What is an Intrusion Detection System (IDS)? A Comprehensive Guide
In today’s interconnected world, safeguarding digital assets is paramount. Organizations face an ever-evolving landscape of cyber threats, making robust security measures essential. One such measure is the Intrusion Detection System (IDS). But what is an intrusion detection system, and how does it contribute to a comprehensive security posture? This article delves into the intricacies of IDS, exploring its purpose, functionality, types, and benefits, providing a clear understanding of its role in modern cybersecurity.
Understanding Intrusion Detection Systems
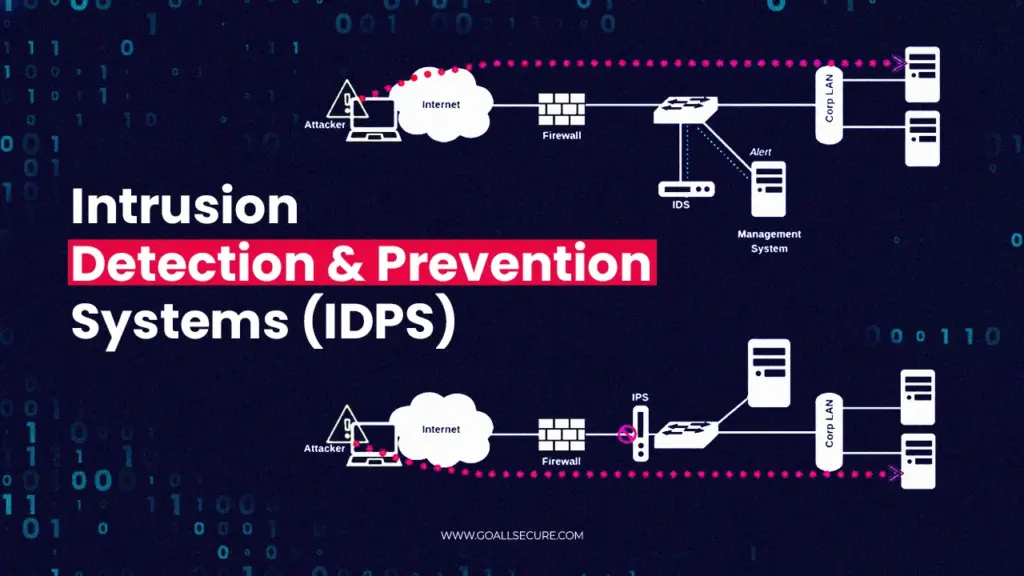
An Intrusion Detection System (IDS) is a security solution designed to monitor network traffic and system activity for malicious or suspicious behavior. It acts as a surveillance system, identifying potential security breaches and alerting administrators to take appropriate action. Unlike firewalls, which primarily focus on preventing unauthorized access, an IDS focuses on detecting intrusions that have already bypassed initial security measures. Think of it as the alarm system in your house – it doesn’t stop burglars from entering, but it alerts you when they do.
Key Functions of an IDS
- Monitoring: Continuously analyzes network traffic, system logs, and other relevant data sources.
- Detection: Identifies suspicious patterns and anomalies that may indicate a security breach.
- Alerting: Notifies administrators of detected intrusions, providing details about the nature of the threat and its potential impact.
- Reporting: Generates reports on security incidents, providing valuable insights for security analysis and incident response.
How Intrusion Detection Systems Work
Intrusion Detection Systems employ various techniques to identify malicious activity. These techniques can be broadly categorized into signature-based detection and anomaly-based detection.
Signature-Based Detection
Signature-based detection, also known as knowledge-based detection, relies on a database of known attack signatures. These signatures are patterns of malicious code or network traffic associated with specific attacks. The IDS compares incoming traffic and system activity against these signatures, flagging any matches as potential intrusions. This method is effective at detecting known attacks but may struggle with novel or zero-day exploits for which signatures have not yet been created.
Anomaly-Based Detection
Anomaly-based detection, also known as behavior-based detection, establishes a baseline of normal network and system behavior. It then monitors activity for deviations from this baseline, flagging any significant anomalies as potential intrusions. This method can detect unknown attacks and insider threats that may not match known signatures. However, it can also generate false positives if normal behavior changes significantly or if the baseline is not properly configured. [See also: Network Security Best Practices]
The Detection Process in Detail
- Data Collection: The IDS gathers data from various sources, including network packets, system logs, and application activity.
- Data Analysis: The collected data is analyzed using either signature-based or anomaly-based detection techniques, or a combination of both.
- Alert Generation: When a potential intrusion is detected, the IDS generates an alert, providing details about the event, such as the source and destination IP addresses, the type of attack, and the severity level.
- Reporting and Logging: The IDS logs all detected events and generates reports that can be used for security analysis and incident response.
Types of Intrusion Detection Systems
Intrusion Detection Systems can be classified into different types based on their deployment location and the data they analyze.
Network Intrusion Detection Systems (NIDS)
Network Intrusion Detection Systems (NIDS) monitor network traffic for suspicious activity. They are typically deployed at strategic points within the network, such as at the perimeter or on critical network segments. NIDS analyze network packets as they traverse the network, looking for patterns that match known attack signatures or deviate from established baselines. They are particularly effective at detecting network-based attacks, such as port scans, denial-of-service attacks, and malware infections.
Host Intrusion Detection Systems (HIDS)
Host Intrusion Detection Systems (HIDS) monitor activity on individual hosts, such as servers or workstations. They analyze system logs, file integrity, and process activity for signs of malicious behavior. HIDS are particularly effective at detecting attacks that target specific hosts, such as malware infections, privilege escalation attempts, and unauthorized file modifications. They are also useful for detecting insider threats that may originate from compromised or malicious users within the organization.
Hybrid Intrusion Detection Systems
Hybrid Intrusion Detection Systems combine the capabilities of both NIDS and HIDS. They provide a more comprehensive view of the security landscape, allowing organizations to detect a wider range of threats. Hybrid IDS can correlate data from network and host-based sensors to identify sophisticated attacks that may be missed by individual systems. [See also: Cybersecurity Threat Landscape]
Benefits of Using an Intrusion Detection System
Implementing an Intrusion Detection System offers numerous benefits for organizations seeking to enhance their security posture.
- Early Threat Detection: IDS can detect threats early in the attack lifecycle, allowing organizations to respond quickly and prevent further damage.
- Improved Security Posture: By identifying and responding to security incidents, IDS helps organizations to improve their overall security posture and reduce their risk of cyberattacks.
- Compliance Requirements: Many regulatory frameworks, such as PCI DSS and HIPAA, require organizations to implement security controls, including intrusion detection systems.
- Incident Response: IDS provides valuable information for incident response teams, helping them to investigate and remediate security incidents more effectively.
- Deterrent Effect: The presence of an IDS can deter attackers from targeting an organization, as they know that their activity is being monitored.
Intrusion Detection System vs. Intrusion Prevention System
While Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) and Intrusion Prevention Systems (IPS) share similar functionalities, there’s a key difference: IDS detects and alerts, while IPS detects and actively prevents. An IPS sits inline with network traffic and can take actions like blocking malicious traffic or terminating connections. Think of an IDS as a security camera and an IPS as a security guard who can physically intervene. Many modern security solutions combine both IDS and IPS capabilities for a more robust defense.
Challenges of Implementing an Intrusion Detection System
Despite the numerous benefits, implementing and maintaining an Intrusion Detection System can present several challenges.
- False Positives: IDS can generate false positives, which are alerts that indicate a security incident when none has occurred. False positives can consume valuable time and resources, as security teams must investigate each alert to determine its validity.
- Performance Impact: IDS can impact network performance, especially when analyzing large volumes of traffic. Organizations must carefully consider the performance implications of deploying an IDS and ensure that it is properly configured to minimize its impact.
- Complexity: IDS can be complex to configure and manage, requiring specialized expertise. Organizations may need to invest in training or hire security professionals with experience in IDS deployment and management.
- Evasion Techniques: Attackers can use various evasion techniques to bypass IDS, such as traffic fragmentation, encryption, and obfuscation. Organizations must stay up-to-date on the latest evasion techniques and ensure that their IDS is configured to detect them.
Best Practices for Implementing an Intrusion Detection System
To maximize the effectiveness of an Intrusion Detection System, organizations should follow these best practices:
- Define Clear Security Objectives: Before deploying an IDS, organizations should define clear security objectives and identify the specific threats they want to detect.
- Choose the Right Type of IDS: Organizations should choose the type of IDS that best suits their needs, considering factors such as network architecture, security requirements, and budget.
- Configure the IDS Properly: IDS should be configured properly to minimize false positives and ensure that it is detecting the threats that are most relevant to the organization.
- Keep the IDS Up-to-Date: IDS should be kept up-to-date with the latest signature updates and software patches to ensure that it is detecting the latest threats.
- Monitor IDS Alerts Regularly: IDS alerts should be monitored regularly by security teams to identify and respond to security incidents in a timely manner.
- Integrate IDS with Other Security Tools: IDS should be integrated with other security tools, such as firewalls and SIEM systems, to provide a more comprehensive view of the security landscape.
The Future of Intrusion Detection Systems
The future of Intrusion Detection Systems is likely to be shaped by several key trends, including:
- Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning: AI and machine learning are being increasingly used to improve the accuracy and efficiency of IDS, enabling them to detect more sophisticated threats and reduce false positives.
- Cloud-Based IDS: Cloud-based IDS are becoming increasingly popular, offering organizations a cost-effective and scalable solution for monitoring their cloud environments.
- Integration with Threat Intelligence: IDS are being integrated with threat intelligence feeds to provide organizations with real-time information about emerging threats.
- Automation: Automation is being used to automate many of the tasks associated with IDS management, such as configuration, monitoring, and incident response.
Conclusion
In conclusion, an Intrusion Detection System (IDS) is a crucial component of a comprehensive cybersecurity strategy. By monitoring network traffic and system activity for malicious behavior, IDS can help organizations to detect threats early, improve their security posture, and comply with regulatory requirements. While implementing and maintaining an IDS can present challenges, following best practices and staying up-to-date on the latest technologies can help organizations to maximize the effectiveness of their IDS. Understanding what is an intrusion detection system is the first step in bolstering your organization’s defenses against the ever-present threat of cyberattacks. As the threat landscape continues to evolve, the role of IDS will become even more critical in protecting digital assets and ensuring business continuity. [See also: Cybersecurity for Small Businesses]
