Networked Computer Definition: Understanding the Basics and Beyond
In today’s interconnected world, understanding the networked computer definition is crucial. A networked computer, at its core, is a computing device connected to a network, enabling it to share resources, communicate with other devices, and access a wealth of information. This connectivity is the foundation of modern computing, powering everything from personal communication to global business operations. This article delves into the networked computer definition, explores its various facets, and examines its significance in our daily lives. We’ll break down the technical jargon and explain it in a way that anyone can understand.
What is a Networked Computer? A Detailed Explanation
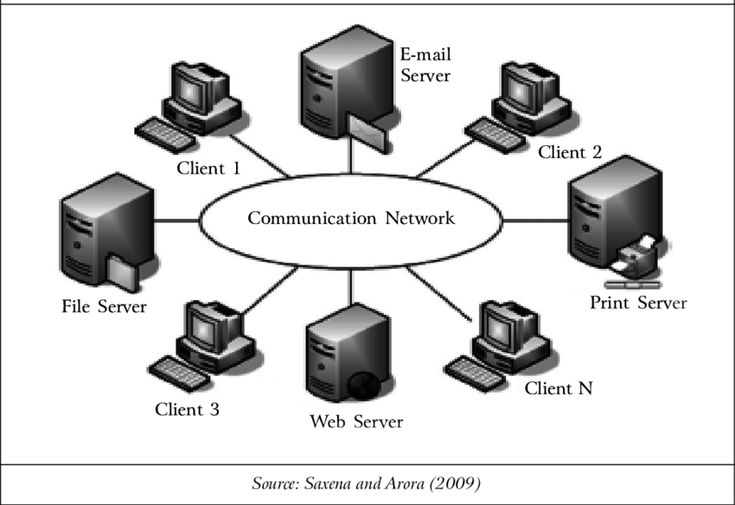
A networked computer isn’t just a standalone device; it’s part of a larger system that allows for data exchange. The networked computer definition involves not only the physical hardware but also the software and protocols that enable communication across the network. This means that a networked computer can be a desktop, laptop, smartphone, server, or even a smart appliance, as long as it’s configured to connect and interact with other devices on a network.
The primary purpose of a networked computer is to facilitate the sharing of resources. These resources can include files, printers, internet connections, and even processing power. By connecting computers in a network, organizations and individuals can improve efficiency, reduce costs, and enhance collaboration. For instance, in an office environment, multiple computers can share a single printer, reducing the need for each employee to have their own dedicated device. Similarly, shared file servers allow employees to easily access and collaborate on documents, regardless of their physical location within the office.
Key Components of a Networked Computer
Several key components are essential for a computer to function effectively as a networked computer:
- Network Interface Card (NIC): The NIC is a hardware component that allows the computer to connect to a network. It provides the physical interface for transmitting and receiving data.
- Network Protocols: These are sets of rules and standards that govern how data is transmitted and received over the network. Common protocols include TCP/IP, HTTP, and FTP.
- Operating System (OS): The OS manages the computer’s hardware and software resources, including network connections. It provides the interface for users to interact with the network.
- Network Software: This includes applications and utilities that enable users to access and utilize network resources, such as web browsers, email clients, and file-sharing programs.
Types of Computer Networks
Understanding the networked computer definition also requires knowledge of the different types of networks that computers can connect to. These networks vary in size, scope, and purpose.
Local Area Network (LAN)
A LAN is a network that connects computers within a limited geographical area, such as a home, office, or school. LANs are typically used to share resources and facilitate communication among users within the same building or campus. [See also: Setting Up a Home LAN].
Wide Area Network (WAN)
A WAN is a network that connects computers over a large geographical area, such as a city, state, or country. The Internet is the largest WAN in the world. WANs are used to connect LANs and allow users to access resources and communicate with others across long distances.
Metropolitan Area Network (MAN)
A MAN is a network that connects computers within a metropolitan area, such as a city or region. MANs are typically larger than LANs but smaller than WANs. They are often used to connect businesses, government agencies, and educational institutions within a specific area.
Personal Area Network (PAN)
A PAN is a network that connects computers and devices within a small area, such as a person’s immediate vicinity. PANs are often used to connect devices such as smartphones, tablets, and laptops to peripherals like printers, keyboards, and headsets.
The Role of Networked Computers in Modern Society
Networked computers play a pivotal role in modern society, impacting virtually every aspect of our lives. From communication and entertainment to education and business, networked computers have transformed the way we live, work, and interact with the world.
Communication
Networked computers have revolutionized communication, enabling us to connect with people across the globe instantly. Email, instant messaging, social media, and video conferencing are all made possible by networked computers. These technologies have made it easier than ever to stay in touch with friends and family, collaborate with colleagues, and conduct business internationally.
Education
Networked computers have also transformed education, providing students with access to a wealth of information and resources. Online learning platforms, digital libraries, and educational software have made it easier for students to learn at their own pace and access educational materials from anywhere in the world. Networked computers have also enabled teachers to create more engaging and interactive learning experiences.
Business
In the business world, networked computers are essential for a wide range of operations. They enable businesses to manage their finances, track inventory, communicate with customers, and market their products and services. E-commerce, online banking, and cloud computing are all powered by networked computers, allowing businesses to operate more efficiently and reach a wider audience. [See also: The Future of Cloud Computing].
Entertainment
Networked computers have also transformed the entertainment industry, providing us with access to a vast library of movies, music, games, and other forms of entertainment. Streaming services, online gaming platforms, and social media have made it easier than ever to consume and share entertainment content.
Security Considerations for Networked Computers
While networked computers offer numerous benefits, they also pose security risks. Connecting a computer to a network exposes it to potential threats such as viruses, malware, and hacking attempts. It’s crucial to take steps to protect networked computers from these threats.
Firewalls
A firewall is a security system that monitors and controls network traffic, blocking unauthorized access to a networked computer. Firewalls can be implemented in hardware or software and are an essential component of network security.
Antivirus Software
Antivirus software is designed to detect and remove viruses, malware, and other malicious software from a networked computer. It’s important to keep antivirus software up to date to protect against the latest threats.
Strong Passwords
Using strong passwords is crucial for protecting networked computers from unauthorized access. Passwords should be at least 12 characters long and include a combination of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and symbols. Avoid using easily guessable passwords such as names, birthdays, or common words.
Regular Software Updates
Software updates often include security patches that fix vulnerabilities in the software. It’s important to install software updates regularly to protect networked computers from known security threats.
The Future of Networked Computers
The future of networked computers is likely to be characterized by increasing connectivity, mobility, and intelligence. As technology advances, we can expect to see even more devices connected to networks, enabling new and innovative applications. The Internet of Things (IoT), artificial intelligence (AI), and 5G technology are all poised to play a significant role in the future of networked computers.
Internet of Things (IoT)
The IoT refers to the growing network of interconnected devices, including appliances, vehicles, and industrial equipment. These devices are equipped with sensors and software that allow them to collect and exchange data over the internet. The IoT is expected to have a profound impact on various industries, including healthcare, manufacturing, and transportation. [See also: IoT Security Best Practices].
Artificial Intelligence (AI)
AI is the development of computer systems that can perform tasks that typically require human intelligence, such as learning, problem-solving, and decision-making. AI is being integrated into networked computers to improve their performance, efficiency, and security. For example, AI-powered security systems can detect and respond to cyber threats more quickly and effectively than traditional security systems.
5G Technology
5G is the next generation of wireless technology, offering faster speeds, lower latency, and greater capacity than previous generations. 5G is expected to enable new and innovative applications for networked computers, such as autonomous vehicles, virtual reality, and augmented reality.
Conclusion
The networked computer definition encompasses much more than just a device connected to a network. It represents a fundamental shift in how we interact with technology and the world around us. Understanding the principles of networked computers, their types, and their security implications is essential for navigating the complexities of the modern digital landscape. As technology continues to evolve, networked computers will undoubtedly play an increasingly important role in our lives, shaping the future of communication, education, business, and entertainment.
