What Does Large Language Model Mean? A Comprehensive Guide
In the rapidly evolving landscape of artificial intelligence, the term “Large Language Model” (LLM) is increasingly prevalent. But what does large language model mean in practical terms? This article aims to demystify LLMs, exploring their definition, architecture, applications, and impact on various industries. We will delve into the core concepts, providing a comprehensive understanding of these powerful AI tools.
Understanding Large Language Models
To grasp what does large language model mean, it’s crucial to break down the components. Essentially, an LLM is a sophisticated AI model designed to understand, generate, and manipulate human language. They are trained on massive datasets of text and code, enabling them to perform a wide range of natural language processing (NLP) tasks.
Key Characteristics of LLMs
- Scale: The “large” in large language model refers to the sheer size of the model, typically measured by the number of parameters (the variables the model learns during training). Modern LLMs can have billions or even trillions of parameters.
- Training Data: LLMs are trained on vast amounts of text data, including books, articles, websites, and code repositories. This extensive training allows them to learn patterns, grammar, and semantics of human language.
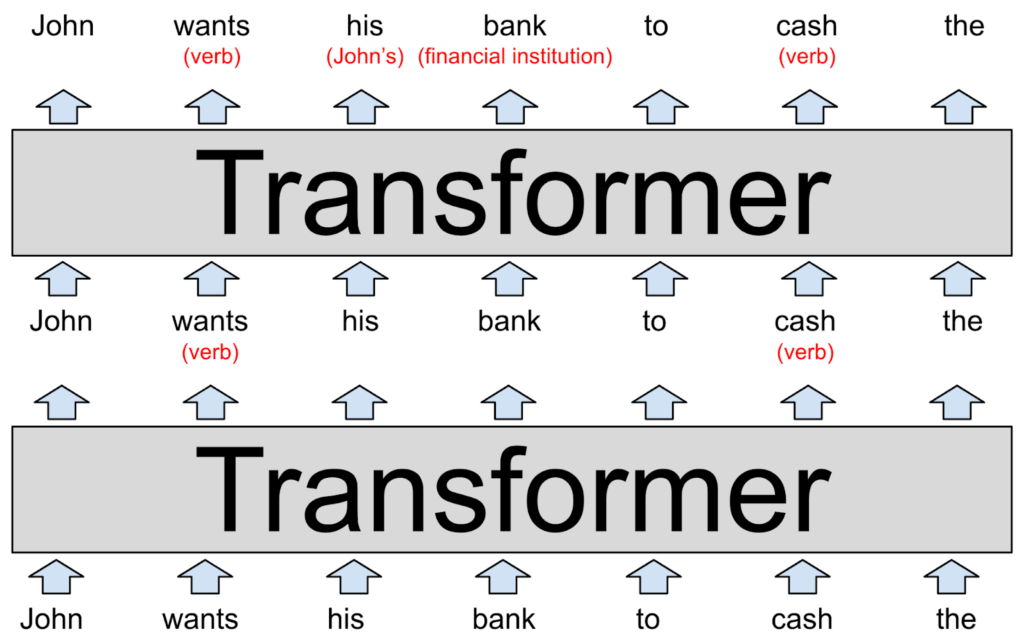
- Transformer Architecture: Most LLMs are based on the transformer architecture, which is particularly well-suited for processing sequential data like text. Transformers use self-attention mechanisms to weigh the importance of different words in a sentence, enabling them to understand context and relationships.
How Large Language Models Work
The functionality of a large language model hinges on its training process and architecture. Here’s a simplified overview:
- Data Ingestion: The model is fed a massive dataset of text and code.
- Training: The model learns to predict the next word in a sequence. For example, given the sentence “The cat sat on the…”, the model would predict “mat” with a high probability.
- Fine-tuning: After initial training, the model can be fine-tuned on specific tasks or datasets to improve its performance in particular areas.
- Inference: Once trained, the model can generate text, answer questions, translate languages, and perform other NLP tasks.
The Role of Parameters
The number of parameters in a large language model is a crucial factor in its performance. More parameters generally allow the model to capture more complex relationships in the data, leading to better accuracy and fluency. However, increasing the number of parameters also increases the computational resources required to train and run the model. [See also: The Future of AI and Its Impact on Society]
Applications of Large Language Models
Large language models have a wide range of applications across various industries. Here are some notable examples:
Content Generation
LLMs can generate human-quality text for various purposes, including:
- Article writing: LLMs can assist in writing articles, blog posts, and news reports.
- Creative writing: LLMs can generate stories, poems, and scripts.
- Marketing copy: LLMs can create compelling marketing materials, such as ad copy and product descriptions.
Chatbots and Virtual Assistants
LLMs power many modern chatbots and virtual assistants, enabling them to understand and respond to user queries in a natural and conversational manner.
Language Translation
LLMs can accurately translate text between different languages, facilitating communication and collaboration across linguistic barriers.
Code Generation
Some LLMs are trained on code and can generate code snippets or even entire programs based on natural language descriptions. This is especially useful for assisting software developers.
Question Answering
LLMs can answer questions based on their training data, providing information and insights on a wide range of topics.
Examples of Large Language Models
Several prominent large language models have been developed by leading AI research organizations. Here are a few examples:
- GPT-3 (Generative Pre-trained Transformer 3): Developed by OpenAI, GPT-3 is one of the most well-known LLMs, capable of generating highly coherent and creative text.
- LaMDA (Language Model for Dialogue Applications): Developed by Google, LaMDA is designed for conversational AI and excels at engaging in natural and informative dialogues.
- BERT (Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers): Also developed by Google, BERT is widely used for various NLP tasks, including text classification, question answering, and sentiment analysis.
- Llama 2: Developed by Meta, Llama 2 is an open-source LLM designed for research and commercial use.
Challenges and Limitations of Large Language Models
While large language models offer numerous benefits, they also have several challenges and limitations:
Bias and Fairness
LLMs can inherit biases from their training data, leading to unfair or discriminatory outputs. Addressing bias in LLMs is a significant challenge in AI research.
Hallucinations
LLMs can sometimes generate incorrect or nonsensical information, a phenomenon known as “hallucinations.” This can be problematic in applications where accuracy is critical.
Computational Cost
Training and running large language models requires significant computational resources, making them expensive to develop and deploy. [See also: Ethical Considerations in Artificial Intelligence Development]
Security Risks
LLMs can be exploited for malicious purposes, such as generating fake news or spreading misinformation. Protecting LLMs from misuse is an important security concern.
The Future of Large Language Models
The field of large language models is rapidly evolving, with ongoing research aimed at improving their performance, addressing their limitations, and expanding their applications. Some key trends include:
- Increased scale: LLMs are expected to continue growing in size, with even more parameters and larger training datasets.
- Improved efficiency: Researchers are exploring ways to make LLMs more efficient, reducing their computational cost and energy consumption.
- Multimodal learning: Future LLMs may be able to process and generate not only text but also images, audio, and video.
- Explainable AI: Efforts are being made to make LLMs more transparent and understandable, allowing users to understand why they make certain decisions.
Conclusion
So, what does large language model mean? It signifies a powerful AI tool capable of understanding and generating human language at an unprecedented scale. While LLMs have limitations and challenges, their potential to transform various industries is undeniable. As research continues, we can expect LLMs to become even more sophisticated, efficient, and versatile, further shaping the future of artificial intelligence. Understanding what does large language model mean is now a fundamental aspect of understanding the trajectory of modern technology. The ongoing development and refinement of large language models promise to revolutionize communication, information processing, and countless other aspects of our lives. The significance of large language model technology continues to grow, making it an essential area of study and innovation. As we continue to explore what does large language model mean, we uncover new possibilities and challenges that will shape the future of AI.
