Unlocking the Potential: Exploring DNS Options for Enhanced Network Performance
In today’s interconnected world, a reliable and efficient Domain Name System (DNS) is crucial for seamless online experiences. DNS translates human-readable domain names (like example.com) into IP addresses that computers use to locate servers. Understanding and optimizing your DNS options can significantly improve your network performance, security, and overall user experience. This article delves into the various DNS options available, providing insights into how to choose the right one for your specific needs.
What is DNS and Why Does it Matter?
Before diving into the specifics of DNS options, it’s essential to understand the fundamental role of DNS. Imagine the internet as a vast phonebook. Instead of remembering long strings of numbers (IP addresses), we use names (domain names). DNS acts as the translator, connecting these names to the corresponding IP addresses. When you type a website address into your browser, a DNS query is initiated to find the server hosting that website. The speed and reliability of this process directly impact your browsing experience. A slow or unreliable DNS server can lead to delays in website loading, connection errors, and even security vulnerabilities.
Types of DNS Servers
Several types of DNS servers play a role in the DNS resolution process:
- Recursive Resolvers: These servers are the first point of contact for DNS queries. They receive requests from your devices and recursively query other DNS servers until they find the answer. Your ISP typically provides a recursive resolver.
- Root Servers: These servers are at the top of the DNS hierarchy and contain information about the top-level domains (TLDs) like .com, .org, and .net.
- TLD Servers: These servers contain information about the authoritative name servers for specific domains within their TLD.
- Authoritative Name Servers: These servers hold the definitive DNS records for a domain. They provide the IP address associated with a domain name.
Exploring Your DNS Options
You have several DNS options to choose from, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. Let’s explore some of the most common:
ISP-Provided DNS Servers
By default, most users rely on the DNS servers provided by their Internet Service Provider (ISP). This is the simplest option, requiring no configuration. However, ISP-provided DNS servers are often slower and less reliable than other DNS options. They may also be subject to censorship or logging practices that compromise your privacy.
Public DNS Servers
Public DNS servers are offered by various organizations, such as Google (8.8.8.8 and 8.8.4.4), Cloudflare (1.1.1.1), and OpenDNS. These servers are generally faster, more reliable, and more secure than ISP-provided DNS servers. They often offer additional features like malware protection and content filtering. Switching to a public DNS server is a simple way to improve your online experience. For example, Cloudflare’s 1.1.1.1 is known for its speed and privacy-focused approach. Google Public DNS is also a popular choice due to its global infrastructure and reliability. Choosing between these DNS options depends on your specific priorities.
Managed DNS Services
Managed DNS services are designed for businesses and organizations that require high availability, performance, and security. These services typically offer advanced features like DNSSEC, geo-based routing, and DDoS protection. Examples of managed DNS providers include Akamai, Dyn, and NS1. These DNS options provide greater control and customization than public DNS servers, but they also come at a higher cost.
Private DNS Servers
For maximum control and privacy, you can set up your own private DNS server. This involves installing and configuring DNS server software on your own hardware. While this option requires technical expertise, it gives you complete control over your DNS settings and data. Private DNS servers are often used by organizations with strict security requirements. However, maintaining a private DNS server can be complex and time-consuming. Consider the operational overhead when evaluating these DNS options.
Factors to Consider When Choosing DNS Options
Selecting the right DNS options depends on several factors:
- Speed: The speed of your DNS server directly impacts website loading times. Choose a DNS server with low latency and high throughput.
- Reliability: A reliable DNS server ensures that your website is always accessible. Look for DNS servers with a high uptime guarantee.
- Security: A secure DNS server protects against DNS hijacking, cache poisoning, and other security threats. Consider DNS servers that support DNSSEC.
- Privacy: Some DNS servers log your DNS queries, which can compromise your privacy. Choose a DNS server with a clear privacy policy.
- Features: Some DNS servers offer additional features like malware protection, content filtering, and geo-based routing.
- Cost: DNS options range from free public DNS servers to expensive managed DNS services. Choose an option that fits your budget.
How to Change Your DNS Settings
Changing your DNS settings is a relatively simple process. The exact steps vary depending on your operating system and network configuration. Here’s a general overview:
Windows
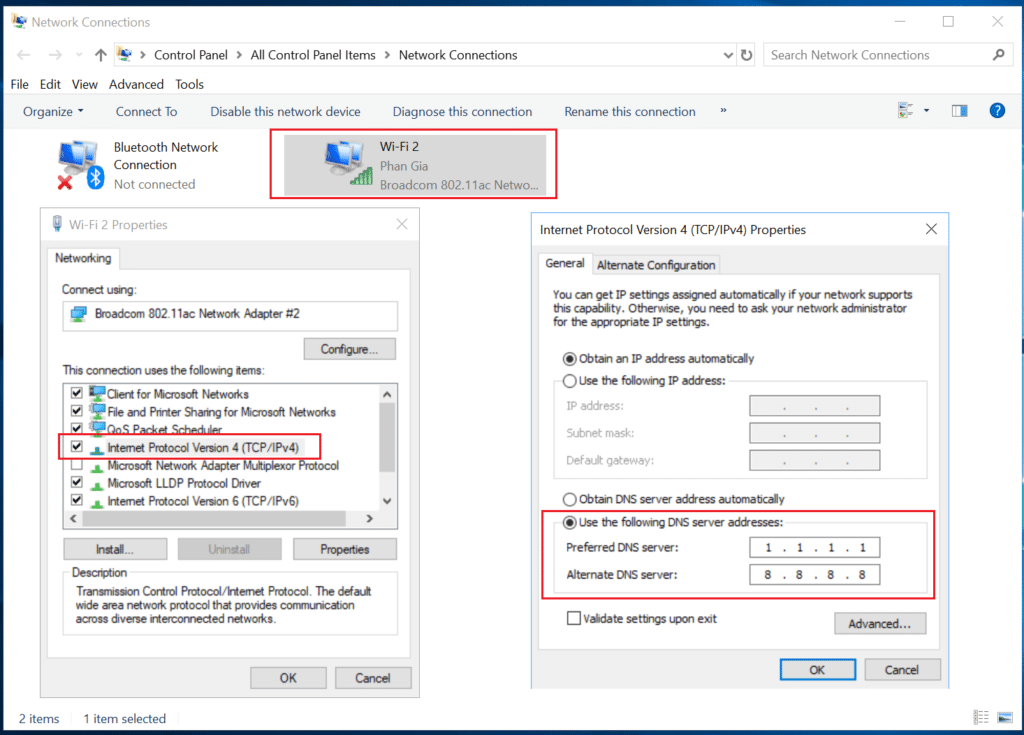
- Open the Control Panel.
- Go to Network and Internet > Network and Sharing Center.
- Click on your network connection.
- Click on Properties.
- Select Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4) and click on Properties.
- Select “Use the following DNS server addresses.”
- Enter the IP addresses of your preferred DNS servers.
- Click OK to save your changes.
macOS
- Open System Preferences.
- Go to Network.
- Select your network connection.
- Click on Advanced.
- Go to the DNS tab.
- Add the IP addresses of your preferred DNS servers.
- Click OK to save your changes.
Routers
You can also change your DNS settings at the router level. This will apply the new DNS settings to all devices connected to your network. Refer to your router’s documentation for specific instructions. Typically, you’ll access your router’s configuration page through a web browser and look for DNS settings under the network or WAN configuration.
The Importance of DNSSEC
DNSSEC (Domain Name System Security Extensions) is a suite of security protocols that add a layer of authentication to the DNS system. It helps prevent DNS spoofing and cache poisoning attacks by digitally signing DNS records. When evaluating DNS options, consider whether they support DNSSEC. Enabling DNSSEC can significantly improve the security of your DNS infrastructure.
DNS and CDN Integration
Content Delivery Networks (CDNs) often rely on DNS to direct users to the closest server. When a user requests content from a CDN, the DNS server resolves the domain name to the IP address of the CDN server that is geographically closest to the user. This ensures faster content delivery and improved user experience. If you’re using a CDN, make sure your DNS settings are properly configured to take advantage of its benefits. Choosing the right DNS options is crucial for optimal CDN performance.
Troubleshooting DNS Issues
DNS issues can manifest in various ways, such as slow website loading times, connection errors, or inability to access certain websites. Here are some common troubleshooting steps:
- Clear your DNS cache: Your operating system and web browser store DNS records in a cache to speed up future lookups. Clearing the cache can resolve issues caused by outdated or corrupted DNS records.
- Flush your DNS resolver cache: Similar to clearing your DNS cache, flushing your DNS resolver cache forces your system to retrieve fresh DNS records.
- Check your DNS settings: Ensure that your DNS settings are configured correctly. Double-check the IP addresses of your DNS servers.
- Test your DNS server: Use online tools to test the speed and reliability of your DNS server.
- Contact your ISP or DNS provider: If you’re still experiencing issues, contact your ISP or DNS provider for assistance.
The Future of DNS
The DNS landscape is constantly evolving. New technologies and protocols are being developed to improve the performance, security, and privacy of DNS. Some of the key trends include:
- DNS over HTTPS (DoH): DoH encrypts DNS queries, protecting them from eavesdropping and manipulation.
- DNS over TLS (DoT): DoT is another protocol that encrypts DNS queries.
- DNSSEC adoption: Increased adoption of DNSSEC is improving the overall security of the DNS system.
- Decentralized DNS: Blockchain-based DNS systems are emerging as an alternative to traditional centralized DNS.
Staying informed about these trends will help you make informed decisions about your DNS options in the future.
Conclusion
Choosing the right DNS options is a critical step in optimizing your network performance, security, and privacy. By understanding the different types of DNS servers and the factors to consider when making your selection, you can ensure a seamless and secure online experience. Whether you opt for a public DNS server, a managed DNS service, or a private DNS server, taking the time to evaluate your DNS options will pay dividends in the long run. Remember to regularly review and update your DNS settings to keep pace with the evolving DNS landscape. Consider the security implications of your DNS options, and always prioritize a reliable and fast DNS resolution for a better internet experience. [See also: Understanding DNS Propagation] [See also: Securing Your Domain with DNSSEC] [See also: The Benefits of Using a CDN]
