Unlocking Business Value: A Deep Dive into Enterprise Edge Computing
In today’s rapidly evolving technological landscape, businesses are constantly seeking innovative solutions to optimize their operations, enhance customer experiences, and gain a competitive edge. One technology that has emerged as a game-changer in this pursuit is enterprise edge computing. This article provides an in-depth exploration of enterprise edge computing, examining its definition, benefits, use cases, challenges, and future trends. We aim to provide a comprehensive understanding of how enterprise edge computing can unlock significant business value for organizations across various industries.
What is Enterprise Edge Computing?
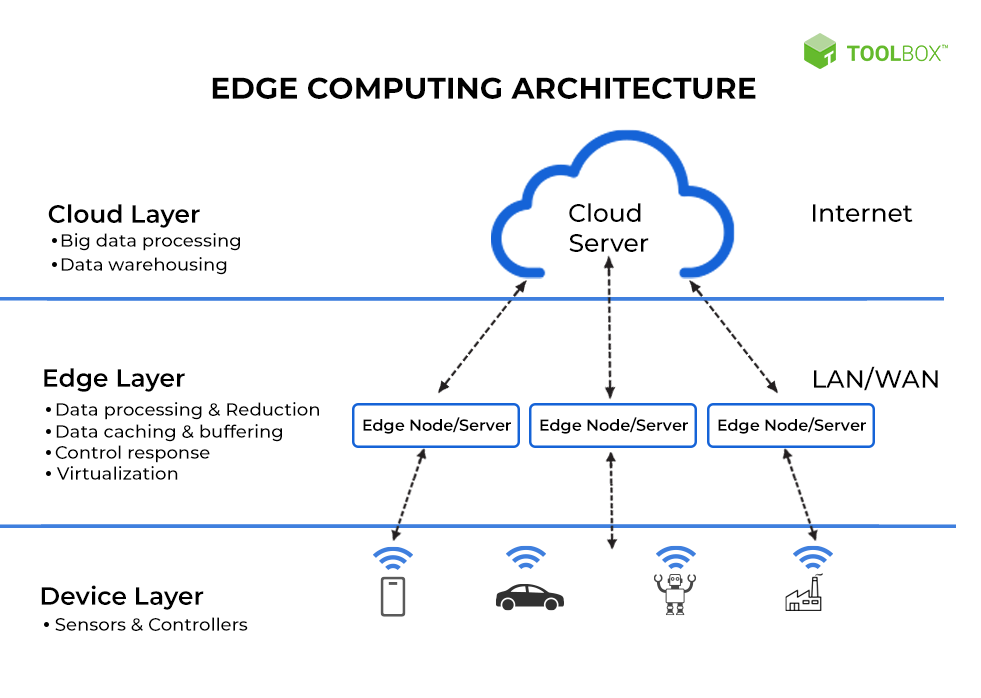
Enterprise edge computing is a distributed computing paradigm that brings data processing and storage closer to the source of data generation, rather than relying solely on centralized data centers or cloud infrastructure. In essence, it involves deploying computing resources – servers, storage devices, and networking equipment – at the “edge” of the network, near where devices, sensors, and users are located. This proximity minimizes latency, reduces bandwidth consumption, and enhances data security and privacy.
Think of it this way: instead of sending all your data to a central processing hub (like the cloud), you process some of it locally, right where it’s created. This is particularly useful when you need real-time insights or have limited bandwidth. The enterprise edge computing architecture allows for faster decision-making, improved efficiency, and enhanced reliability, which is critical for many modern applications.
Key Benefits of Enterprise Edge Computing
The adoption of enterprise edge computing offers a multitude of advantages for businesses:
- Reduced Latency: By processing data closer to the source, enterprise edge computing minimizes the time it takes to analyze and act on information. This is crucial for applications requiring real-time responsiveness, such as autonomous vehicles, industrial automation, and augmented reality.
- Lower Bandwidth Costs: Processing data locally reduces the amount of data that needs to be transmitted over the network, resulting in significant savings on bandwidth costs. This is especially beneficial for organizations with remote locations or limited network connectivity.
- Enhanced Reliability: Enterprise edge computing can improve the reliability of applications by enabling them to operate even when network connectivity is intermittent or unavailable. This is critical for mission-critical applications that cannot tolerate downtime.
- Improved Security and Privacy: Processing sensitive data at the edge can enhance security and privacy by reducing the risk of data breaches and complying with data residency regulations. Data is less vulnerable when it’s not constantly being transmitted back and forth to a central location.
- Scalability and Flexibility: Enterprise edge computing allows organizations to scale their computing resources more easily and adapt to changing business needs. Edge deployments can be tailored to specific requirements, providing greater flexibility and control.
Real-World Use Cases of Enterprise Edge Computing
The versatility of enterprise edge computing makes it applicable across a wide range of industries and use cases:
Manufacturing
In manufacturing, enterprise edge computing enables real-time monitoring and control of production processes, predictive maintenance of equipment, and improved quality control. Imagine sensors on a factory floor constantly feeding data to an edge server, which analyzes the information and identifies potential issues before they lead to downtime. This proactive approach can save manufacturers significant amounts of money and improve overall efficiency. [See also: Predictive Maintenance with Edge Computing]
Retail
Retailers can leverage enterprise edge computing to enhance customer experiences, optimize inventory management, and improve security. For example, edge-based video analytics can be used to monitor foot traffic, identify customer preferences, and prevent theft. Furthermore, processing transactions at the edge can speed up checkout times and reduce reliance on network connectivity.
Healthcare
In healthcare, enterprise edge computing enables remote patient monitoring, telemedicine, and improved diagnostics. Wearable devices can collect patient data and transmit it to an edge server for analysis, allowing healthcare providers to monitor patients remotely and intervene proactively. Moreover, edge computing can facilitate faster image processing for medical imaging, enabling quicker and more accurate diagnoses. [See also: The Role of Edge Computing in Telemedicine]
Transportation
Enterprise edge computing is crucial for autonomous vehicles, traffic management, and logistics. Autonomous vehicles rely on edge computing to process sensor data in real time, enabling them to navigate safely and make informed decisions. Edge computing can also be used to optimize traffic flow, manage logistics operations, and improve public transportation.
Oil and Gas
The oil and gas industry benefits from enterprise edge computing by enabling remote monitoring of pipelines and equipment, predictive maintenance, and improved safety. Edge deployments can collect and analyze data from sensors in remote locations, allowing operators to identify potential problems and prevent accidents. This is especially important in harsh and remote environments where network connectivity is limited.
Challenges of Implementing Enterprise Edge Computing
While enterprise edge computing offers numerous benefits, it also presents certain challenges that organizations need to address:
- Complexity: Deploying and managing a distributed enterprise edge computing infrastructure can be complex, requiring specialized skills and tools.
- Security: Securing edge devices and data is crucial to prevent unauthorized access and data breaches.
- Management: Managing a large number of edge devices can be challenging, requiring centralized management tools and processes.
- Connectivity: Maintaining reliable network connectivity to edge devices can be difficult, especially in remote locations.
- Cost: The initial investment in edge computing infrastructure can be significant, although the long-term benefits often outweigh the costs.
Future Trends in Enterprise Edge Computing
The enterprise edge computing landscape is constantly evolving, with several key trends shaping its future:
- Increased Adoption of AI and Machine Learning: AI and machine learning are being increasingly deployed at the edge to enable real-time analytics and automated decision-making.
- Integration with 5G Networks: The rollout of 5G networks will provide faster and more reliable connectivity to edge devices, further enhancing the capabilities of enterprise edge computing.
- Rise of Edge-as-a-Service: Edge-as-a-Service (EaaS) offerings are emerging, providing organizations with a more flexible and cost-effective way to deploy and manage edge computing infrastructure.
- Focus on Security and Privacy: As edge computing becomes more prevalent, there will be a greater focus on security and privacy to protect sensitive data.
- Convergence of Edge and Cloud: Edge and cloud computing will increasingly converge, with organizations leveraging both technologies to create a hybrid computing environment.
Conclusion
Enterprise edge computing is a transformative technology that empowers businesses to unlock new levels of efficiency, agility, and innovation. By bringing computing resources closer to the source of data, enterprise edge computing enables real-time insights, reduces bandwidth costs, enhances reliability, and improves security. While there are challenges associated with implementing enterprise edge computing, the benefits are undeniable. As the technology continues to evolve and mature, we can expect to see even wider adoption across various industries, driving significant business value for organizations that embrace this paradigm shift. Investing in an enterprise edge computing strategy is no longer a luxury but a necessity for businesses looking to thrive in the digital age. The ability to process and analyze data closer to the source provides a competitive advantage that is increasingly difficult to ignore. [See also: Edge Computing vs. Cloud Computing: A Comprehensive Comparison]
