Privacy by Design Means: Embedding Privacy into Every Step
In today’s data-driven world, the concept of privacy is no longer an afterthought; it’s a fundamental requirement. One approach that champions this principle is Privacy by Design. But what does privacy by design means in practice? It’s about embedding privacy considerations into the entire lifecycle of systems, products, and services, from the very beginning. This proactive approach aims to minimize privacy risks and ensure that privacy is a core feature, not just an add-on.
Understanding Privacy by Design
Privacy by Design (PbD) is a framework that promotes integrating privacy considerations into the design and architecture of information technologies, networked systems, and business practices. It was developed by Dr. Ann Cavoukian, former Information and Privacy Commissioner of Ontario, Canada, and is based on seven foundational principles.
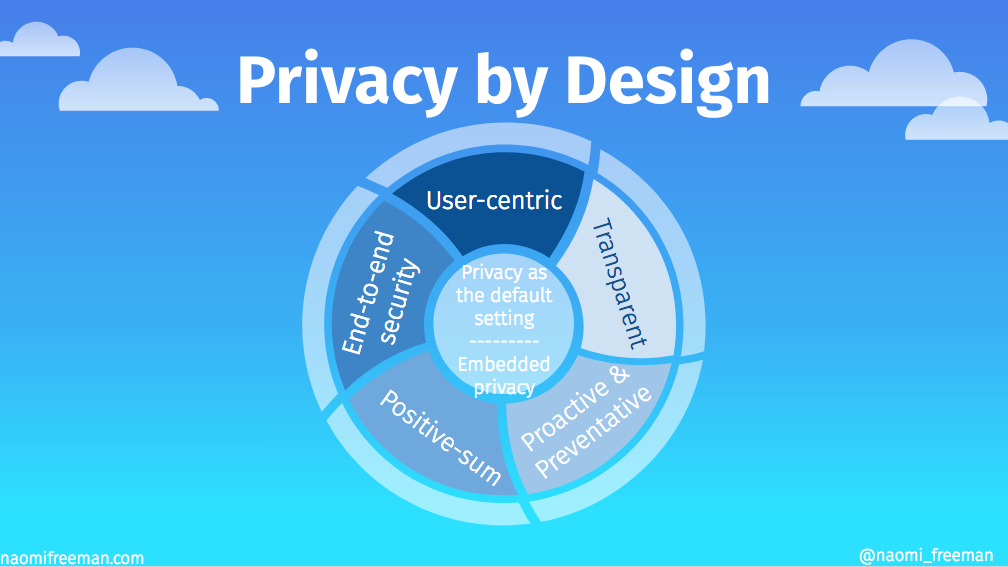
The Seven Foundational Principles of Privacy by Design
- Proactive not Reactive; Preventative not Remedial: This principle emphasizes anticipating privacy issues and preventing them from occurring, rather than reacting to them after they’ve happened. It is a core concept of what privacy by design means.
- Privacy as the Default Setting: Individuals should not have to take action to protect their privacy. The system should be designed so that personal data is automatically protected.
- Privacy Embedded into Design: Privacy should be an integral component of the system’s design and architecture, not just an added feature.
- Full Functionality – Positive-Sum, not Zero-Sum: Privacy should be compatible with other legitimate objectives, such as security and functionality. There shouldn’t be a trade-off between privacy and other goals.
- End-to-End Security – Full Lifecycle Protection: Privacy measures should be implemented throughout the entire lifecycle of the data, from collection to deletion.
- Visibility and Transparency – Keep it Open: The system’s privacy practices should be transparent and easily accessible to individuals.
- Respect for User Privacy – Keep it User-Centric: The system should be designed with the user’s interests in mind, providing them with control over their personal data.
Why is Privacy by Design Important?
There are several compelling reasons why privacy by design is crucial in today’s digital landscape:
- Enhanced Privacy Protection: By embedding privacy into the design process, organizations can significantly reduce the risk of privacy breaches and data misuse.
- Increased Trust: Implementing privacy by design means demonstrating a commitment to protecting individuals’ privacy, which can foster trust and improve customer relationships.
- Reduced Costs: Addressing privacy issues early in the development process is often less expensive than fixing them later on.
- Compliance with Regulations: Many privacy regulations, such as the GDPR and CCPA, emphasize the importance of privacy by design. Adopting PbD can help organizations comply with these regulations and avoid costly penalties. [See also: GDPR Compliance Checklist]
- Competitive Advantage: In an increasingly privacy-conscious world, organizations that prioritize privacy can gain a competitive advantage.
Examples of Privacy by Design in Practice
So, what does privacy by design means in the real world? Here are some practical examples:
- Data Minimization: Collecting only the data that is strictly necessary for a specific purpose.
- Anonymization and Pseudonymization: Removing or replacing identifying information to protect individuals’ privacy.
- Encryption: Protecting data by converting it into an unreadable format.
- Access Controls: Limiting access to personal data to authorized personnel only.
- Privacy-Enhancing Technologies (PETs): Using technologies that help to protect privacy, such as differential privacy and federated learning.
- Transparent Data Processing: Clearly informing individuals about how their data is being collected, used, and shared.
- User Consent Mechanisms: Implementing mechanisms that allow individuals to provide informed consent to the collection and use of their data.
Implementing Privacy by Design
Implementing Privacy by Design requires a comprehensive approach that involves all stakeholders, from designers and developers to legal and compliance professionals. Here are some key steps to consider:
- Conduct a Privacy Impact Assessment (PIA): A PIA helps to identify and assess the privacy risks associated with a particular project or system.
- Develop Privacy Requirements: Based on the PIA, define specific privacy requirements that must be met.
- Incorporate Privacy into the Design Process: Integrate privacy considerations into all stages of the design process, from initial planning to implementation and testing.
- Choose Appropriate Privacy Technologies: Select and implement appropriate privacy-enhancing technologies to protect personal data.
- Train Employees on Privacy: Provide employees with training on privacy principles and best practices.
- Monitor and Evaluate Privacy Performance: Regularly monitor and evaluate the effectiveness of privacy measures.
- Document Privacy Practices: Maintain clear and comprehensive documentation of privacy practices.
The Future of Privacy by Design
Privacy by design is becoming increasingly important as technology continues to evolve and data collection becomes more pervasive. As new technologies emerge, such as artificial intelligence and the Internet of Things, it’s crucial to embed privacy considerations into their design from the outset. This proactive approach will help to ensure that privacy is protected in the face of new and emerging threats. Understanding what privacy by design means is no longer optional for any organization handling personal data.
Moreover, regulatory bodies worldwide are increasingly emphasizing the principles of privacy by design in their data protection laws. This trend suggests that PbD will become an even more critical requirement for organizations in the future. Ignoring the principles of privacy by design means potentially facing significant legal and reputational risks.
Challenges to Implementing Privacy by Design
While the benefits of privacy by design are clear, implementing it in practice can be challenging. Some common challenges include:
- Lack of Awareness: Many organizations are still not fully aware of the principles of privacy by design and their importance.
- Resistance to Change: Implementing PbD may require significant changes to existing processes and workflows, which can be met with resistance.
- Complexity: Designing privacy into complex systems can be challenging, requiring specialized knowledge and expertise.
- Cost: Implementing PbD may involve additional costs, such as investing in privacy-enhancing technologies and training employees.
- Conflicting Objectives: Privacy objectives may sometimes conflict with other objectives, such as security or functionality.
Overcoming the Challenges
Despite these challenges, it’s possible to successfully implement privacy by design by taking a strategic and proactive approach. Here are some tips for overcoming the challenges:
- Raise Awareness: Educate employees and stakeholders about the principles of privacy by design and their benefits.
- Secure Management Support: Obtain buy-in from senior management to ensure that PbD is prioritized and supported.
- Develop a Privacy Framework: Create a comprehensive privacy framework that outlines the organization’s privacy principles, policies, and procedures.
- Provide Training: Provide employees with training on privacy best practices and how to implement PbD in their work.
- Collaborate with Experts: Engage with privacy experts and consultants to obtain specialized knowledge and guidance.
- Use Privacy Tools: Utilize privacy-enhancing technologies and tools to automate and streamline privacy processes.
- Monitor and Evaluate: Regularly monitor and evaluate the effectiveness of privacy measures and make adjustments as needed.
Conclusion
Privacy by Design is not just a buzzword; it’s a fundamental approach to protecting privacy in the digital age. By embedding privacy considerations into the design and architecture of systems, products, and services, organizations can significantly reduce the risk of privacy breaches and build trust with their customers. Understanding what privacy by design means is crucial for any organization handling personal data. While implementing PbD can be challenging, the benefits far outweigh the costs. As privacy regulations become more stringent and individuals become more privacy-conscious, privacy by design will become an increasingly essential requirement for success. Embracing privacy by design means embracing a future where privacy is respected and protected.
In conclusion, when you ask what privacy by design means, the answer lies in proactive, preventative, and user-centric approaches to data protection throughout the entire lifecycle of any system or service that handles personal information. It’s a commitment to building a privacy-respecting world.
