Unlocking Cybersecurity: A Deep Dive into SEIM Software
In today’s digital landscape, cybersecurity threats are becoming increasingly sophisticated and frequent. Organizations face a constant barrage of attacks that can compromise sensitive data, disrupt operations, and damage their reputation. To combat these threats, businesses are turning to Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) software. This article provides a comprehensive overview of SEIM software, its functionalities, benefits, and how it helps organizations strengthen their cybersecurity posture.
What is SEIM Software?
SEIM software is a security solution that aggregates and analyzes security logs and event data from various sources across an organization’s IT infrastructure. These sources include servers, network devices, applications, databases, and security tools. By centralizing this data, SEIM software provides a comprehensive view of an organization’s security landscape, enabling security teams to detect, investigate, and respond to threats more effectively.
Essentially, SEIM software acts as a central nervous system for cybersecurity, collecting information from all parts of the body (the IT infrastructure) and processing it to identify potential problems (threats). It then alerts security personnel, allowing them to take appropriate action.
Key Functionalities of SEIM Software
SEIM software offers a wide range of functionalities designed to improve an organization’s security posture. Some of the key functionalities include:
- Log Management: SEIM software collects, normalizes, and stores security logs from various sources. This centralized log management makes it easier to search and analyze logs for security incidents.
- Event Correlation: SEIM software correlates events from different sources to identify patterns and anomalies that may indicate a security threat. This correlation helps security teams to prioritize incidents and focus on the most critical threats.
- Threat Detection: SEIM software uses various techniques, such as rule-based detection, anomaly detection, and threat intelligence feeds, to identify potential security threats.
- Incident Response: SEIM software provides tools and workflows to help security teams respond to security incidents quickly and effectively. This includes incident investigation, containment, and remediation.
- Reporting and Compliance: SEIM software generates reports on security events and incidents, which can be used to demonstrate compliance with regulatory requirements.
Benefits of Implementing SEIM Software
Implementing SEIM software offers numerous benefits for organizations of all sizes. Some of the key benefits include:
- Improved Threat Detection: SEIM software helps organizations to detect threats more quickly and accurately by providing a comprehensive view of their security landscape and correlating events from different sources.
- Faster Incident Response: SEIM software provides tools and workflows to help security teams respond to security incidents more quickly and effectively, minimizing the impact of breaches.
- Reduced Security Costs: By automating many of the tasks associated with security monitoring and incident response, SEIM software can help organizations to reduce their security costs.
- Enhanced Compliance: SEIM software helps organizations to demonstrate compliance with regulatory requirements by providing detailed reports on security events and incidents.
- Centralized Security Management: SEIM software provides a central platform for managing all aspects of security, making it easier for security teams to monitor, investigate, and respond to threats.
Choosing the Right SEIM Software
Selecting the right SEIM software is crucial for maximizing its benefits. Organizations should consider the following factors when choosing a SEIM software solution:
- Scalability: The SEIM software should be able to scale to meet the growing needs of the organization.
- Integration: The SEIM software should integrate with the organization’s existing security tools and IT infrastructure.
- Ease of Use: The SEIM software should be easy to use and manage, even for organizations with limited security expertise.
- Cost: The SEIM software should be affordable and provide a good return on investment.
- Vendor Reputation: Choose a reputable SEIM software vendor with a proven track record.
Different vendors offer various approaches to SEIM software. Some focus on ease of use and pre-configured rules, making them suitable for smaller organizations. Others offer more advanced features and customization options, catering to the needs of larger enterprises with complex security requirements. Evaluating your organization’s specific needs and resources is essential when making a decision.
Deployment Options for SEIM Software
SEIM software can be deployed in various ways, depending on the organization’s needs and resources. The most common deployment options include:
- On-Premise: The SEIM software is installed and managed on the organization’s own servers and infrastructure. This option provides the most control over the data and security of the SEIM software.
- Cloud-Based: The SEIM software is hosted and managed by a third-party provider in the cloud. This option offers greater scalability and flexibility, but it may also raise concerns about data security and privacy.
- Hybrid: A combination of on-premise and cloud-based deployment. Some data is stored and processed on-premise, while other data is stored and processed in the cloud.
The Future of SEIM Software
SEIM software is constantly evolving to meet the changing needs of the cybersecurity landscape. Some of the key trends shaping the future of SEIM software include:
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML): AI and ML are being used to improve the accuracy and efficiency of threat detection and incident response.
- Security Orchestration, Automation, and Response (SOAR): SOAR is being integrated with SEIM software to automate security tasks and workflows.
- Cloud-Native SEIM: Cloud-native SEIM software is designed to take advantage of the scalability and flexibility of the cloud.
- User and Entity Behavior Analytics (UEBA): UEBA is being integrated with SEIM software to detect insider threats and other anomalous behavior.
These advancements are making SEIM software more powerful and effective than ever before, enabling organizations to stay ahead of the ever-evolving threat landscape.
Real-World Examples of SEIM Software in Action
To illustrate the practical application of SEIM software, consider the following scenarios:
- Detecting a Brute-Force Attack: SEIM software can identify a brute-force attack by monitoring failed login attempts across multiple systems. When a user account experiences an unusually high number of failed login attempts within a short period, the SEIM software can trigger an alert, allowing security personnel to investigate and block the attacker’s IP address.
- Identifying Malware Infections: SEIM software can detect malware infections by analyzing network traffic and system logs for suspicious activity. For example, if a system suddenly starts communicating with a known command-and-control server, the SEIM software can flag it as a potential malware infection.
- Detecting Insider Threats: SEIM software can detect insider threats by monitoring user activity and identifying anomalous behavior. For example, if an employee suddenly starts accessing sensitive data that they don’t normally access, the SEIM software can trigger an alert.
- Ensuring Compliance: SEIM software can help organizations to meet compliance requirements by providing detailed reports on security events and incidents. For example, SEIM software can generate reports on access control, data security, and incident response, which can be used to demonstrate compliance with regulations such as HIPAA and PCI DSS.
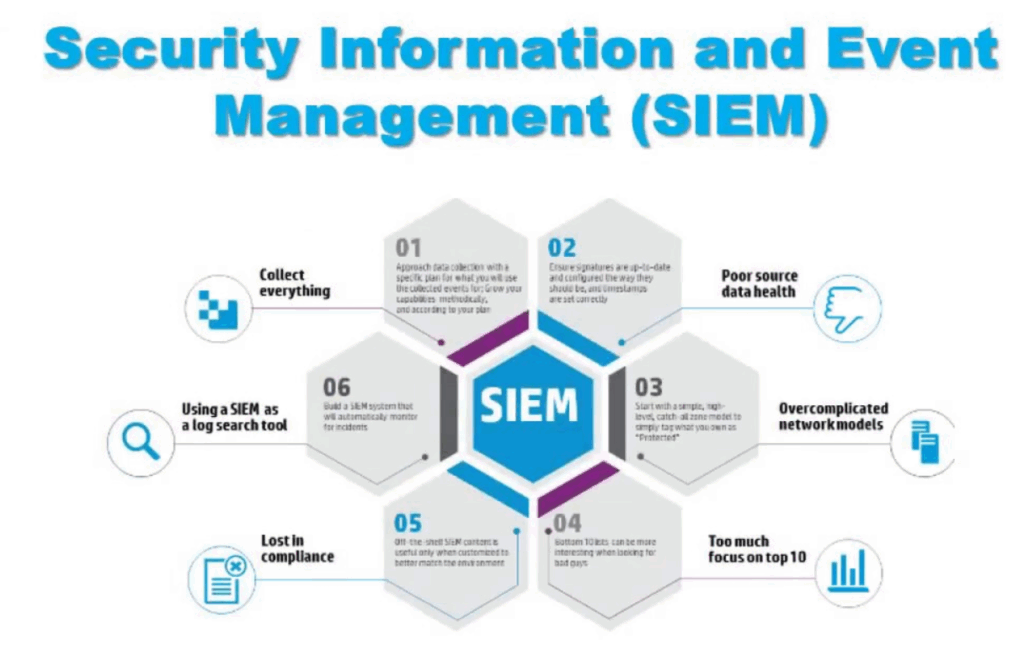
Implementation Considerations for SEIM Software
Successfully implementing SEIM software requires careful planning and execution. Here are some key considerations:
- Define Clear Objectives: Clearly define the goals and objectives for implementing SEIM software. What specific security challenges are you trying to address? What compliance requirements do you need to meet?
- Identify Data Sources: Identify all the relevant data sources that need to be integrated with the SEIM software. This includes servers, network devices, applications, databases, and security tools.
- Develop Use Cases: Develop specific use cases for the SEIM software. These use cases should outline the specific threats and vulnerabilities that the SEIM software will be used to detect and respond to.
- Configure Rules and Alerts: Configure the SEIM software with appropriate rules and alerts to detect suspicious activity. This requires a thorough understanding of the organization’s security environment and the types of threats it faces.
- Provide Training: Provide adequate training to security personnel on how to use the SEIM software. This includes training on how to monitor the SEIM software, investigate alerts, and respond to incidents.
- Regularly Review and Update: Regularly review and update the SEIM software configuration to ensure that it is effectively detecting and responding to threats. This includes updating rules and alerts, adding new data sources, and incorporating new threat intelligence.
Conclusion
SEIM software is an essential tool for organizations seeking to strengthen their cybersecurity posture. By aggregating and analyzing security data from various sources, SEIM software enables organizations to detect threats more quickly, respond to incidents more effectively, and comply with regulatory requirements. Choosing the right SEIM software and implementing it effectively requires careful planning and execution, but the benefits are well worth the effort. As the threat landscape continues to evolve, SEIM software will remain a critical component of any comprehensive cybersecurity strategy.
[See also: Related Article Titles]
