensures the reliable and efficient operation of the infrastructure that powers our digital world. By understanding the key components, challenges, and best practices of data centre management, organizations can optimize their data centre operations, minimize downtime, and maximize performance. As technology continues to evolve, data centre management will become even more complex and challenging, requiring a proactive and strategic approach. Effective data centre management is not just about keeping the lights on; it’s about enabling innovation, driving business growth, and ensuring the continued availability of the services we rely on every day. The successful implementation of a robust data centre management strategy is paramount for any organization that depends on its data and IT infrastructure. Implementing the right strategies for data centre management can lead to significant cost savings and improved operational efficiency.
