PC Hardware Definition: Understanding the Core Components of Your Computer
In the ever-evolving world of technology, understanding the fundamental building blocks of your computer is crucial. This article delves into the PC hardware definition, providing a comprehensive overview of the essential components that make your personal computer function. Whether you’re a seasoned tech enthusiast or a curious beginner, grasping the intricacies of PC hardware will empower you to make informed decisions about upgrades, troubleshooting, and overall system maintenance. The term “PC hardware” encompasses all the physical parts of a computer, the tangible elements you can see and touch. From the central processing unit (CPU) to the graphics card, each component plays a vital role in the seamless operation of your system. Understanding the PC hardware definition is the first step towards optimizing your computer’s performance and extending its lifespan.
What Exactly is PC Hardware? A Deeper Dive
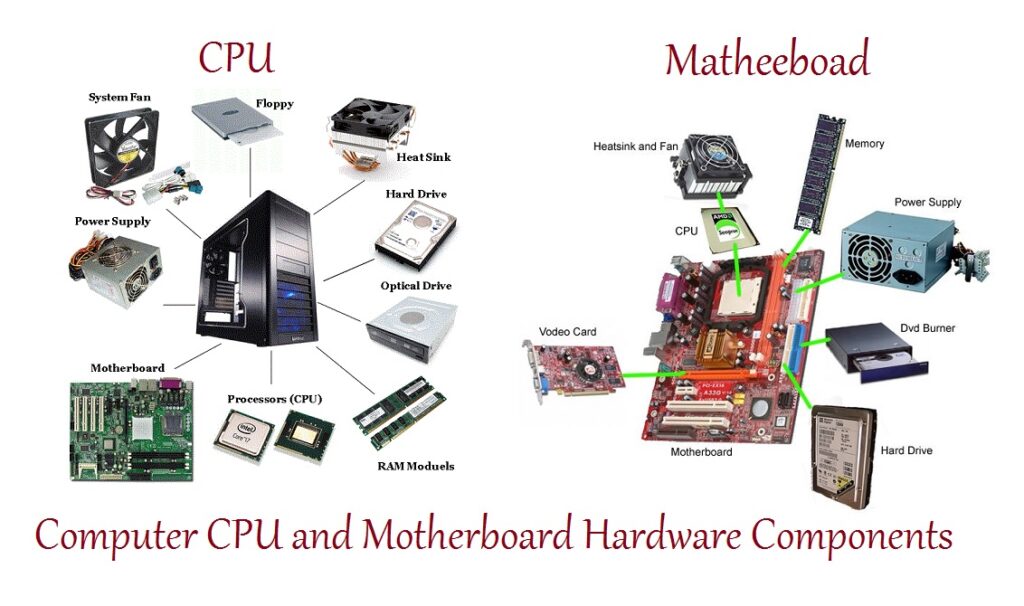
The PC hardware definition extends beyond simply listing components. It’s about understanding how these pieces interact and contribute to the overall computing experience. PC hardware includes everything inside and sometimes outside the computer case. Let’s break down the key components:
- Central Processing Unit (CPU): Often referred to as the “brain” of the computer, the CPU executes instructions and performs calculations. Its speed and core count significantly impact system performance.
- Motherboard: The central circuit board that connects all the other components. It provides the pathways for data to travel between the CPU, RAM, storage, and peripherals.
- Random Access Memory (RAM): Temporary storage used to hold data and instructions that the CPU is actively using. More RAM allows for smoother multitasking and faster loading times.
- Graphics Processing Unit (GPU): Responsible for rendering images, videos, and other visual content. Essential for gaming, video editing, and other graphics-intensive tasks.
- Storage Devices: These include Hard Disk Drives (HDDs) and Solid State Drives (SSDs). HDDs store data magnetically, while SSDs use flash memory for faster access times.
- Power Supply Unit (PSU): Provides the necessary power to all the components in the system. A reliable PSU is crucial for system stability.
- Cooling System: Includes fans, heatsinks, and liquid coolers that dissipate heat generated by the CPU, GPU, and other components. Proper cooling prevents overheating and ensures optimal performance.
- Case: The enclosure that houses all the internal components, providing protection and airflow.
The Importance of Understanding Your PC Hardware
Knowing the PC hardware definition and the role of each component offers numerous benefits. Firstly, it enables you to troubleshoot problems more effectively. When your computer malfunctions, understanding the hardware can help you pinpoint the source of the issue, whether it’s a faulty RAM module or an overheating CPU. Secondly, it allows you to make informed decisions about upgrades. Knowing the specifications of your current hardware, you can choose compatible and beneficial upgrades to enhance performance. Finally, understanding PC hardware can help you optimize your system settings for specific tasks, such as gaming or video editing.
CPU: The Central Processing Unit Explained
The CPU is the primary component responsible for executing instructions and processing data. Modern CPUs are characterized by their clock speed (measured in GHz), core count, and cache size. A higher clock speed generally indicates faster performance, while more cores allow the CPU to handle multiple tasks simultaneously. The CPU interacts with the RAM to quickly access data needed for processing. Choosing the right CPU is crucial for overall system performance, depending on your intended use. For instance, gamers and video editors often require CPUs with high clock speeds and multiple cores.
Motherboard: The Foundation of Your PC
The motherboard serves as the central hub connecting all the other components. It dictates the type of CPU, RAM, and expansion cards that can be used. Different motherboards come with varying features, such as the number of RAM slots, PCIe slots, and USB ports. The motherboard also houses the chipset, which controls communication between the CPU and other components. Selecting a motherboard that supports your desired components and offers the necessary features is essential for building a compatible and functional system. [See also: Best Motherboards for Gaming]
RAM: Random Access Memory and its Role
RAM is temporary storage used to hold data and instructions that the CPU is actively using. Unlike permanent storage devices like HDDs and SSDs, RAM is volatile, meaning that data is lost when the power is turned off. More RAM allows your computer to handle more tasks simultaneously without slowing down. The amount of RAM required depends on your usage patterns. For general use, 8GB of RAM may be sufficient, while gamers and content creators may need 16GB or more. The speed of RAM, measured in MHz, also affects performance.
GPU: Graphics Processing Unit for Visuals
The GPU is responsible for rendering images, videos, and other visual content. It’s a crucial component for gamers, video editors, and anyone who works with graphics-intensive applications. GPUs come in two main types: integrated and dedicated. Integrated GPUs are built into the CPU or motherboard and share system memory, while dedicated GPUs are separate cards with their own dedicated memory. Dedicated GPUs offer significantly better performance than integrated GPUs, making them essential for demanding tasks. The performance of a GPU is determined by its clock speed, memory size, and architecture. [See also: Choosing the Right Graphics Card]
Storage Devices: HDD vs. SSD
Storage devices are used to store data permanently. The two main types of storage devices are Hard Disk Drives (HDDs) and Solid State Drives (SSDs). HDDs store data magnetically and are generally cheaper and offer more storage capacity. SSDs, on the other hand, use flash memory and offer significantly faster access times. This results in faster boot times, application loading times, and overall system responsiveness. Many modern computers use a combination of both HDDs and SSDs, with the SSD used for the operating system and frequently used applications, and the HDD used for storing large files. The choice between HDD and SSD depends on your budget and performance requirements.
Power Supply Unit (PSU): Providing the Juice
The PSU provides the necessary power to all the components in the system. It converts AC power from the wall outlet to DC power that the components can use. A reliable PSU is crucial for system stability and preventing damage to your hardware. The wattage of the PSU should be sufficient to power all the components in your system, with some headroom for future upgrades. It’s important to choose a PSU from a reputable brand to ensure quality and reliability. A poorly designed PSU can damage your components or even cause a fire.
Cooling System: Keeping Things Cool
The cooling system is responsible for dissipating heat generated by the CPU, GPU, and other components. Overheating can lead to reduced performance, instability, and even permanent damage. Cooling systems come in various forms, including fans, heatsinks, and liquid coolers. Fans and heatsinks are the most common and affordable options, while liquid coolers offer superior cooling performance but are more expensive and complex to install. Choosing the right cooling system depends on the thermal output of your components and your budget. Proper cooling is essential for maintaining optimal performance and extending the lifespan of your hardware. Understanding the PC hardware definition includes knowing how to keep it running efficiently.
PC Hardware Troubleshooting Tips
Even with the best PC hardware, problems can arise. Here are some basic troubleshooting tips:
- Check Connections: Ensure all cables and connectors are securely plugged in.
- Monitor Temperatures: Use monitoring software to check CPU and GPU temperatures. Overheating can cause crashes and instability.
- Run Diagnostics: Use built-in or third-party diagnostic tools to test individual components.
- Update Drivers: Ensure you have the latest drivers for your graphics card, motherboard, and other devices.
- Reinstall Operating System: If all else fails, reinstalling the operating system can often resolve software-related issues.
Future Trends in PC Hardware
The world of PC hardware is constantly evolving. Some of the key trends to watch include:
- Increased Performance: Manufacturers are continually pushing the boundaries of performance with new CPU and GPU architectures.
- Miniaturization: Components are becoming smaller and more power-efficient, allowing for smaller and more portable PCs.
- Advanced Cooling: New cooling technologies are being developed to handle the increasing heat output of high-performance components.
- Solid State Storage Dominance: SSDs are becoming more affordable and are expected to replace HDDs as the primary storage device in most PCs.
- Connectivity: Faster and more versatile connection standards such as USB4 and Thunderbolt continue to evolve.
Conclusion: Mastering the PC Hardware Definition
Understanding the PC hardware definition is essential for anyone who wants to get the most out of their computer. By learning about the different components and how they work together, you can troubleshoot problems, make informed upgrade decisions, and optimize your system for specific tasks. Whether you’re a casual user or a hardcore gamer, a solid understanding of PC hardware will empower you to take control of your computing experience. The knowledge of PC hardware also helps in making informed decisions when buying a new computer or building one from scratch. This knowledge is not just for tech experts; it’s for anyone who wants to understand the technology they use every day. By understanding the PC hardware definition and keeping up with the latest trends, you can ensure that your computer remains a powerful and reliable tool for years to come.
