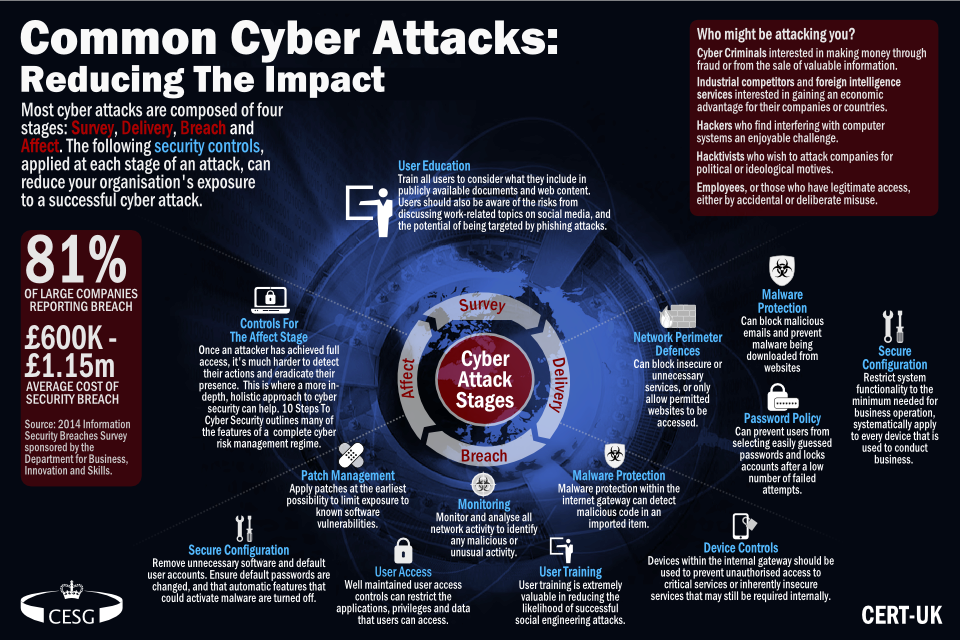
Understanding Cyber Attacks: A Comprehensive Guide to Threats, Prevention, and Response
In today’s interconnected world, cyber attacks pose a significant threat to individuals, businesses, and governments alike. From data breaches and ransomware to phishing scams and distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks, the landscape of cyber threats is constantly evolving. Understanding the nature of these attacks, their potential impact, and the strategies for prevention and response is crucial for maintaining cybersecurity in the digital age. This article provides a comprehensive overview of cyber attacks, exploring different types, motivations, and essential measures to protect against them.
What are Cyber Attacks?
A cyber attack is any malicious attempt to access, damage, disrupt, or steal information from a computer system, network, or device. These attacks can originate from various sources, including individual hackers, organized crime groups, state-sponsored actors, and even disgruntled insiders. The motivations behind cyber attacks can range from financial gain and espionage to political activism and personal vendettas.
Common Types of Cyber Attacks
- Malware: Malicious software designed to infiltrate and damage computer systems. This includes viruses, worms, Trojans, and spyware. [See also: Understanding Malware and Its Impact on Cybersecurity]
- Phishing: Deceptive attempts to trick individuals into revealing sensitive information, such as usernames, passwords, and credit card details, often through fraudulent emails or websites.
- Ransomware: A type of malware that encrypts a victim’s files and demands a ransom payment in exchange for the decryption key.
- DDoS Attacks: Overwhelming a target server or network with a flood of traffic, rendering it unavailable to legitimate users.
- SQL Injection: Exploiting vulnerabilities in database applications to gain unauthorized access to sensitive data.
- Man-in-the-Middle (MitM) Attacks: Intercepting and altering communication between two parties without their knowledge.
- Zero-Day Exploits: Attacks that exploit vulnerabilities that are unknown to the software vendor, leaving systems vulnerable until a patch is released.
The Anatomy of a Cyber Attack
While the specific techniques used in cyber attacks vary, most follow a general pattern:
- Reconnaissance: Gathering information about the target, including its network infrastructure, software versions, and security policies.
- Scanning: Probing the target system for vulnerabilities that can be exploited.
- Exploitation: Using identified vulnerabilities to gain unauthorized access to the system.
- Installation: Installing malware or other tools to maintain access and control over the compromised system.
- Exfiltration: Stealing sensitive data from the compromised system.
- Maintaining Presence: Establishing a persistent foothold on the system to launch future attacks.
Motivations Behind Cyber Attacks
Understanding the motivations behind cyber attacks is essential for developing effective security strategies.
- Financial Gain: This is a primary motivation for many cyber attacks, including ransomware attacks, phishing scams, and credit card fraud.
- Espionage: State-sponsored actors and corporate spies may conduct cyber attacks to steal trade secrets, intellectual property, or sensitive government information.
- Political Activism (Hacktivism): Hackers may launch cyber attacks to disrupt or deface websites, leak sensitive information, or otherwise promote a political agenda.
- Revenge: Disgruntled employees or former business partners may launch cyber attacks to retaliate against an organization.
- Disruption: Some cyber attacks are designed to disrupt critical infrastructure, such as power grids, transportation systems, or financial networks.
The Impact of Cyber Attacks
The impact of cyber attacks can be devastating, ranging from financial losses and reputational damage to legal liabilities and operational disruptions.
- Financial Losses: Cyber attacks can result in significant financial losses due to data breaches, ransomware payments, fraud, and business interruption.
- Reputational Damage: A successful cyber attack can damage an organization’s reputation, leading to loss of customer trust and business opportunities.
- Legal Liabilities: Organizations that fail to adequately protect sensitive data may face legal liabilities and regulatory fines.
- Operational Disruptions: Cyber attacks can disrupt business operations, leading to downtime, lost productivity, and supply chain disruptions.
- Data Loss: Sensitive data, including customer information, trade secrets, and financial records, can be stolen or destroyed in a cyber attack.
Preventing Cyber Attacks: A Proactive Approach
Prevention is the best defense against cyber attacks. Implementing a proactive cybersecurity strategy can significantly reduce the risk of a successful attack.
Key Security Measures
- Strong Passwords and Multi-Factor Authentication: Enforce the use of strong, unique passwords and enable multi-factor authentication (MFA) for all accounts.
- Regular Software Updates: Keep all software, including operating systems, applications, and security software, up to date with the latest patches and security updates.
- Firewalls and Intrusion Detection Systems: Implement firewalls and intrusion detection systems (IDS) to monitor network traffic and detect malicious activity.
- Antivirus and Anti-Malware Software: Install and maintain antivirus and anti-malware software on all devices.
- Employee Training and Awareness: Educate employees about the risks of phishing scams, social engineering, and other cyber attacks. [See also: The Importance of Cybersecurity Awareness Training]
- Data Encryption: Encrypt sensitive data both in transit and at rest to protect it from unauthorized access.
- Regular Backups: Back up critical data regularly and store backups in a secure, offsite location.
- Vulnerability Scanning and Penetration Testing: Conduct regular vulnerability scans and penetration tests to identify and address security weaknesses.
- Incident Response Plan: Develop and implement an incident response plan to guide the organization’s response to a cyber attack.
Responding to a Cyber Attack
Even with the best prevention measures in place, cyber attacks can still occur. Having a well-defined incident response plan is crucial for minimizing the impact of an attack.
Steps to Take During a Cyber Attack
- Detection: Identify the cyber attack as quickly as possible. This may involve monitoring network traffic, analyzing security logs, or receiving reports from users.
- Containment: Isolate the affected systems and prevent the attack from spreading to other parts of the network.
- Eradication: Remove the malware or other malicious code from the affected systems.
- Recovery: Restore the affected systems to their normal operating state. This may involve restoring data from backups or rebuilding systems from scratch.
- Post-Incident Analysis: Conduct a thorough analysis of the cyber attack to identify the root cause, determine the extent of the damage, and improve security measures to prevent future attacks.
The Future of Cyber Attacks
The landscape of cyber attacks is constantly evolving, with new threats emerging all the time. As technology advances, attackers will continue to develop more sophisticated techniques to exploit vulnerabilities and bypass security measures. Organizations must stay vigilant and adapt their security strategies to keep pace with the evolving threat landscape. Investing in cybersecurity training, implementing advanced security technologies, and fostering a culture of security awareness are essential for protecting against cyber attacks in the future.
Cyber attacks are a persistent and growing threat in the digital age. By understanding the nature of these attacks, implementing proactive security measures, and developing a robust incident response plan, individuals and organizations can significantly reduce their risk of becoming victims.
