Platform as a Service (PaaS): Understanding Key Examples and Use Cases
In today’s rapidly evolving tech landscape, businesses are constantly seeking innovative solutions to streamline their operations, reduce costs, and accelerate their time to market. One such solution that has gained significant traction is Platform as a Service (PaaS). This article delves into the concept of PaaS, exploring its core components, benefits, and providing concrete examples of Platform as a Service in action. We will also examine various use cases to illustrate how PaaS can empower organizations across different industries.
What is Platform as a Service (PaaS)?
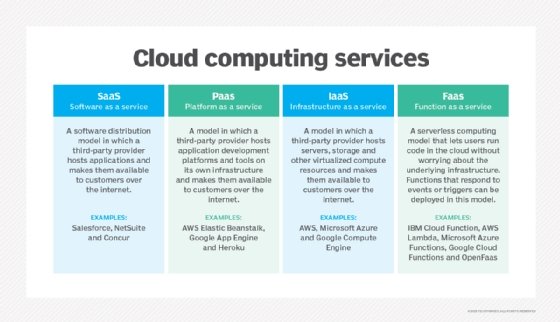
Platform as a Service (PaaS) is a cloud computing model that delivers a complete platform – including hardware, software, and infrastructure – for developing, running, and managing applications. Unlike Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), which provides access to raw computing resources, PaaS offers a higher-level abstraction, providing developers with the tools and services they need to build and deploy applications without the complexity of managing the underlying infrastructure. Essentially, PaaS allows developers to focus solely on coding and innovation, leaving the infrastructure management to the service provider.
Think of it as renting a fully equipped kitchen rather than just the ingredients. With IaaS, you get the ingredients (servers, storage, networking), and you’re responsible for everything else – cooking, cleaning, and maintaining the kitchen. With Platform as a Service, you get the kitchen pre-stocked with all the necessary appliances, tools, and utilities. You just focus on creating the dish (your application).
Key Components of a PaaS Platform
A typical PaaS example comprises the following key components:
- Operating Systems: A pre-configured operating system, such as Linux or Windows Server.
- Programming Languages and Frameworks: Support for various programming languages (e.g., Java, Python, Node.js, Ruby) and frameworks (e.g., Spring, Django, Ruby on Rails).
- Databases: Integrated database services, such as MySQL, PostgreSQL, MongoDB, or cloud-native databases.
- Development Tools: Integrated development environments (IDEs), debuggers, and other tools to facilitate application development.
- Deployment Tools: Tools for deploying and managing applications, including continuous integration and continuous delivery (CI/CD) pipelines.
- Scaling and Management Tools: Tools for automatically scaling applications based on demand and managing resources efficiently.
- Security Features: Security features to protect applications and data, including authentication, authorization, and encryption.
Benefits of Using Platform as a Service
Adopting a Platform as a Service solution offers numerous benefits to businesses, including:
- Reduced Costs: PaaS eliminates the need for businesses to invest in and maintain their own infrastructure, resulting in significant cost savings.
- Faster Time to Market: PaaS accelerates the development and deployment process, allowing businesses to bring their applications to market faster.
- Increased Agility: PaaS enables developers to quickly adapt to changing business requirements and market demands.
- Improved Collaboration: PaaS facilitates collaboration among development teams by providing a shared platform for building and deploying applications.
- Enhanced Scalability: PaaS automatically scales applications based on demand, ensuring optimal performance and availability.
- Simplified Management: PaaS simplifies the management of applications by providing a centralized platform for monitoring, logging, and troubleshooting.
Examples of Platform as a Service Providers
Several prominent vendors offer robust Platform as a Service solutions. Here are a few noteworthy examples of Platform as a Service providers:
AWS Elastic Beanstalk
AWS Elastic Beanstalk is a PaaS offering from Amazon Web Services (AWS). It allows developers to easily deploy and manage web applications and services in various languages and frameworks, including Java, .NET, PHP, Node.js, Python, Ruby, and Go. Elastic Beanstalk automatically handles the deployment, capacity provisioning, load balancing, auto-scaling, and application health monitoring.
Google App Engine
Google App Engine is a PaaS offering from Google Cloud Platform (GCP). It enables developers to build and deploy web applications and mobile backends using various languages, including Python, Java, Go, PHP, and Node.js. App Engine automatically scales applications based on demand and provides built-in support for various Google Cloud services, such as Cloud SQL, Cloud Storage, and Cloud Datastore.
Microsoft Azure App Service
Microsoft Azure App Service is a PaaS offering from Microsoft Azure. It provides a fully managed platform for building, deploying, and scaling web applications, mobile backends, and APIs. App Service supports various languages and frameworks, including .NET, Java, Node.js, Python, and PHP. It also integrates with other Azure services, such as Azure SQL Database, Azure Cosmos DB, and Azure Functions.
Heroku
Heroku is a popular Platform as a Service provider known for its ease of use and focus on developer experience. It supports various languages and frameworks, including Ruby, Python, Java, Node.js, Go, PHP, and Scala. Heroku provides a simple and intuitive interface for deploying and managing applications, making it a popular choice for startups and small businesses.
Red Hat OpenShift
Red Hat OpenShift is a container-based PaaS built on Kubernetes. It allows developers to build, deploy, and manage applications in containers across various environments, including on-premises, public cloud, and hybrid cloud. OpenShift supports various languages and frameworks and provides a rich set of features for managing containerized applications, including CI/CD, scaling, and monitoring.
Use Cases for Platform as a Service
PaaS can be used in a variety of scenarios, including:
- Web Application Development: PaaS is an ideal platform for developing and deploying web applications, providing developers with the tools and services they need to build and manage complex web applications.
- Mobile Backend Development: PaaS can be used to build and deploy mobile backends, providing developers with the services they need to support mobile applications, such as authentication, data storage, and push notifications.
- API Development: PaaS can be used to develop and deploy APIs, providing developers with the tools and services they need to build and manage APIs for various applications and services.
- Big Data Analytics: PaaS can be used to process and analyze large datasets, providing data scientists with the tools and services they need to perform data analysis and machine learning.
- Internet of Things (IoT) Applications: PaaS can be used to build and deploy IoT applications, providing developers with the services they need to connect and manage IoT devices, such as data ingestion, device management, and analytics.
- Microservices Architecture: PaaS platforms like Kubernetes-based solutions are excellent for deploying and managing microservices, offering features like service discovery, load balancing, and automated scaling.
Choosing the Right PaaS Provider
Selecting the right Platform as a Service provider is crucial for the success of your application development efforts. Consider the following factors when evaluating PaaS providers:
- Supported Languages and Frameworks: Ensure that the PaaS provider supports the languages and frameworks that your development team uses.
- Scalability and Performance: Evaluate the PaaS provider’s ability to scale applications based on demand and ensure optimal performance.
- Integration with Other Services: Check whether the PaaS provider integrates with other services that you use, such as databases, storage, and messaging services.
- Pricing: Compare the pricing models of different PaaS providers and choose the one that best fits your budget.
- Security: Ensure that the PaaS provider offers robust security features to protect your applications and data.
- Support and Documentation: Evaluate the quality of the PaaS provider’s support and documentation.
Conclusion
Platform as a Service is a powerful cloud computing model that can significantly benefit businesses by reducing costs, accelerating time to market, and increasing agility. By providing developers with a complete platform for building, running, and managing applications, PaaS enables them to focus on innovation and deliver value to their customers. Understanding the different examples of Platform as a Service and their respective use cases is essential for making informed decisions about which PaaS solution is best suited for your organization’s needs. As cloud computing continues to evolve, PaaS will undoubtedly play an increasingly important role in enabling businesses to thrive in the digital age.
When considering Platform as a Service, remember to evaluate your specific requirements, including the languages and frameworks you use, the scalability you need, and the integrations you require with other services. Careful consideration will lead you to the PaaS solution that best empowers your development teams and drives your business forward.
[See also: Cloud Computing Models: IaaS vs PaaS vs SaaS]
[See also: Serverless Computing: A Comprehensive Guide]
