What is an Enterprise Data Warehouse: A Comprehensive Guide
In today’s data-driven world, organizations are constantly seeking ways to extract valuable insights from vast amounts of information. An enterprise data warehouse (EDW) serves as a central repository for structured and semi-structured data, enabling businesses to analyze trends, improve decision-making, and gain a competitive edge. This comprehensive guide will explore what an enterprise data warehouse is, its key components, benefits, and how it differs from other data management solutions.
Understanding the Enterprise Data Warehouse
An enterprise data warehouse is a system used for reporting and data analysis. It is a central repository of integrated data from one or more disparate sources. EDWs store current and historical data in one single place, and are used for creating analytical reports for workers throughout the enterprise. The data stored in the warehouse is typically structured, meaning it is organized in a predefined format, and may also include semi-structured data. This structure allows for efficient querying and analysis.
Think of an enterprise data warehouse as a digital archive of your company’s collective knowledge. It takes information from various departments – sales, marketing, finance, operations – and organizes it in a way that allows you to see the bigger picture. Instead of relying on isolated spreadsheets or departmental reports, an EDW provides a unified view of the business.
Key Characteristics of an Enterprise Data Warehouse
- Subject-Oriented: Data is organized around key business subjects, such as customers, products, or sales, rather than application-specific processes.
- Integrated: Data from different sources is cleansed, transformed, and integrated into a consistent format. This ensures data accuracy and reliability.
- Time-Variant: Data is stored with a time dimension, allowing for historical analysis and trend identification. This means you can track changes over time and understand how your business has evolved.
- Non-Volatile: Data is read-only and not updated in real-time. This ensures data integrity and prevents accidental modifications. The data is loaded periodically, typically in batches.
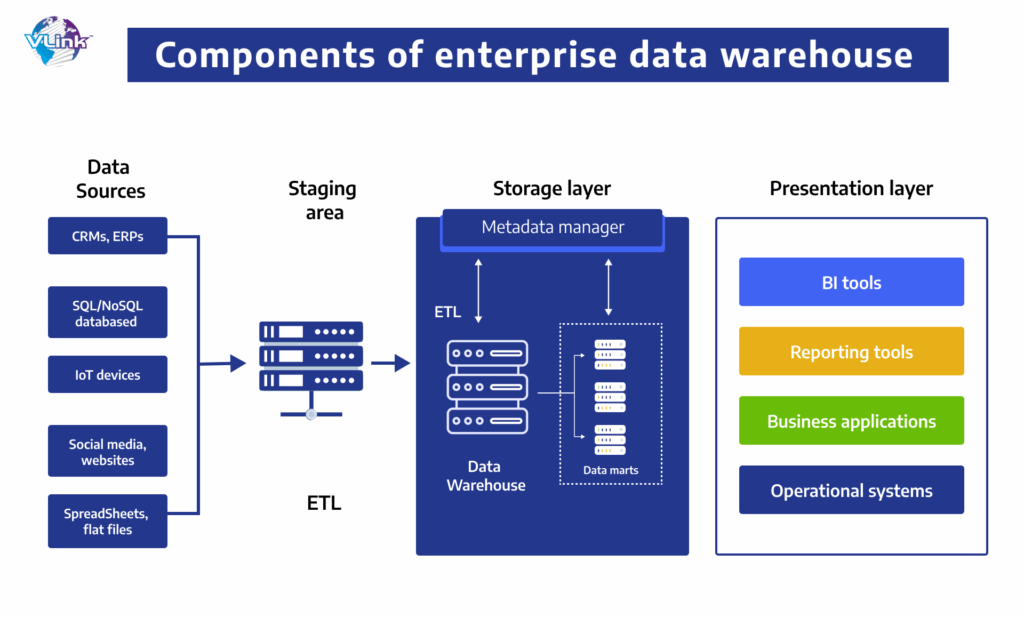
Core Components of an Enterprise Data Warehouse
An enterprise data warehouse is not a single piece of software, but rather a collection of interconnected components that work together to store, manage, and analyze data. These components include:
- Data Sources: These are the various systems and applications that generate the data that is loaded into the EDW. Examples include CRM systems, ERP systems, marketing automation platforms, and transactional databases.
- ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) Process: This is the process of extracting data from source systems, transforming it into a consistent format, and loading it into the data warehouse. ETL tools are used to automate this process.
- Data Warehouse Database: This is the central repository where the data is stored. It is typically a relational database management system (RDBMS) optimized for analytical queries. Examples include Snowflake, Amazon Redshift, Google BigQuery, and Teradata.
- Metadata Repository: This stores information about the data in the warehouse, such as its source, format, and meaning. Metadata is essential for understanding the data and ensuring its quality.
- Data Access Tools: These are the tools that users use to access and analyze the data in the warehouse. Examples include business intelligence (BI) tools, reporting tools, and data mining tools.
Benefits of Implementing an Enterprise Data Warehouse
Implementing an enterprise data warehouse can provide numerous benefits to organizations, including:
- Improved Decision-Making: By providing a unified view of data, an EDW enables businesses to make more informed and data-driven decisions.
- Enhanced Business Intelligence: EDWs provide a foundation for business intelligence (BI) initiatives, allowing users to create reports, dashboards, and visualizations that provide insights into business performance.
- Increased Efficiency: By centralizing data and automating data integration processes, EDWs can improve efficiency and reduce the time spent on data preparation.
- Better Customer Understanding: EDWs can help businesses gain a deeper understanding of their customers by integrating data from various sources, such as CRM systems, marketing automation platforms, and social media.
- Competitive Advantage: By leveraging data to identify trends, optimize processes, and improve customer experience, EDWs can help businesses gain a competitive advantage.
- Single Source of Truth: An enterprise data warehouse acts as a single source of truth, ensuring everyone in the organization is working with the same data. This reduces confusion and improves collaboration.
Enterprise Data Warehouse vs. Data Mart vs. Data Lake
It’s important to understand the difference between an enterprise data warehouse, a data mart, and a data lake. While all three are used for data storage and analysis, they have different characteristics and use cases.
Data Mart
A data mart is a subset of an enterprise data warehouse that focuses on a specific business area or department, such as marketing, sales, or finance. Data marts are typically smaller and less complex than EDWs, and they are designed to meet the specific needs of a particular group of users. They can be dependent, independent, or hybrid, depending on their relationship with the EDW.
Data Lake
A data lake is a repository that stores data in its raw, unprocessed format. Data lakes can store structured, semi-structured, and unstructured data, and they are often used for data exploration and discovery. Unlike an enterprise data warehouse, data lakes do not require data to be transformed before it is stored. This allows for greater flexibility and agility.
Here’s a table summarizing the key differences:
| Feature | Enterprise Data Warehouse | Data Mart | Data Lake |
|---|---|---|---|
| Scope | Enterprise-wide | Departmental | Enterprise-wide |
| Data Type | Structured, Semi-structured | Structured, Semi-structured | Structured, Semi-structured, Unstructured |
| Data Processing | Processed and transformed | Processed and transformed | Raw and unprocessed |
| Purpose | Reporting and analysis | Specific reporting and analysis | Data exploration and discovery |
When to Use an Enterprise Data Warehouse
An enterprise data warehouse is a good choice when:
- You need a single source of truth for data across the entire organization.
- You need to perform complex analysis and reporting on large volumes of data.
- You need to integrate data from multiple disparate sources.
- You need to track data changes over time.
- You need to ensure data quality and consistency.
Implementing an Enterprise Data Warehouse: Best Practices
Implementing an enterprise data warehouse can be a complex and challenging project. To ensure success, it’s important to follow best practices, including:
- Define Clear Business Requirements: Before starting the project, clearly define the business requirements that the EDW will address. This will help to ensure that the project stays focused and delivers value.
- Choose the Right Technology: Select the technology that best meets your business requirements and budget. Consider factors such as scalability, performance, and ease of use.
- Develop a Robust ETL Process: The ETL process is critical to the success of an EDW. Ensure that the ETL process is robust, reliable, and scalable.
- Establish Data Governance Policies: Establish data governance policies to ensure data quality, consistency, and security.
- Provide User Training: Provide user training to ensure that users understand how to access and analyze the data in the warehouse.
- Iterate and Improve: An enterprise data warehouse is not a one-time project. Continuously iterate and improve the EDW based on user feedback and changing business requirements.
The Future of Enterprise Data Warehousing
The future of enterprise data warehousing is being shaped by several trends, including:
- Cloud-Based Data Warehouses: Cloud-based data warehouses are becoming increasingly popular due to their scalability, cost-effectiveness, and ease of use. Platforms like Snowflake, Amazon Redshift, and Google BigQuery are leading the charge.
- Data Virtualization: Data virtualization allows users to access data from multiple sources without having to physically move it into the data warehouse. This can simplify data integration and reduce the time and cost of building an EDW.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML): AI and ML are being used to automate data preparation, improve data quality, and generate insights from data. Expect to see more AI-powered features in future data warehousing solutions.
- Real-Time Data Warehousing: The demand for real-time data warehousing is increasing as businesses need to make faster decisions. This requires new technologies and architectures that can handle streaming data.
Conclusion
An enterprise data warehouse is a powerful tool that can help organizations unlock the value of their data. By providing a unified view of data, EDWs enable businesses to make more informed decisions, improve efficiency, and gain a competitive advantage. While implementing an EDW can be a complex project, following best practices and staying up-to-date on the latest trends can help ensure success. Consider carefully if an enterprise data warehouse is right for your organization, and how it can help you leverage your data to achieve your business goals. The ability to effectively manage and analyze data is crucial in today’s competitive landscape, and an EDW can be a key enabler for success. Choosing the right solution often hinges on a deep understanding of “what is an enterprise data warehouse” and its potential impact.
[See also: Data Lake vs Data Warehouse: Choosing the Right Solution]
[See also: Best Practices for Data Warehouse Implementation]
