VPN vs. Proxy Server: Understanding the Key Differences for Online Security
In today’s digital landscape, online security and privacy are paramount. Two common tools used to enhance these aspects are VPNs (Virtual Private Networks) and proxy servers. While both aim to mask your IP address and provide a layer of anonymity, they operate differently and offer varying levels of protection. Understanding the core differences between a VPN vs. proxy server is crucial for making informed decisions about your online security strategy. This article will delve into the functionalities of each, highlighting their strengths and weaknesses, and ultimately helping you determine which solution best suits your needs.
What is a VPN?
A VPN, or Virtual Private Network, creates a secure, encrypted connection between your device and a remote server operated by the VPN provider. All your internet traffic is routed through this encrypted tunnel, effectively masking your IP address and making it difficult for third parties to track your online activity. Think of it as building a private, secure highway for your data to travel on, shielding it from prying eyes.
How a VPN Works
When you connect to a VPN, your device first establishes a connection with the VPN server. The VPN client on your device encrypts all the data being sent and received, making it unreadable to anyone intercepting the traffic. The VPN server then decrypts the data and forwards it to its destination. The response from the destination is encrypted by the VPN server and sent back to your device, where it is decrypted by the VPN client. This entire process happens in the background, providing a seamless and secure browsing experience.
Benefits of Using a VPN
- Enhanced Security: VPNs encrypt your internet traffic, protecting your data from hackers, eavesdroppers, and even your ISP (Internet Service Provider).
- Privacy Protection: By masking your IP address, VPNs prevent websites and online services from tracking your location and browsing habits.
- Access to Geo-Restricted Content: VPNs allow you to bypass geographical restrictions and access content that may be blocked in your region. For instance, you can access streaming services or news websites from different countries.
- Secure Public Wi-Fi Usage: Public Wi-Fi networks are notoriously insecure. Using a VPN on public Wi-Fi protects your data from being intercepted by malicious actors.
- Bypass Censorship: In countries with strict internet censorship, VPNs can be used to bypass restrictions and access blocked websites and information.
Limitations of Using a VPN
- Speed Reduction: The encryption and decryption process can sometimes slow down your internet speed. The distance to the VPN server can also affect speed.
- Cost: Most reliable VPN services require a subscription fee. While free VPNs exist, they often come with limitations, such as data caps, slower speeds, and potential security risks.
- Trusting the VPN Provider: You are essentially trusting the VPN provider with your data. It’s crucial to choose a reputable provider with a strong privacy policy and a proven track record of security.
- Legality: VPN usage is legal in most countries, but some countries have restrictions or outright bans on VPNs.
What is a Proxy Server?
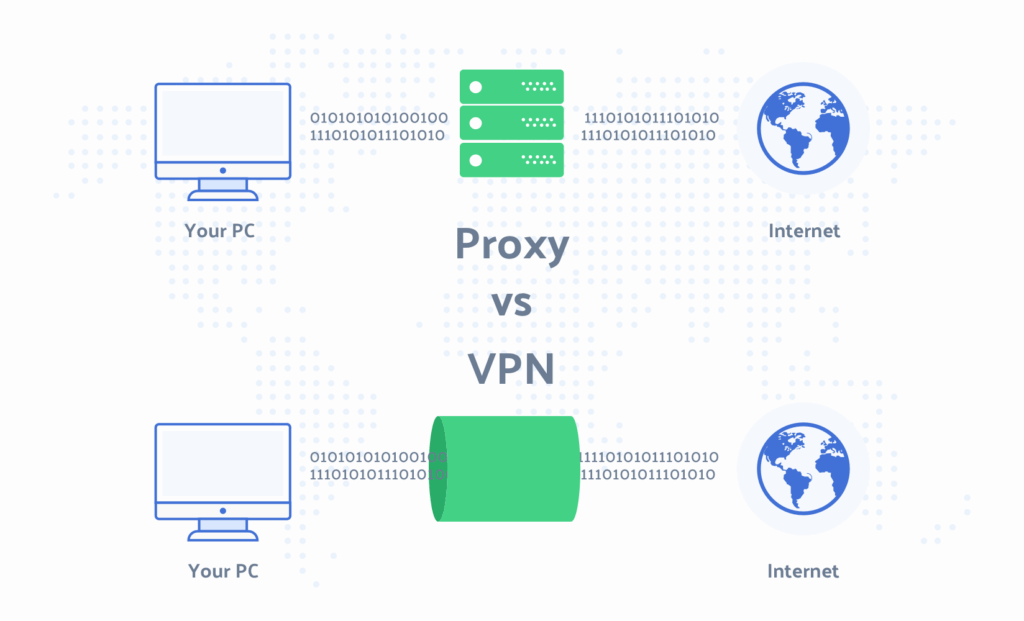
A proxy server acts as an intermediary between your device and the internet. When you connect to a proxy server, your internet traffic is routed through the proxy server, which then forwards it to its destination. The destination website or service sees the IP address of the proxy server, not your actual IP address. Unlike VPNs, many proxy servers do not encrypt your traffic.
How a Proxy Server Works
When you send a request to a website through a proxy server, the request first goes to the proxy server. The proxy server then forwards the request to the website on your behalf. The website sends the response back to the proxy server, which then forwards it to your device. This process effectively hides your IP address and can provide a degree of anonymity.
Types of Proxy Servers
- HTTP Proxy: Designed for web traffic (HTTP and HTTPS). It’s the most common type of proxy server.
- SOCKS Proxy: More versatile than HTTP proxies, as they can handle any type of internet traffic, including email, FTP, and peer-to-peer file sharing.
- Transparent Proxy: These proxies are often used by organizations to monitor and filter internet traffic. Users may not even be aware that they are using a transparent proxy.
- Anonymous Proxy: Designed to hide your IP address and provide a degree of anonymity. However, they may not encrypt your traffic.
- Distorting Proxy: Similar to anonymous proxies, but they also provide a false IP address, making it more difficult to track your actual location.
Benefits of Using a Proxy Server
- IP Address Masking: Proxy servers hide your IP address, making it more difficult for websites and online services to track your location.
- Access to Geo-Restricted Content: Similar to VPNs, proxy servers can be used to bypass geographical restrictions and access content that may be blocked in your region.
- Content Filtering: Proxy servers can be used to filter internet traffic and block access to certain websites or types of content. This is often used by organizations to enforce internet usage policies.
- Improved Performance: Proxy servers can cache frequently accessed content, which can improve website loading times.
Limitations of Using a Proxy Server
- Lack of Encryption: Many proxy servers do not encrypt your internet traffic, leaving your data vulnerable to interception.
- Limited Security: Proxy servers typically offer less security than VPNs. They may not protect you from all types of online threats.
- Speed Reduction: Proxy servers can sometimes slow down your internet speed.
- Trusting the Proxy Provider: You are essentially trusting the proxy provider with your data. It’s crucial to choose a reputable provider.
- Logging: Some proxy servers log your internet activity, which can compromise your privacy.
Key Differences: VPN vs. Proxy Server
The main difference between a VPN vs. proxy server lies in their level of security and functionality. VPNs encrypt all your internet traffic, providing a secure and private connection. Proxy servers, on the other hand, primarily mask your IP address and may not encrypt your traffic. Here’s a table summarizing the key differences:
| Feature | VPN | Proxy Server |
|---|---|---|
| Encryption | Yes, encrypts all traffic | Often no encryption |
| Security | High | Low to Medium |
| Privacy | High | Medium |
| Speed | Can be slower due to encryption | Can be faster, but depends on the server |
| Cost | Typically requires a subscription | Free options available, but often unreliable |
| Scope | Protects all internet traffic | Protects traffic for specific applications (e.g., web browser) |
When to Use a VPN
A VPN is the ideal choice when you need robust security and privacy protection. Consider using a VPN in the following situations:
- Using Public Wi-Fi: Protect your data from being intercepted on insecure public Wi-Fi networks.
- Accessing Sensitive Information: When accessing banking information, online shopping, or other sensitive data.
- Bypassing Censorship: Accessing blocked websites and information in countries with strict internet censorship.
- Protecting Your Privacy: Preventing websites and online services from tracking your location and browsing habits.
- Downloading Torrents: Protecting your IP address and identity while downloading torrents.
When to Use a Proxy Server
A proxy server can be a suitable option when you need to bypass geographical restrictions or simply want to mask your IP address for basic anonymity. Consider using a proxy server in the following situations:
- Accessing Geo-Restricted Content: Accessing streaming services or news websites that are blocked in your region.
- Bypassing Basic Content Filters: Circumventing simple content filters that block access to certain websites.
- Improving Website Loading Times: Using a proxy server with caching capabilities to improve website loading times.
- Hiding Your IP Address for Basic Anonymity: Masking your IP address to prevent websites from tracking your location (note: this is not a substitute for a VPN for serious privacy concerns).
Choosing the Right Solution
The best choice between a VPN vs. proxy server depends on your specific needs and priorities. If security and privacy are your primary concerns, a VPN is the clear winner. If you simply need to bypass geographical restrictions or want to mask your IP address for basic anonymity, a proxy server may suffice. However, it’s important to remember that proxy servers typically offer less security than VPNs. Always consider the potential risks and choose a reputable provider with a strong privacy policy.
When selecting a VPN, look for a provider that offers strong encryption, a no-logs policy, and a wide range of server locations. Read reviews and compare different providers to find the best fit for your needs. Similarly, when choosing a proxy server, research the provider’s reputation and ensure that they do not log your internet activity.
Conclusion: Making an Informed Decision
Understanding the differences between a VPN vs. proxy server is essential for protecting your online security and privacy. While both tools can mask your IP address, VPNs offer a much higher level of security due to their encryption capabilities. By carefully considering your needs and priorities, you can choose the solution that best suits your individual requirements. Remember to prioritize security and privacy when making your decision, and always choose reputable providers with strong privacy policies.
[See also: How to Choose the Best VPN for Your Needs]
[See also: The Importance of Online Privacy in the Digital Age]
