Network Definition Computer: Understanding the Fundamentals of Computer Networks
In today’s interconnected world, understanding the network definition computer is crucial for anyone involved in technology, business, or even daily internet usage. A computer network, at its core, is a collection of interconnected computing devices that can communicate and share resources, such as data, applications, and hardware. This article delves into the intricacies of network definition computer, exploring its components, types, architectures, and significance in our digital age. We’ll break down complex concepts into easily digestible information, ensuring a clear understanding of how these networks function and impact our lives.
What is a Computer Network? A Detailed Network Definition
The network definition computer can be expanded to encompass a system that facilitates communication and resource sharing between two or more computers. These computers, often referred to as nodes, are connected via communication links, which can be physical cables (e.g., Ethernet) or wireless connections (e.g., Wi-Fi). The primary purpose of a computer network is to enable users to access and share information and resources efficiently and effectively. This resource sharing can include printers, files, internet access, and even processing power.
A well-defined computer network allows for streamlined data transfer, enhanced collaboration, and improved productivity. It also plays a vital role in enabling various online services, such as email, web browsing, and online gaming. Without computer networks, the modern internet and many of its associated applications would be impossible.
Key Components of a Computer Network
Understanding the components that make up a computer network is essential for grasping the network definition computer. These components work together to ensure the seamless flow of data and resources. Key components include:
- Nodes: These are the individual devices connected to the network, such as computers, servers, printers, and smartphones. Each node has a unique identifier (e.g., IP address) that allows it to be located and communicated with on the network.
- Communication Links: These are the physical or wireless media that connect the nodes, allowing data to be transmitted between them. Examples include Ethernet cables, fiber optic cables, Wi-Fi, and Bluetooth.
- Network Interface Cards (NICs): These are hardware components that enable devices to connect to a network. Each NIC has a unique MAC address, which is used for identifying the device on the local network.
- Routers: These are devices that forward data packets between networks. Routers examine the destination IP address of each packet and determine the best path to send it along.
- Switches: These are devices that connect multiple devices within the same network. Switches learn the MAC addresses of connected devices and forward data only to the intended recipient, improving network efficiency.
- Firewalls: These are security devices that protect the network from unauthorized access and malicious traffic. Firewalls examine network traffic and block any packets that do not meet predefined security rules.
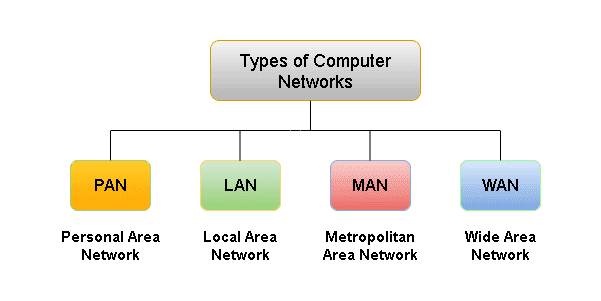
Types of Computer Networks
Computer networks can be classified based on their size, geographical scope, and architecture. Understanding these different types is crucial for a comprehensive network definition computer:
Local Area Network (LAN)
A LAN is a network that connects devices within a limited geographical area, such as a home, office, or school. LANs are typically used to share resources, such as printers, files, and internet access, among users within the same location. LANs are characterized by their high speed and low cost.
Wide Area Network (WAN)
A WAN is a network that connects devices over a large geographical area, such as a city, country, or even the entire world. The Internet is the largest WAN in existence. WANs are used to connect multiple LANs together, allowing users in different locations to communicate and share resources. WANs are typically slower and more expensive than LANs.
Metropolitan Area Network (MAN)
A MAN is a network that connects devices within a metropolitan area, such as a city or a large campus. MANs are typically used to connect multiple LANs together, providing high-speed connectivity between different locations within the same metropolitan area.
Personal Area Network (PAN)
A PAN is a network that connects devices within a small area, such as a person’s immediate surroundings. PANs are typically used to connect devices such as smartphones, laptops, and headphones. Technologies such as Bluetooth and Wi-Fi Direct are commonly used to create PANs.
Virtual Private Network (VPN)
A VPN is a network that creates a secure connection over a public network, such as the Internet. VPNs are used to protect data privacy and security by encrypting all traffic between the user’s device and the VPN server. VPNs are commonly used by remote workers and individuals who want to protect their online privacy.
Network Architectures
The architecture of a computer network defines how the different components are organized and interact with each other. Two common network architectures are client-server and peer-to-peer. Understanding these architectures adds another layer to the network definition computer.
Client-Server Architecture
In a client-server architecture, one or more servers provide resources and services to client devices. Clients request services from the server, and the server responds to those requests. Examples of client-server applications include web browsing, email, and file sharing. This architecture is typically used in larger networks, where centralized management and security are required.
Peer-to-Peer Architecture
In a peer-to-peer (P2P) architecture, all devices are equal and can communicate directly with each other. There is no central server that provides resources or services. P2P networks are typically used for file sharing and other collaborative applications. This architecture is often used in smaller networks, where centralized management is not required.
Network Protocols
Network protocols are sets of rules that govern how data is transmitted and received over a computer network. These protocols ensure that devices can communicate with each other in a standardized and reliable manner. Several key protocols are fundamental to the network definition computer.
- TCP/IP (Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol): This is the foundation of the Internet. TCP provides reliable, connection-oriented communication, while IP provides addressing and routing capabilities.
- HTTP (Hypertext Transfer Protocol): This protocol is used for transferring web pages and other content over the Internet.
- HTTPS (Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure): This is a secure version of HTTP that uses encryption to protect data privacy.
- FTP (File Transfer Protocol): This protocol is used for transferring files between computers.
- SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol): This protocol is used for sending email messages.
- POP3 (Post Office Protocol version 3): This protocol is used for retrieving email messages from a server.
- IMAP (Internet Message Access Protocol): This protocol is also used for retrieving email messages from a server, but it offers more advanced features than POP3.
The Importance of Network Security
Network security is the process of protecting a computer network from unauthorized access, use, disclosure, disruption, modification, or destruction. With the increasing reliance on computer networks, network security has become more important than ever. A deep understanding of security is vital to the complete network definition computer.
Common network security threats include:
- Malware: This includes viruses, worms, Trojans, and other malicious software that can infect computers and steal data.
- Hacking: This involves gaining unauthorized access to a computer network or system.
- Phishing: This is a type of social engineering attack that attempts to trick users into revealing sensitive information, such as passwords and credit card numbers.
- Denial-of-Service (DoS) Attacks: These attacks attempt to flood a network or system with traffic, making it unavailable to legitimate users.
To protect against these threats, organizations must implement a comprehensive network security strategy that includes:
- Firewalls: These devices block unauthorized access to the network.
- Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS): These systems monitor network traffic for suspicious activity.
- Antivirus Software: This software detects and removes malware from computers.
- Strong Passwords: Users should be required to use strong passwords that are difficult to guess.
- Regular Security Updates: Software and operating systems should be updated regularly to patch security vulnerabilities.
Future Trends in Computer Networking
The field of computer networking is constantly evolving, with new technologies and trends emerging all the time. Some of the key trends shaping the future of computer networking include:
- 5G: This is the next generation of wireless technology, offering faster speeds, lower latency, and increased capacity.
- Software-Defined Networking (SDN): This technology allows network administrators to manage and control network resources programmatically.
- Network Functions Virtualization (NFV): This technology allows network functions, such as firewalls and routers, to be implemented as software on standard hardware.
- Cloud Networking: This involves using cloud-based resources to build and manage computer networks.
- Internet of Things (IoT): The increasing number of connected devices is driving the need for more sophisticated and scalable computer networks.
Understanding these trends is crucial for staying ahead of the curve and ensuring that your computer network is prepared for the future. By understanding the fundamental network definition computer and its evolving landscape, individuals and organizations can leverage the power of networking to achieve their goals.
In conclusion, the network definition computer encompasses a complex and multifaceted system that enables communication and resource sharing between devices. From understanding the basic components to exploring different types of networks and architectures, a comprehensive understanding of computer networks is essential in today’s digital world. As technology continues to evolve, staying informed about the latest trends and security measures is crucial for effectively leveraging the power of computer networks. [See also: Network Security Best Practices] and [See also: Understanding Network Topologies]
