Unveiling the Definition for Computer Network: A Comprehensive Guide
In today’s interconnected world, understanding the definition for computer network is crucial. From small home setups to sprawling enterprise infrastructures, computer networks underpin nearly every aspect of modern communication and data exchange. This article delves into the core concepts of computer networks, exploring their components, types, benefits, and evolving landscape. We aim to provide a clear, concise, and comprehensive definition for computer network, suitable for both beginners and those seeking a refresher on the fundamentals.
What is a Computer Network? A Detailed Definition
At its most basic, a computer network is a collection of two or more computers that are interconnected and can communicate with each other. This connection allows them to share resources, data, and applications. The definition for computer network extends beyond just the physical connection; it also encompasses the protocols, rules, and standards that govern how these devices interact. The primary goal of a computer network is to enable efficient and reliable communication between devices, regardless of their location or the type of data being transmitted.
Key Components of a Computer Network
Understanding the components of a computer network is essential to grasping its overall functionality. These components work together to facilitate communication and data transfer.
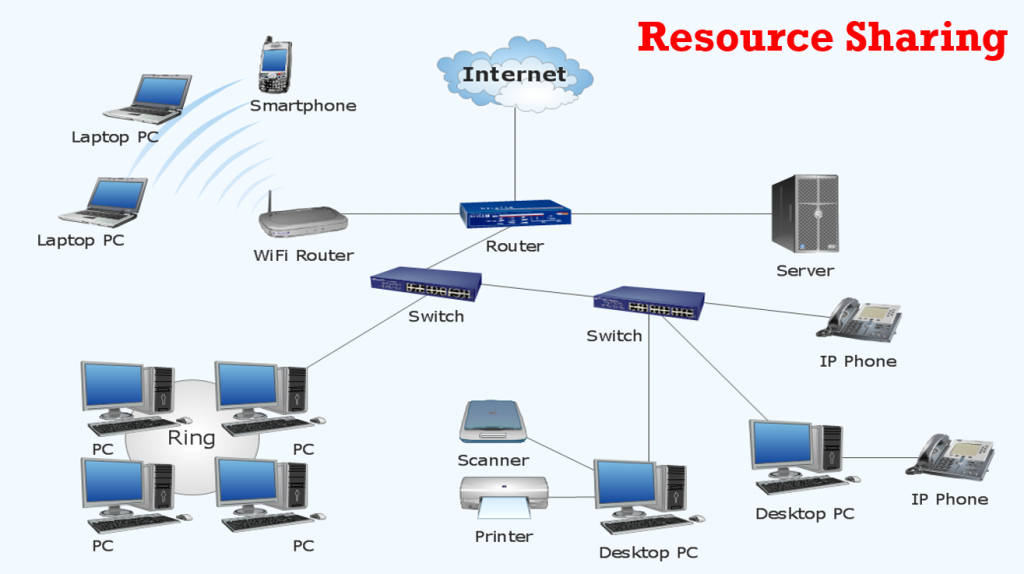
- Nodes: These are the devices connected to the network, such as computers, servers, printers, and smartphones. Each node has a unique address that allows it to be identified on the network.
- Links: These are the communication pathways between nodes. Links can be wired (e.g., Ethernet cables) or wireless (e.g., Wi-Fi).
- Network Interface Cards (NICs): These are hardware components that allow devices to connect to a network. They provide the physical interface for connecting to the network medium.
- Routers: These are devices that forward data packets between different networks. They act as traffic controllers, ensuring that data reaches its intended destination efficiently. [See also: Understanding Router Configuration]
- Switches: These are devices that connect multiple devices within the same network. They operate at the data link layer of the OSI model and forward data based on MAC addresses.
- Hubs: While less common now, hubs were early network devices that connected multiple devices. Unlike switches, hubs broadcast data to all connected devices.
- Cables and Connectors: These provide the physical connections between devices. Common types include Ethernet cables (Cat5e, Cat6) and fiber optic cables.
- Software: This includes operating systems, network management tools, and communication protocols.
Types of Computer Networks
Computer networks can be classified based on their size, scope, and architecture. Here are some of the most common types:
Personal Area Network (PAN)
A PAN is a small network typically used by a single person. Examples include a Bluetooth connection between a smartphone and a headset, or a USB connection between a computer and a printer. The range of a PAN is typically limited to a few meters.
Local Area Network (LAN)
A LAN connects devices within a limited geographical area, such as a home, office, or school. LANs are typically used to share resources such as printers, files, and internet access. Ethernet and Wi-Fi are common technologies used in LANs.
Metropolitan Area Network (MAN)
A MAN connects devices within a city or metropolitan area. MANs are larger than LANs but smaller than WANs. They are often used by businesses and government agencies to connect multiple locations within a city. [See also: MAN vs WAN: Key Differences]
Wide Area Network (WAN)
A WAN connects devices over a large geographical area, such as a country or continent. The internet is the largest WAN in the world. WANs are typically used by businesses and organizations to connect remote offices and branches. Technologies used in WANs include leased lines, MPLS, and VPNs.
Virtual Private Network (VPN)
A VPN creates a secure, encrypted connection over a public network, such as the internet. VPNs are often used to protect sensitive data and to bypass geographical restrictions. They allow users to access resources as if they were connected to a private network.
Storage Area Network (SAN)
A SAN is a specialized network that provides block-level access to storage devices. SANs are typically used in data centers and enterprise environments to provide high-performance storage for applications and databases. [See also: SAN Storage Solutions for Enterprises]
Network Topologies
Network topology refers to the physical or logical arrangement of devices in a network. Different topologies have different advantages and disadvantages in terms of cost, performance, and reliability.
Bus Topology
In a bus topology, all devices are connected to a single cable, called the bus. This is a simple and inexpensive topology, but it is vulnerable to failure if the bus cable breaks.
Star Topology
In a star topology, all devices are connected to a central hub or switch. This is a more reliable topology than the bus topology, as a failure of one device does not affect the rest of the network.
Ring Topology
In a ring topology, each device is connected to two other devices, forming a closed loop. Data travels around the ring in one direction. This topology can be more resilient than the bus topology, but it can be complex to implement.
Mesh Topology
In a mesh topology, each device is connected to multiple other devices. This provides high redundancy and reliability, but it can be expensive to implement. Mesh topologies are often used in critical infrastructure, such as military networks.
Tree Topology
A tree topology combines elements of bus and star topologies. It consists of multiple star networks connected to a bus.
Benefits of Computer Networks
Computer networks offer numerous benefits to individuals, businesses, and organizations.
- Resource Sharing: Networks allow users to share resources such as printers, files, and internet connections.
- Data Sharing: Networks enable users to easily share data and information.
- Communication: Networks facilitate communication through email, instant messaging, and video conferencing.
- Centralized Management: Networks allow for centralized management of resources and security.
- Cost Savings: Networks can reduce costs by sharing resources and centralizing management.
- Increased Productivity: Networks can improve productivity by providing users with access to the resources and information they need.
The Evolving Landscape of Computer Networks
The field of computer networks is constantly evolving, driven by technological advancements and changing user needs. Some of the key trends shaping the future of networking include:
- Cloud Computing: Cloud computing is transforming the way networks are designed and managed. Cloud-based networks offer scalability, flexibility, and cost savings.
- Software-Defined Networking (SDN): SDN allows for centralized control of network resources, making networks more programmable and adaptable.
- Network Function Virtualization (NFV): NFV virtualizes network functions, such as firewalls and routers, allowing them to be deployed on commodity hardware.
- 5G: 5G is the next generation of wireless technology, offering faster speeds, lower latency, and increased capacity.
- Internet of Things (IoT): The IoT is connecting billions of devices to the internet, creating new challenges and opportunities for networking.
Security Considerations in Computer Networks
Security is a critical consideration in computer networks. Networks are vulnerable to a variety of threats, including viruses, malware, hacking, and data breaches. It is important to implement security measures to protect networks and data.
- Firewalls: Firewalls act as a barrier between a network and the outside world, blocking unauthorized access.
- Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS): IDS monitor network traffic for suspicious activity and alert administrators.
- Antivirus Software: Antivirus software protects devices from viruses and malware.
- Encryption: Encryption protects data by scrambling it so that it cannot be read by unauthorized users.
- Access Control: Access control limits access to network resources based on user identity and permissions.
Conclusion
The definition for computer network encompasses a complex and evolving ecosystem of interconnected devices and technologies. Understanding the fundamentals of computer networks is essential for anyone working in IT or related fields. By understanding the components, types, topologies, benefits, and security considerations of computer networks, individuals and organizations can leverage the power of networking to improve communication, collaboration, and productivity. As technology continues to advance, the importance of computer networks will only continue to grow. A solid understanding of the definition for computer network is more valuable than ever. The ongoing evolution of the computer network will present new challenges and opportunities, making continuous learning and adaptation crucial for success. The initial definition for computer network may seem straightforward, but the underlying intricacies are substantial. Therefore, a thorough comprehension of the computer network definition and its implications is vital for navigating the digital landscape.
