Network System Definition: A Comprehensive Guide
In today’s interconnected world, understanding the network system definition is crucial for anyone involved in technology, business, or even everyday internet usage. A network system, at its core, is a collection of interconnected devices that can communicate and share resources. This seemingly simple definition encompasses a vast range of complexities and functionalities. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of network systems, exploring their components, types, benefits, and future trends. By the end of this article, you’ll have a solid grasp of the network system definition and its significance in our digital lives.
Understanding the Basic Components of a Network System
A network system isn’t just about computers connected to the internet. It’s a sophisticated ecosystem comprised of several key components working in harmony. Let’s break down these core elements:
- Nodes: These are the devices connected to the network. Nodes can be computers, servers, printers, smartphones, or any other device with a network interface.
- Links: These are the communication pathways between nodes. Links can be physical cables (like Ethernet cables) or wireless connections (like Wi-Fi).
- Network Interface Cards (NICs): Each node requires a NIC to connect to the network. The NIC translates data into a format that can be transmitted over the network.
- Network Protocols: These are the rules that govern how data is transmitted and received on the network. Common protocols include TCP/IP, HTTP, and DNS.
- Network Operating System (NOS): This is the software that manages the network resources and provides services to the nodes.
Types of Network Systems
Network systems come in various shapes and sizes, each designed to meet specific needs. Here are some of the most common types:
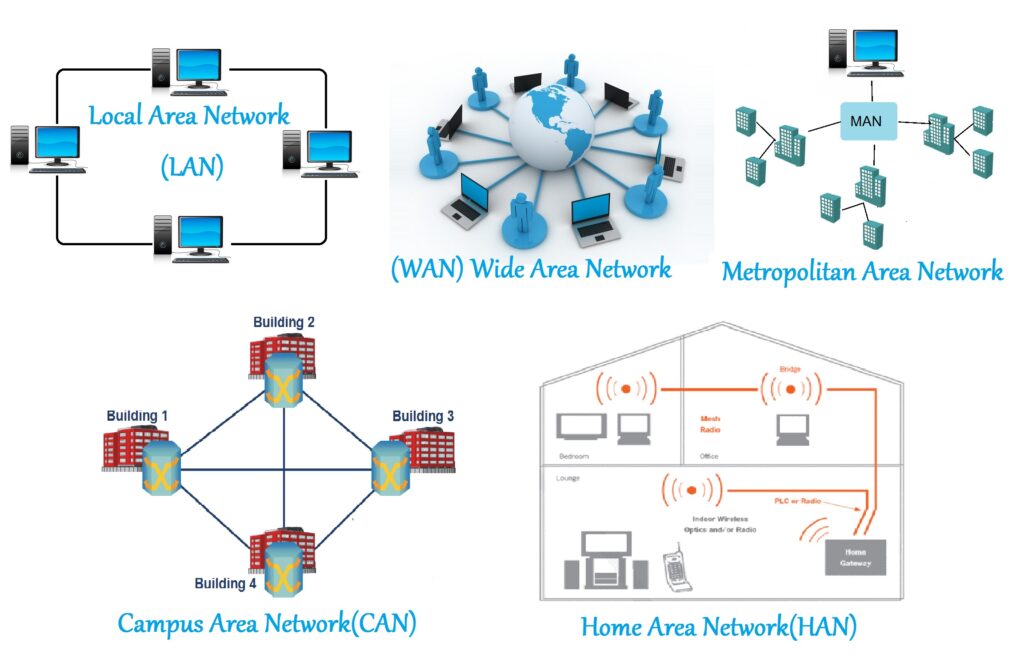
Local Area Network (LAN)
A LAN connects devices within a limited geographical area, such as a home, office, or school. LANs are typically used for sharing files, printers, and internet access. Ethernet and Wi-Fi are the most common technologies used in LANs. Understanding network system definition in the context of a LAN is crucial for setting up a home or small business network.
Wide Area Network (WAN)
A WAN spans a large geographical area, connecting multiple LANs together. The internet is the largest WAN in the world. WANs are used by businesses and organizations to connect offices in different cities or countries. Technologies like MPLS and VPNs are often used in WANs to ensure secure and reliable communication. The network system architecture of a WAN is significantly more complex than that of a LAN.
Metropolitan Area Network (MAN)
A MAN covers a city or metropolitan area. MANs are larger than LANs but smaller than WANs. They are often used by universities, government agencies, and businesses with multiple locations within a city. Fiber optic cables are commonly used in MANs to provide high-speed connectivity.
Personal Area Network (PAN)
A PAN is a small network that connects devices within a person’s immediate vicinity, such as a Bluetooth headset, a smartphone, and a laptop. PANs are typically used for personal communication and data sharing.
Virtual Private Network (VPN)
A VPN creates a secure connection over a public network, such as the internet. VPNs are used to encrypt data and protect privacy. They are often used by businesses to allow employees to securely access the corporate network from remote locations. Understanding how a VPN fits into the broader network system definition is essential for cybersecurity.
Benefits of Implementing a Network System
Implementing a network system offers numerous benefits to individuals and organizations:
- Resource Sharing: Networks allow users to share resources such as printers, files, and internet connections.
- Communication: Networks facilitate communication between users through email, instant messaging, and video conferencing.
- Centralized Management: Networks allow administrators to centrally manage resources and security policies.
- Data Backup and Recovery: Networks make it easier to back up and recover data in case of a disaster.
- Increased Efficiency: Networks streamline workflows and improve productivity.
Network Topologies: The Architecture of Connectivity
Network topology refers to the physical or logical arrangement of devices (nodes) and connections (links) in a network system. Different topologies offer varying levels of redundancy, performance, and cost. Here are some common network topologies:
Bus Topology
In a bus topology, all devices are connected to a single cable, called the bus. This is a simple and inexpensive topology, but it is also vulnerable to failure. If the bus cable breaks, the entire network goes down.
Star Topology
In a star topology, all devices are connected to a central hub or switch. This is a more robust topology than the bus topology, as a failure of one device does not affect the rest of the network. Star topology is one of the most common topologies used in modern LANs. The central hub makes managing the network system easier.
Ring Topology
In a ring topology, each device is connected to two other devices, forming a closed loop. Data travels around the ring until it reaches its destination. Ring topologies are less common than star topologies but are still used in some specialized applications.
Mesh Topology
In a mesh topology, each device is connected to multiple other devices. This provides high redundancy and fault tolerance, but it is also more expensive to implement. Mesh topologies are often used in critical infrastructure networks.
Tree Topology
A tree topology combines elements of bus and star topologies. It has a hierarchical structure with a root node and branches of connected devices. Tree topologies are often used in large organizations with multiple departments.
Network Security: Protecting Your Data
Security is a critical aspect of any network system. Networks are vulnerable to a variety of threats, including viruses, malware, hacking, and data breaches. Implementing robust security measures is essential to protect sensitive data and maintain the integrity of the network.
Firewalls
Firewalls act as a barrier between the network and the outside world, blocking unauthorized access. They can be implemented in hardware or software.
Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) and Intrusion Prevention Systems (IPS)
IDSs monitor network traffic for suspicious activity and alert administrators. IPSs take it a step further by automatically blocking or mitigating threats.
Antivirus Software
Antivirus software protects devices from viruses and malware. It is important to keep antivirus software up to date to protect against the latest threats.
VPNs
As mentioned earlier, VPNs encrypt data and protect privacy. They are particularly useful for protecting data when using public Wi-Fi networks.
Access Control
Access control measures restrict access to network resources based on user roles and permissions. This helps to prevent unauthorized access to sensitive data.
The Future of Network Systems
Network systems are constantly evolving to meet the demands of a rapidly changing world. Here are some of the key trends shaping the future of networking:
- 5G and Beyond: The next generation of wireless technology promises faster speeds, lower latency, and increased capacity. This will enable new applications such as autonomous vehicles, augmented reality, and the Internet of Things (IoT).
- Software-Defined Networking (SDN): SDN separates the control plane from the data plane, allowing for more flexible and programmable networks. This makes it easier to manage and optimize network resources.
- Network Function Virtualization (NFV): NFV virtualizes network functions, such as firewalls and routers, allowing them to be deployed on commodity hardware. This reduces costs and increases agility.
- Cloud Networking: Cloud networking allows organizations to extend their networks into the cloud. This provides access to a wide range of cloud services and resources.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML): AI and ML are being used to automate network management, improve security, and optimize performance.
Conclusion
Understanding the network system definition is essential in today’s digital age. From basic LANs to complex WANs, network systems connect us to the world and enable countless applications and services. By understanding the components, types, benefits, and security considerations of network systems, you can make informed decisions about how to leverage them to achieve your goals. As technology continues to evolve, the importance of network systems will only continue to grow. [See also: Network Security Best Practices] [See also: Understanding Network Topologies] [See also: Future of Networking Technologies]
