Understanding Network Types: A Comprehensive Guide to Different Network Classifications
In today’s interconnected world, understanding network types is crucial for businesses, IT professionals, and even everyday users. Networks facilitate communication, resource sharing, and data transfer, forming the backbone of modern infrastructure. This comprehensive guide explores various classifications of network types, shedding light on their characteristics, advantages, and disadvantages.
Classifying Networks by Geographical Span
One of the most common ways to categorize network types is by their geographical scope. This classification highlights the area covered by the network and helps determine its suitability for different applications.
Personal Area Network (PAN)
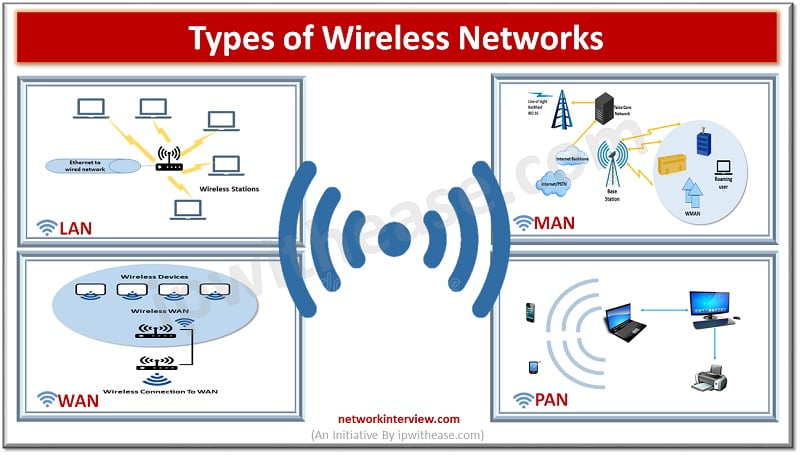
A Personal Area Network (PAN) is the smallest type of network, typically covering a range of a few meters. It’s designed to connect devices used by a single person. Examples include connecting a smartphone to a Bluetooth headset, a wireless keyboard to a laptop, or a smartwatch to a mobile device. PANs are characterized by their simplicity and low cost.
Local Area Network (LAN)
A Local Area Network (LAN) connects devices within a limited area, such as a home, office, or school. LANs enable resource sharing, like printers and file servers, and facilitate communication among connected devices. Ethernet and Wi-Fi are common technologies used in LANs. Due to their limited size, LANs offer high speeds and low latency. [See also: Network Security Best Practices for Small Businesses]
Metropolitan Area Network (MAN)
A Metropolitan Area Network (MAN) covers a larger geographical area than a LAN, typically spanning a city or metropolitan region. MANs are often used by businesses and government organizations to connect multiple LANs together. They provide high-speed connectivity and can support a wide range of applications. Examples include cable television networks and municipal broadband networks. Understanding the different network types helps in choosing the right solution for specific needs.
Wide Area Network (WAN)
A Wide Area Network (WAN) is the largest type of network, covering a wide geographical area, such as a country or even the entire world. The Internet is the most prominent example of a WAN. WANs connect multiple LANs and MANs together, enabling communication and data transfer across vast distances. Technologies like MPLS, VPNs, and dedicated leased lines are commonly used in WANs. Choosing between different network types depends on the scale and requirements of the organization.
Classifying Networks by Topology
Network topology refers to the physical or logical arrangement of devices in a network. Different topologies have different characteristics in terms of cost, performance, and reliability. Selecting the appropriate topology is crucial for optimizing network performance. The various network types based on topology are discussed below.
Bus Topology
In a bus topology, all devices are connected to a single cable, called the bus. Data is transmitted along the bus, and all devices receive the data. However, only the device with the matching address processes the data. Bus topologies are simple to implement but can suffer from performance issues when the network is heavily loaded. A break in the bus cable can disrupt the entire network.
Star Topology
In a star topology, all devices are connected to a central hub or switch. Data is transmitted from the sending device to the central hub, which then forwards the data to the intended recipient. Star topologies are more reliable than bus topologies because a failure of a single device or cable only affects that device. They are also easier to troubleshoot and manage. Star topologies are commonly used in modern LANs. Different network types offer varying levels of reliability.
Ring Topology
In a ring topology, devices are connected in a closed loop. Data is transmitted around the ring from one device to the next until it reaches the destination device. Ring topologies can be relatively expensive to implement and maintain. A break in the ring can disrupt the entire network, although dual-ring topologies can provide redundancy. Understanding the different network types is essential for building resilient infrastructure.
Mesh Topology
In a mesh topology, each device is connected to multiple other devices. This provides redundancy and high availability. If one connection fails, data can be routed through another path. Mesh topologies are commonly used in critical infrastructure and wireless networks. They are more complex and expensive to implement than other topologies. Exploring the various network types is crucial for selecting the most appropriate one for your needs.
Tree Topology
A tree topology combines characteristics of bus and star topologies. It consists of a hierarchical structure with a root node connected to multiple branches, which in turn connect to other nodes. Tree topologies are often used in large organizations to connect different departments or branches. They offer a balance between cost and performance. Different network types offer unique advantages and disadvantages.
Classifying Networks by Protocol
Network protocols are sets of rules that govern how data is transmitted and received over a network. Different protocols are designed for different purposes and have different characteristics in terms of speed, security, and reliability. The choice of protocol significantly impacts the functionality of various network types.
TCP/IP
TCP/IP (Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol) is the foundation of the Internet. It is a suite of protocols that enables communication between devices on a network. TCP provides reliable, connection-oriented communication, while IP provides addressing and routing. TCP/IP is used in virtually all modern networks. It is fundamental to understanding different network types.
HTTP/HTTPS
HTTP (Hypertext Transfer Protocol) is used for transferring web pages and other content over the Internet. HTTPS (Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure) is a secure version of HTTP that uses encryption to protect data in transit. HTTPS is essential for secure online transactions and protecting sensitive information. The security aspect influences the choice of network types.
FTP
FTP (File Transfer Protocol) is used for transferring files between computers on a network. FTP is commonly used for uploading and downloading files from web servers. While still used, it’s often replaced by more secure methods like SFTP. Different network types may require different protocols for file transfer.
SMTP
SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol) is used for sending email messages. SMTP is used by email clients to send messages to email servers, which then forward the messages to the recipient’s email server. SMTP is a critical protocol for email communication. Understanding the underlying protocols helps in appreciating the functionality of different network types.
Classifying Networks by Architecture
Network architecture refers to the overall design and structure of a network. Different architectures have different characteristics in terms of scalability, security, and manageability. Choosing the right architecture is essential for building a robust and efficient network.
Client-Server
In a client-server architecture, one or more servers provide resources and services to client devices. Clients request services from the server, and the server responds to the requests. Client-server architectures are commonly used in enterprise networks and the Internet. They offer centralized management and security. The architecture directly impacts the performance of various network types.
Peer-to-Peer
In a peer-to-peer (P2P) architecture, all devices have equal capabilities and can share resources with each other. P2P networks are decentralized and do not rely on a central server. P2P networks are commonly used for file sharing and online gaming. They can be more difficult to manage and secure than client-server networks. Understanding the different architectures is crucial for designing efficient network types.
Security Considerations for Different Network Types
Security is a critical consideration for all network types. Different networks have different security vulnerabilities and require different security measures. Implementing robust security measures is essential for protecting data and preventing unauthorized access. [See also: The Ultimate Guide to Cybersecurity for Beginners]
Firewalls
Firewalls are a key security component for protecting networks from unauthorized access. Firewalls act as a barrier between the network and the outside world, blocking malicious traffic and preventing unauthorized users from accessing the network. Firewalls are essential for all network types.
Intrusion Detection and Prevention Systems (IDS/IPS)
Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) and Intrusion Prevention Systems (IPS) are used to detect and prevent malicious activity on a network. IDS monitors network traffic for suspicious patterns and alerts administrators to potential security threats. IPS takes proactive measures to block malicious traffic and prevent attacks. IDS/IPS are important for securing different network types.
VPNs
Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) create a secure, encrypted connection between a device and a network. VPNs are commonly used to protect data in transit, especially when using public Wi-Fi networks. VPNs are essential for remote access and securing sensitive data. They enhance the security of various network types.
Access Control
Access control mechanisms are used to restrict access to network resources based on user identity and permissions. Access control helps prevent unauthorized users from accessing sensitive data and performing unauthorized actions. Implementing proper access control is crucial for all network types.
Conclusion
Understanding the different network types is crucial for building and managing effective and secure networks. By considering factors such as geographical span, topology, protocol, and architecture, organizations can choose the right network solution for their specific needs. Implementing robust security measures is essential for protecting data and preventing unauthorized access. As technology evolves, staying informed about the latest trends in network types is essential for staying ahead of the curve. Choosing the right network types involves careful consideration of various factors. The future of network types is constantly evolving, with new technologies and approaches emerging regularly. Staying updated on the latest advancements in network types is essential for making informed decisions. The diversity of network types allows for tailored solutions to meet specific requirements. Understanding the nuances of different network types empowers informed decision-making.
