Understanding PaaS: Real-World Examples and Use Cases
Platform as a Service (PaaS) has revolutionized software development, offering a comprehensive environment for developers to build, deploy, and manage applications without the complexities of managing the underlying infrastructure. This article delves into the specifics of PaaS, providing real-world example of PaaS implementations and highlighting its benefits across various industries. We will explore different types of PaaS and dissect how they address common challenges faced by developers today. Whether you are a seasoned developer or just starting, understanding example of PaaS solutions can significantly enhance your development workflow and efficiency.
What is Platform as a Service (PaaS)?
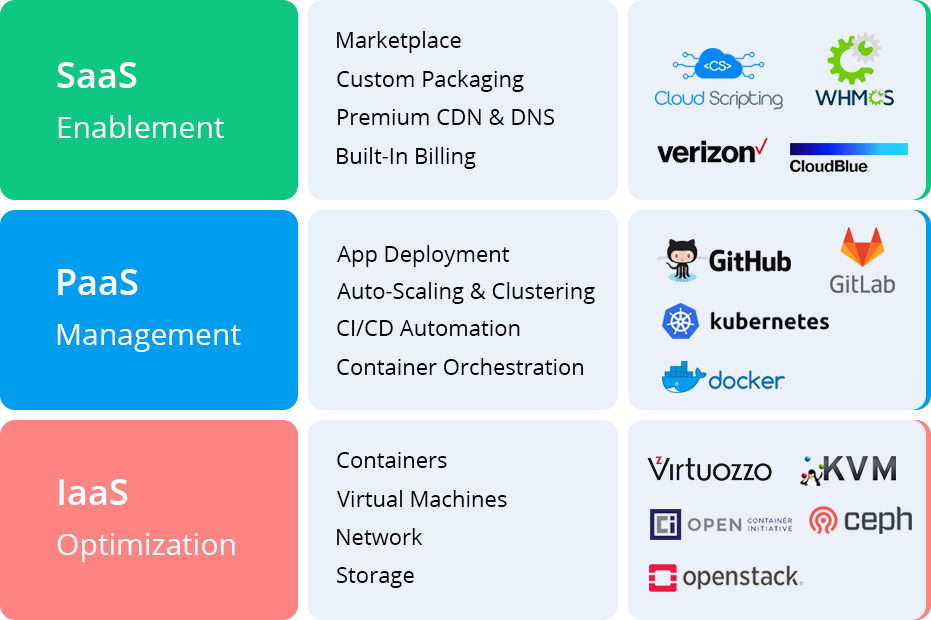
PaaS is a cloud computing model that delivers a platform allowing customers to develop, run, and manage applications without the complexity of building and maintaining the infrastructure typically associated with developing and launching an app. In essence, it sits between Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) and Software as a Service (SaaS), providing a complete development and deployment environment in the cloud.
The key components of a PaaS offering usually include:
- Operating systems
- Programming-language execution environment
- Database
- Web server
By abstracting away the infrastructure management, PaaS allows developers to focus solely on writing code and innovating, accelerating the development lifecycle. The example of PaaS usage is widespread and spans many different industries.
Benefits of Using PaaS
The advantages of adopting a PaaS solution are numerous. Here are some of the most significant benefits:
- Reduced Operational Overhead: PaaS providers handle the underlying infrastructure, freeing up developers to focus on coding and innovation.
- Faster Time to Market: With a pre-configured development environment, applications can be developed and deployed more quickly.
- Cost Savings: PaaS eliminates the need for significant upfront investments in hardware and software, reducing overall IT costs.
- Scalability and Flexibility: PaaS platforms easily scale resources to meet changing demands, ensuring optimal performance.
- Improved Collaboration: PaaS facilitates collaboration among developers, enabling seamless teamwork and knowledge sharing.
These benefits make example of PaaS implementations attractive to organizations of all sizes.
Types of PaaS
PaaS solutions can be categorized into several types, each catering to different needs and use cases:
Public PaaS
Public PaaS is hosted on the cloud provider’s infrastructure and offered to multiple users. It’s a cost-effective option for organizations that don’t require strict control over their infrastructure. An example of PaaS in the public cloud includes offerings from AWS, Google Cloud, and Microsoft Azure.
Private PaaS
Private PaaS is hosted within an organization’s own data center, providing greater control over security and compliance. It’s suitable for companies with stringent regulatory requirements. Red Hat OpenShift is a common example of PaaS used in private cloud environments.
Hybrid PaaS
Hybrid PaaS combines the benefits of both public and private PaaS, allowing organizations to deploy applications in the most suitable environment based on their specific needs. This approach offers flexibility and scalability. Consider a scenario where sensitive data is kept on-premise (private PaaS) while the application’s front-end is deployed on a public PaaS for scalability.
Mobile PaaS (mPaaS)
Mobile PaaS focuses on providing tools and services specifically for developing mobile applications. It includes features like push notifications, mobile backend as a service (MBaaS), and cross-platform development tools. Firebase is an example of PaaS that significantly supports mobile app development.
Open PaaS
Open PaaS is based on open-source technologies, offering greater flexibility and customization options. It allows organizations to avoid vendor lock-in and tailor the platform to their specific requirements. Cloud Foundry is a notable example of PaaS in the open-source space.
Real-World Examples of PaaS
To better understand the practical applications of PaaS, let’s examine some real-world examples:
Salesforce Heroku
Heroku is a popular PaaS platform known for its ease of use and robust support for various programming languages. It allows developers to quickly deploy and scale web applications. An example of PaaS use case is a startup using Heroku to build and deploy a customer relationship management (CRM) system. Heroku’s managed infrastructure enables the startup to focus on developing features and acquiring customers rather than managing servers.
Google App Engine
Google App Engine is a PaaS offering that allows developers to build and run web applications on Google’s infrastructure. It supports multiple programming languages and provides automatic scaling and load balancing. An example of PaaS application is a media company using Google App Engine to host its news website. The platform’s scalability ensures the website can handle traffic spikes during major news events without performance degradation.
Microsoft Azure App Service
Azure App Service is a comprehensive PaaS solution that supports web apps, mobile backends, and APIs. It integrates seamlessly with other Azure services and provides a rich set of development tools. A retail company might use Azure App Service to build and deploy its e-commerce platform. The PaaS solution provides the necessary tools and services for managing the platform, integrating payment gateways, and handling customer data securely. This is a perfect example of PaaS benefiting a large enterprise.
AWS Elastic Beanstalk
AWS Elastic Beanstalk is a PaaS offering that simplifies the deployment and management of web applications and services on AWS. It supports various programming languages and deployment environments. A software development company might use AWS Elastic Beanstalk to quickly deploy and manage its web applications in a scalable and reliable environment. This example of PaaS allows the company to focus on developing new features and improving the user experience without worrying about infrastructure management.
Red Hat OpenShift
Red Hat OpenShift is a container-based PaaS platform that supports the development and deployment of applications using Docker and Kubernetes. It provides a flexible and scalable environment for building and running applications. An enterprise might use Red Hat OpenShift to build and deploy its microservices-based applications. The platform’s containerization capabilities enable the enterprise to easily manage and scale its applications across different environments, ensuring high availability and performance. This example of PaaS shows the power of containerization.
Choosing the Right PaaS Solution
Selecting the right PaaS solution depends on various factors, including:
- Specific Requirements: Understand your application’s requirements, such as programming languages, database support, and scalability needs.
- Budget: Evaluate the pricing models of different PaaS providers and choose a solution that fits your budget.
- Security and Compliance: Ensure the PaaS provider meets your security and compliance requirements.
- Integration: Consider how well the PaaS solution integrates with your existing infrastructure and tools.
- Support: Evaluate the level of support provided by the PaaS vendor.
By carefully considering these factors, you can select a PaaS solution that best meets your organization’s needs. Each example of PaaS listed above has different strengths and weaknesses.
The Future of PaaS
The future of PaaS is bright, with ongoing advancements in cloud computing and containerization technologies. PaaS is expected to continue to evolve, offering even more powerful tools and services for developers. Some trends to watch include:
- Serverless Computing: PaaS platforms are increasingly incorporating serverless computing capabilities, allowing developers to build and run applications without managing servers.
- Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning: PaaS platforms are integrating AI and ML services, enabling developers to build intelligent applications.
- Low-Code/No-Code Platforms: PaaS platforms are evolving to include low-code/no-code development environments, empowering citizen developers to build applications with minimal coding.
These trends suggest that PaaS will continue to play a crucial role in the future of software development, enabling organizations to innovate faster and more efficiently. Understanding each example of PaaS and its unique features will be critical.
Conclusion
Platform as a Service (PaaS) offers a powerful and efficient way to develop, deploy, and manage applications in the cloud. By abstracting away the complexities of infrastructure management, PaaS allows developers to focus on innovation and deliver value to their organizations. Understanding the different types of PaaS and their real-world applications is essential for making informed decisions about adopting this technology. The example of PaaS implementations mentioned in this article demonstrate the versatility and potential of PaaS across various industries. As PaaS continues to evolve, it will undoubtedly remain a key enabler of digital transformation.
[See also: Cloud Computing Models: IaaS, PaaS, SaaS]
[See also: The Benefits of Using a PaaS Platform]
[See also: How to Choose the Right PaaS Provider]
