Understanding DNS Server IP Addresses: A Comprehensive Guide
In the digital age, the Domain Name System (DNS) is a cornerstone of internet functionality, often working silently in the background to ensure seamless browsing experiences. Understanding the intricacies of DNS server IP addresses is crucial for anyone aiming to troubleshoot network issues, optimize internet performance, or enhance online security. This article provides a comprehensive overview of DNS server IP addresses, exploring their function, significance, and how to manage them effectively. We’ll delve into the role of DNS server IP addresses in translating domain names into IP addresses, discuss different types of DNS server IP addresses, and provide practical guidance on how to find and change them. Whether you’re a seasoned IT professional or a curious internet user, this guide aims to demystify the world of DNS server IP addresses.
What is a DNS Server and Why is its IP Address Important?
To grasp the significance of a DNS server IP address, it’s essential to understand what a DNS server is. In simple terms, a DNS server acts as an internet phonebook. When you type a domain name like ‘example.com’ into your browser, your computer needs to find the corresponding IP address (e.g., 93.184.216.34) to connect to the server hosting the website. The DNS server performs this translation, resolving the human-readable domain name into a machine-readable IP address. The DNS server IP address is the specific address of the server that performs this translation.
Without DNS, you would need to remember and enter the IP addresses of every website you want to visit, which would be incredibly cumbersome. Therefore, the DNS server IP address is vitally important for enabling easy and efficient internet browsing. Properly configured DNS server IP addresses ensure that your requests are routed correctly and efficiently, leading to faster loading times and a smoother online experience.
Types of DNS Servers and Their IP Addresses
There are several types of DNS servers, each playing a specific role in the DNS resolution process. Understanding these different types can help you appreciate the complexities involved in translating domain names to IP addresses.
Recursive DNS Servers
Recursive DNS servers are the servers that your computer directly queries. These servers are typically provided by your Internet Service Provider (ISP) or a third-party DNS server IP service. When you request to visit a website, your computer sends a query to the recursive DNS server, which then begins the process of finding the correct IP address. If the recursive server doesn’t already have the IP address cached, it will query other DNS servers to find it. Some popular recursive DNS server IP addresses include Google’s (8.8.8.8 and 8.8.4.4) and Cloudflare’s (1.1.1.1 and 1.0.0.1).
Authoritative DNS Servers
Authoritative DNS servers hold the definitive records for specific domain names. These servers are responsible for providing the correct IP address for a given domain. When a recursive DNS server needs to find the IP address for ‘example.com,’ it will eventually query the authoritative DNS servers for that domain. The authoritative server responds with the correct IP address, which is then passed back to your computer. The DNS server IP address of the authoritative server is crucial for ensuring that domain names are resolved correctly.
Root DNS Servers
Root DNS servers are at the top of the DNS hierarchy. They are the first servers queried by a recursive DNS server when it doesn’t have the IP address cached. Root servers don’t know the IP addresses for every domain, but they know the addresses of the top-level domain (TLD) servers (e.g., .com, .org, .net). They direct the recursive server to the appropriate TLD server, which can then provide information about the authoritative servers for the domain. The DNS server IP addresses of these root servers are essential for the initial stages of DNS resolution.
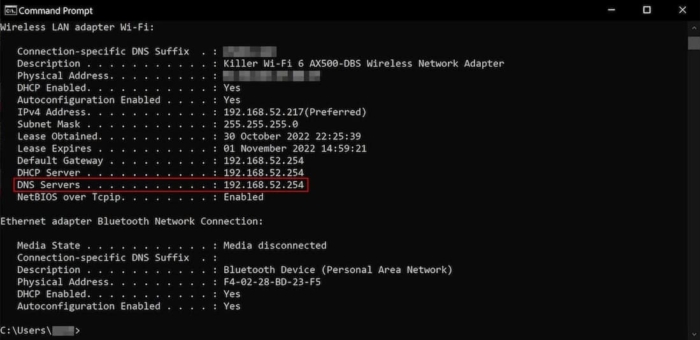
How to Find Your Current DNS Server IP Address
Finding your current DNS server IP address can be useful for troubleshooting network issues or verifying that your settings are correct. The method for finding your DNS server IP address varies depending on your operating system.
Windows
- Open the Command Prompt.
- Type `ipconfig /all` and press Enter.
- Look for the section related to your network adapter (e.g., Ethernet or Wi-Fi).
- Find the line labeled “DNS Servers.” The IP addresses listed there are your current DNS server IP addresses.
macOS
- Open System Preferences.
- Click on “Network.”
- Select your network connection (e.g., Wi-Fi or Ethernet).
- Click on “Advanced.”
- Go to the “DNS” tab. The IP addresses listed there are your current DNS server IP addresses.
Linux
- Open a terminal.
- Type `cat /etc/resolv.conf` and press Enter.
- The lines starting with “nameserver” show your current DNS server IP addresses.
How to Change Your DNS Server IP Address
Changing your DNS server IP address can improve your internet speed, enhance your online security, or bypass censorship. Here’s how to change your DNS server IP address on different operating systems:
Windows
- Open the Control Panel.
- Click on “Network and Internet.”
- Click on “Network and Sharing Center.”
- Click on your network connection (e.g., Ethernet or Wi-Fi).
- Click on “Properties.”
- Select “Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4)” and click on “Properties.”
- Select “Use the following DNS server addresses.”
- Enter your preferred DNS server IP addresses in the “Preferred DNS server” and “Alternate DNS server” fields.
- Click “OK” to save your changes.
macOS
- Open System Preferences.
- Click on “Network.”
- Select your network connection (e.g., Wi-Fi or Ethernet).
- Click on “Advanced.”
- Go to the “DNS” tab.
- Click the “+” button to add new DNS server IP addresses.
- Enter your preferred DNS server IP addresses.
- Click “OK” to save your changes.
Linux
The method for changing your DNS server IP address on Linux varies depending on your distribution and network configuration. One common method is to edit the `/etc/resolv.conf` file. However, this file is often overwritten by network management tools. A more persistent method is to configure your network settings through your distribution’s network manager.
Popular DNS Server IP Address Options
Several popular DNS server IP options are available, each offering different features and benefits. Here are some of the most commonly used DNS server IP addresses:
- Google Public DNS: 8.8.8.8 and 8.8.4.4. Known for its reliability and speed.
- Cloudflare DNS: 1.1.1.1 and 1.0.0.1. Focuses on privacy and speed.
- OpenDNS: 208.67.222.222 and 208.67.220.220. Offers content filtering and security features.
- Quad9: 9.9.9.9 and 149.112.112.112. Provides security by blocking malicious domains.
Troubleshooting Common DNS Issues
Even with properly configured DNS server IP addresses, you may occasionally encounter DNS-related issues. Here are some common problems and how to troubleshoot them:
- Website Not Found: This error often indicates a DNS resolution problem. Try flushing your DNS cache or changing your DNS server IP address. [See also: How to Clear Your DNS Cache]
- Slow Internet Speed: A slow DNS server can significantly impact your browsing speed. Consider switching to a faster DNS server IP address.
- Intermittent Connectivity: This can be caused by unreliable DNS servers. Try using a more stable DNS server IP address.
Security Considerations for DNS Server IP Addresses
Choosing a secure DNS server IP address is crucial for protecting your online privacy and security. Some DNS servers offer additional security features, such as blocking malicious domains and preventing DNS hijacking. It’s important to research and select a DNS server IP address that aligns with your security needs. [See also: DNS Security Best Practices]
Conclusion
Understanding DNS server IP addresses is essential for anyone seeking to optimize their internet experience. By knowing how DNS server IP addresses work, how to find and change them, and how to troubleshoot common DNS issues, you can take control of your network settings and improve your online security and performance. Whether you choose to use the default DNS server IP provided by your ISP or switch to a third-party option like Google or Cloudflare, understanding the role of DNS server IP addresses empowers you to make informed decisions about your internet connectivity. Remember to always prioritize security and privacy when selecting a DNS server IP address to ensure a safe and reliable browsing experience. The world of DNS server IP addresses may seem complex, but with the right knowledge, you can navigate it with confidence.
