Understanding Metropolitan Area Networks: A Large Computer Network Spanning a City
In today’s interconnected world, the ability to transmit data quickly and efficiently across geographical areas is paramount. One key technology facilitating this is the Metropolitan Area Network (MAN). Defined as a large computer network usually spanning a city or metropolitan area, a MAN plays a crucial role in connecting businesses, institutions, and individuals. This article delves into the intricacies of MANs, exploring their architecture, benefits, and significance in modern communication infrastructure. Understanding what constitutes a large computer network usually spanning a city is essential for anyone involved in IT infrastructure or telecommunications.
What is a Metropolitan Area Network (MAN)?
A large computer network usually spanning a city, a MAN is larger than a Local Area Network (LAN) but smaller than a Wide Area Network (WAN). Its primary function is to connect multiple LANs within a specific geographical area, such as a city or a large campus. This allows different organizations or departments to share resources, communicate effectively, and access the internet through a shared high-speed connection. Unlike WANs, which can span across countries or even continents, MANs are confined to a smaller, more concentrated area.
Key Characteristics of a MAN
- Geographic Scope: As the definition suggests, a large computer network usually spanning a city covers a metropolitan area, connecting various locations within that region.
- High-Speed Connectivity: MANs typically offer high-speed data transfer rates, enabling efficient communication and resource sharing.
- Ownership: MANs can be owned and operated by a single organization or a consortium of organizations. Alternatively, they can be provided as a service by a telecommunications company.
- Technology: MANs utilize various technologies, including fiber optics, wireless communication, and high-speed copper cables, to ensure reliable and fast data transmission.
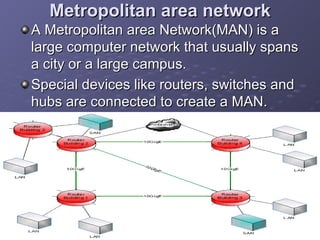
Architecture of a Metropolitan Area Network
The architecture of a MAN can vary depending on its specific requirements and the technology used. However, a typical MAN architecture includes the following components:
Core Layer
The core layer forms the backbone of the MAN and is responsible for high-speed data transmission between different parts of the network. It typically consists of high-performance routers and switches connected by fiber optic cables.
Distribution Layer
The distribution layer connects the core layer to the access layer. It aggregates traffic from multiple access points and forwards it to the core layer. This layer often uses technologies like Ethernet or wireless communication to connect to the access layer.
Access Layer
The access layer provides connectivity to end-users and devices. It typically consists of LANs, wireless access points, and other network devices that allow users to connect to the MAN. This layer is crucial for ensuring that users can access the network resources they need.
Benefits of Using a Metropolitan Area Network
Implementing a large computer network usually spanning a city offers several significant benefits to organizations and communities:
- Improved Communication: MANs facilitate seamless communication between different departments, branches, or organizations within a city, enhancing collaboration and productivity.
- Resource Sharing: By connecting multiple LANs, a MAN allows organizations to share resources such as printers, servers, and internet connections, reducing costs and improving efficiency.
- Enhanced Security: MANs can provide centralized security management, protecting sensitive data and preventing unauthorized access to network resources.
- High-Speed Internet Access: MANs often provide high-speed internet access to businesses and residents, enabling them to take advantage of online services and applications.
- Disaster Recovery: MANs can be used to create backup and disaster recovery solutions, ensuring that critical data and applications remain available even in the event of a local outage.
Applications of Metropolitan Area Networks
The applications of a large computer network usually spanning a city are diverse and span various sectors:
Business
Businesses use MANs to connect their different offices and branches within a city, allowing them to share resources, collaborate on projects, and communicate effectively. This is especially important for large corporations with multiple locations.
Education
Educational institutions use MANs to connect different campuses and schools within a city, enabling students and faculty to access shared resources and collaborate on research projects. This can enhance the learning experience and improve educational outcomes. [See also: The Future of Educational Networks]
Government
Government agencies use MANs to connect different departments and offices, allowing them to share information, coordinate services, and improve citizen engagement. This can lead to more efficient and effective government operations.
Healthcare
Healthcare providers use MANs to connect different hospitals, clinics, and medical facilities, enabling them to share patient data, coordinate care, and improve healthcare outcomes. Secure and reliable data transmission is critical in this sector.
Public Safety
Public safety agencies use MANs to connect police stations, fire departments, and emergency response centers, allowing them to coordinate responses to emergencies and improve public safety. Quick and reliable communication is paramount in these situations.
Technologies Used in Metropolitan Area Networks
Several technologies are used to implement MANs, each with its own advantages and disadvantages:
Fiber Optics
Fiber optics is the most common technology used in MANs due to its high bandwidth, low latency, and long-distance capabilities. Fiber optic cables can transmit data at speeds of up to 100 Gbps or more, making them ideal for high-speed data transmission. A robust large computer network usually spanning a city relies heavily on fiber optic infrastructure.
Ethernet
Ethernet is a widely used technology for connecting devices within a LAN. It can also be used to connect LANs within a MAN. Ethernet is relatively inexpensive and easy to deploy, making it a popular choice for many organizations.
Wireless Communication
Wireless communication technologies such as Wi-Fi and cellular networks can be used to connect devices and LANs within a MAN. Wireless communication is particularly useful for connecting remote locations or providing connectivity to mobile users.
Microwave
Microwave technology can be used to transmit data wirelessly over long distances. It is often used to connect remote locations or to provide backup connectivity in case of a fiber optic cable failure.
Challenges in Implementing a MAN
While MANs offer numerous benefits, implementing and maintaining them can also present several challenges:
- Cost: Implementing a MAN can be expensive, particularly if it requires laying new fiber optic cables or deploying wireless infrastructure.
- Security: MANs can be vulnerable to security threats such as hacking and data breaches. It is important to implement robust security measures to protect sensitive data.
- Scalability: MANs need to be scalable to accommodate future growth and changing needs. It is important to design the network architecture in a way that allows it to be easily expanded and upgraded.
- Maintenance: MANs require ongoing maintenance and support to ensure that they continue to operate reliably. This can include tasks such as monitoring network performance, troubleshooting problems, and applying security patches.
The Future of Metropolitan Area Networks
The future of MANs is bright, with several emerging trends promising to further enhance their capabilities and applications:
5G Technology
The deployment of 5G technology will enable MANs to provide even faster and more reliable wireless connectivity. 5G networks offer significantly higher bandwidth and lower latency than previous generations of wireless technology, making them ideal for supporting bandwidth-intensive applications such as video streaming and virtual reality.
Software-Defined Networking (SDN)
SDN allows network administrators to manage and control network resources centrally, making it easier to optimize network performance and respond to changing needs. SDN can also be used to automate network tasks and improve security.
Network Function Virtualization (NFV)
NFV allows network functions such as firewalls and load balancers to be virtualized and run on commodity hardware. This can reduce costs and improve flexibility by allowing organizations to deploy network functions on demand.
Internet of Things (IoT)
The growth of the IoT is driving the demand for more bandwidth and connectivity. MANs will play a crucial role in connecting IoT devices and enabling them to communicate with each other and with central servers. A robust large computer network usually spanning a city is vital for supporting the IoT ecosystem.
Conclusion
A large computer network usually spanning a city, the Metropolitan Area Network, is a critical component of modern communication infrastructure. It enables businesses, institutions, and individuals to connect, communicate, and share resources efficiently. As technology continues to evolve, MANs will play an increasingly important role in supporting the growing demand for bandwidth and connectivity. Understanding the architecture, benefits, and challenges of MANs is essential for anyone involved in IT infrastructure or telecommunications. With ongoing advancements in technology, the future of MANs looks promising, offering even greater capabilities and applications in the years to come. The continued development and optimization of a large computer network usually spanning a city will undoubtedly shape the future of urban connectivity and communication.
