Navigating the SASE Vendor Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide
In today’s rapidly evolving digital landscape, organizations are facing increasingly complex security and networking challenges. Traditional security models, designed for a perimeter-based world, are no longer sufficient to protect distributed workforces and cloud-based applications. This is where Secure Access Service Edge (SASE) comes in. SASE, pronounced “sassy,” is a network architecture that combines network and security functions into a single, cloud-delivered service. Choosing the right SASE vendor is crucial for a successful implementation. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of the SASE vendor landscape, helping you navigate the complexities and make informed decisions.
Understanding the SASE Framework
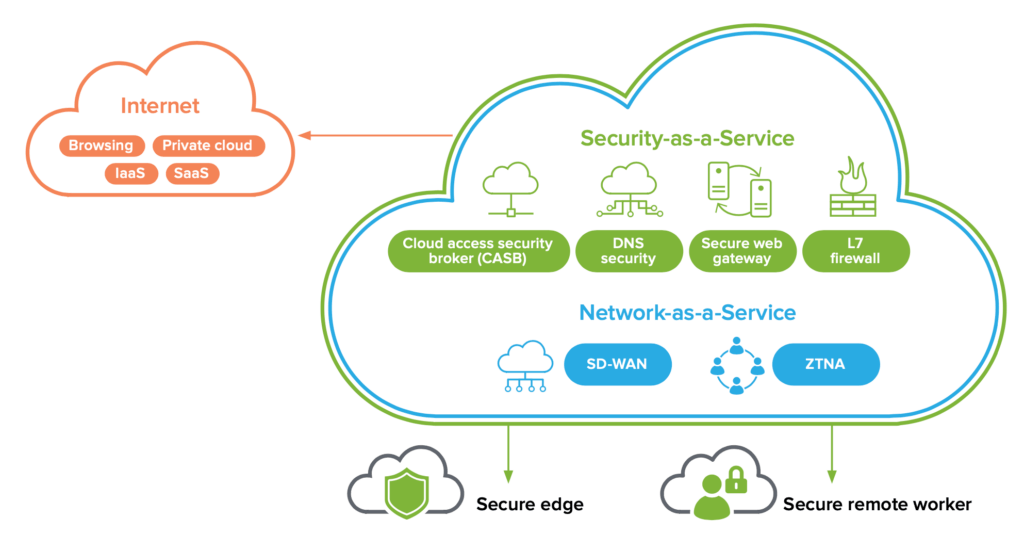
Before diving into the SASE vendor options, it’s essential to understand the core components of the SASE framework. SASE aims to deliver secure, reliable, and optimized access to applications and data, regardless of the user’s location. Key components include:
- Software-Defined Wide Area Network (SD-WAN): Optimizes network traffic routing and provides application performance guarantees.
- Secure Web Gateway (SWG): Filters malicious web content and enforces security policies.
- Cloud Access Security Broker (CASB): Provides visibility and control over cloud application usage.
- Firewall as a Service (FWaaS): Delivers firewall functionality from the cloud, protecting against network threats.
- Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA): Provides secure access to applications based on identity and context.
A SASE vendor should ideally offer a comprehensive suite of these services, integrated into a single platform. However, some vendors may specialize in certain areas, requiring organizations to integrate solutions from multiple providers.
Key Considerations When Evaluating SASE Vendors
Selecting the right SASE vendor requires careful consideration of your organization’s specific needs and requirements. Here are some key factors to evaluate:
Security Capabilities
A robust security posture is paramount for any SASE solution. Evaluate the vendor’s capabilities in areas such as threat detection, intrusion prevention, data loss prevention (DLP), and malware protection. Look for vendors that offer advanced security features like behavioral analytics and machine learning to proactively identify and mitigate emerging threats. A strong SASE vendor will prioritize security at every layer.
Networking Performance
SASE should not only enhance security but also improve network performance. Consider the vendor’s SD-WAN capabilities, including their ability to optimize traffic routing, prioritize critical applications, and provide reliable connectivity. Look for vendors that offer global points of presence (PoPs) to minimize latency and ensure a consistent user experience, regardless of location. Optimizing network performance is a key benefit of selecting the right SASE vendor.
Integration and Interoperability
Seamless integration with existing infrastructure is crucial for a successful SASE deployment. Evaluate the vendor’s ability to integrate with your current security tools, identity providers, and cloud platforms. Look for vendors that offer open APIs and support industry-standard protocols to facilitate interoperability. A good SASE vendor will ensure a smooth transition and minimize disruption to your existing operations.
Scalability and Flexibility
SASE should be able to scale to meet your organization’s growing needs. Consider the vendor’s ability to support a large number of users, devices, and locations. Look for vendors that offer flexible deployment options, such as cloud-based, on-premises, or hybrid deployments. The chosen SASE vendor should be adaptable to future growth and changing business requirements.
Management and Visibility
A centralized management console is essential for simplifying SASE administration. Evaluate the vendor’s ability to provide comprehensive visibility into network traffic, security events, and user activity. Look for vendors that offer intuitive dashboards and reporting tools to help you monitor performance, identify threats, and enforce policies. Effective management and visibility are critical for maximizing the value of your SASE vendor investment.
Cost and Licensing
SASE pricing models can vary significantly between vendors. Carefully evaluate the vendor’s pricing structure, including any upfront costs, recurring fees, and usage-based charges. Consider the total cost of ownership (TCO), including the cost of implementation, maintenance, and support. A cost-effective SASE vendor will offer a transparent and predictable pricing model.
Vendor Reputation and Support
Choose a SASE vendor with a proven track record of success and a strong reputation in the industry. Research the vendor’s customer reviews, industry recognition, and financial stability. Evaluate the vendor’s support capabilities, including their response time, expertise, and availability. Reliable support is essential for ensuring a smooth SASE deployment and ongoing operation.
Leading SASE Vendors in the Market
The SASE vendor landscape is rapidly evolving, with a growing number of providers offering solutions. Here are some of the leading vendors in the market:
- Palo Alto Networks: Offers a comprehensive SASE platform with integrated security and networking capabilities.
- VMware: Provides a SASE solution based on its SD-WAN and security technologies.
- Cisco: Offers a SASE platform that combines its networking and security products.
- Fortinet: Delivers a SASE solution with a focus on security and threat prevention.
- Zscaler: A cloud-native security vendor that offers a SASE platform with a focus on zero trust access.
- Netskope: Specializes in cloud security and offers a SASE solution with strong CASB capabilities.
- Forcepoint: Provides a SASE platform with a focus on data loss prevention and insider threat protection.
This is not an exhaustive list, and the best SASE vendor for your organization will depend on your specific requirements. It’s important to conduct thorough research and evaluate multiple vendors before making a decision.
SASE Implementation Best Practices
Implementing SASE requires careful planning and execution. Here are some best practices to follow:
- Define Your Requirements: Clearly define your organization’s security and networking requirements before evaluating vendors.
- Conduct a Proof of Concept (POC): Test the vendor’s solution in a real-world environment to validate its performance and functionality.
- Develop a Phased Deployment Plan: Implement SASE in a phased approach to minimize disruption and ensure a smooth transition.
- Train Your Staff: Provide adequate training to your IT staff on how to manage and operate the SASE solution.
- Monitor and Optimize: Continuously monitor the performance of your SASE solution and optimize it as needed.
The Future of SASE
SASE is poised to become the dominant network architecture for organizations of all sizes. As organizations continue to embrace cloud-based applications and a distributed workforce, the need for secure, reliable, and optimized access to resources will only increase. The SASE vendor landscape will continue to evolve, with new players and innovative solutions emerging. Organizations that adopt SASE will be well-positioned to meet the challenges of the modern digital landscape.
Conclusion
Choosing the right SASE vendor is a critical decision that can significantly impact your organization’s security posture, network performance, and overall business agility. By carefully evaluating your requirements, researching the available options, and following best practices for implementation, you can select a SASE vendor that meets your specific needs and helps you achieve your business goals. The SASE vendor you choose becomes a strategic partner in navigating the complexities of modern networking and security. Remember to prioritize security, performance, integration, and scalability when evaluating potential SASE vendor solutions.
[See also: SD-WAN vs SASE: Understanding the Differences]
[See also: Top Cybersecurity Threats in 2024]
[See also: How Zero Trust Architecture Enhances Security]
