Master Data Management Definition: A Comprehensive Guide
In today’s data-driven world, organizations rely heavily on information to make informed decisions, optimize operations, and gain a competitive edge. However, the value of this data is contingent on its accuracy, consistency, and accessibility. This is where master data management (MDM) definition becomes crucial. MDM is not merely a buzzword; it’s a strategic discipline that ensures the reliability and integrity of an organization’s most critical data assets. Understanding the master data management definition is the first step towards leveraging its power to improve business outcomes.
This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of master data management definition, exploring its core principles, benefits, implementation strategies, and future trends. We’ll examine how MDM differs from other data management approaches and provide practical insights for organizations looking to establish or enhance their MDM capabilities. Whether you’re a seasoned data professional or just beginning to explore the world of data governance, this article will provide you with a solid understanding of the master data management definition and its significance.
Understanding the Core Concepts of Master Data Management
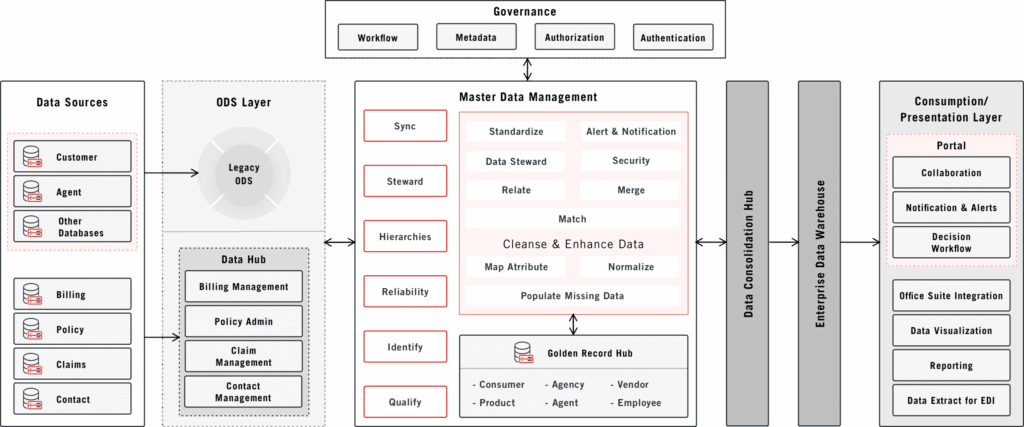
At its core, master data management (MDM) definition refers to a set of processes, technologies, and governance practices that ensure the accuracy, consistency, and completeness of an organization’s master data. Master data represents the critical business entities that are shared across multiple systems and departments. These entities typically include customers, products, suppliers, locations, and employees. The goal of MDM is to create a single, trusted source of truth for these entities, eliminating data silos and inconsistencies that can lead to inaccurate reporting, flawed decision-making, and operational inefficiencies.
Key Components of Master Data Management
- Data Governance: Establishing policies, procedures, and responsibilities for managing master data. This includes defining data ownership, data quality standards, and data security protocols.
- Data Modeling: Defining the structure and relationships of master data entities. This involves creating a common data model that can be used across different systems and applications.
- Data Integration: Integrating data from various source systems into a central repository. This often involves data cleansing, data transformation, and data matching.
- Data Quality: Ensuring the accuracy, completeness, and consistency of master data. This includes implementing data quality rules, data validation processes, and data monitoring tools.
- Data Stewardship: Assigning individuals or teams to be responsible for the quality and maintenance of specific master data entities. Data stewards play a crucial role in ensuring that master data remains accurate and up-to-date.
Why is Master Data Management Important?
The importance of master data management (MDM) definition stems from its ability to address the challenges posed by fragmented and inconsistent data. Without a robust MDM strategy, organizations often struggle with:
- Inaccurate Reporting: Inconsistent data can lead to inaccurate reports and analyses, making it difficult to gain a clear understanding of business performance.
- Poor Decision-Making: Flawed data can result in poor decisions that negatively impact profitability, customer satisfaction, and operational efficiency.
- Operational Inefficiencies: Data silos and inconsistencies can create bottlenecks in business processes, leading to delays, errors, and increased costs.
- Regulatory Compliance Issues: Inaccurate or incomplete data can lead to regulatory compliance issues, resulting in fines and reputational damage.
- Poor Customer Experience: Inconsistent customer data can result in poor customer service, inaccurate billing, and ineffective marketing campaigns.
By implementing an effective MDM strategy, organizations can overcome these challenges and unlock the full potential of their data. A well-defined master data management definition contributes to:
- Improved Data Quality: MDM ensures that master data is accurate, complete, and consistent, leading to improved data quality across the organization.
- Better Decision-Making: With a single, trusted source of truth for master data, organizations can make more informed decisions based on reliable information.
- Increased Operational Efficiency: MDM streamlines business processes by eliminating data silos and inconsistencies, reducing errors and delays.
- Enhanced Customer Experience: Accurate and consistent customer data enables organizations to provide better customer service, personalized experiences, and targeted marketing campaigns.
- Reduced Costs: By improving data quality and streamlining business processes, MDM can help organizations reduce costs associated with data errors, rework, and inefficiencies.
Different Approaches to Master Data Management
There are several different approaches to master data management (MDM) definition, each with its own strengths and weaknesses. The best approach for a particular organization will depend on its specific needs, data landscape, and business objectives.
Registry Style MDM
In a registry style MDM implementation, the master data is not physically stored in a central repository. Instead, the MDM system maintains a registry of pointers to the master data in the source systems. This approach is typically used when it is not feasible or desirable to consolidate the master data into a single location. Registry style MDM is often faster and less expensive to implement than other approaches, but it may not provide the same level of data quality and consistency.
Consolidation Style MDM
Consolidation style MDM involves consolidating the master data from various source systems into a central repository. This approach allows for data cleansing, data transformation, and data matching to be performed in a centralized location. Consolidation style MDM typically provides better data quality and consistency than registry style MDM, but it can be more complex and expensive to implement.
Centralized Style MDM
Centralized style MDM takes the consolidation approach a step further by not only consolidating the master data into a central repository but also making it the system of record for master data. This means that all changes to master data must be made in the MDM system, which then propagates the changes to the source systems. Centralized style MDM provides the highest level of data quality and consistency, but it can be the most complex and expensive to implement.
Coexistence Style MDM
Coexistence style MDM is a hybrid approach that combines elements of both registry style and consolidation style MDM. In this approach, some master data is consolidated into a central repository, while other master data remains in the source systems. Coexistence style MDM allows organizations to address specific data quality issues without having to completely overhaul their existing systems.
Implementing a Master Data Management Strategy
Implementing a successful master data management (MDM) definition strategy requires careful planning, execution, and ongoing maintenance. Here are some key steps to consider:
- Define Business Objectives: Clearly define the business objectives that you hope to achieve with MDM. This will help you to prioritize your efforts and measure your success.
- Assess Current State: Conduct a thorough assessment of your current data landscape, including data sources, data quality, and data governance practices.
- Select an MDM Approach: Choose the MDM approach that best fits your organization’s needs, data landscape, and business objectives.
- Develop a Data Model: Create a common data model that defines the structure and relationships of your master data entities.
- Implement Data Governance Policies: Establish clear data governance policies, procedures, and responsibilities.
- Implement Data Integration Processes: Integrate data from various source systems into the MDM system, ensuring data cleansing, data transformation, and data matching.
- Implement Data Quality Monitoring: Implement data quality rules, data validation processes, and data monitoring tools to ensure the accuracy, completeness, and consistency of master data.
- Train Data Stewards: Train data stewards to be responsible for the quality and maintenance of specific master data entities.
- Monitor and Evaluate: Continuously monitor and evaluate the effectiveness of your MDM strategy, making adjustments as needed.
The Future of Master Data Management
The field of master data management (MDM) definition is constantly evolving, driven by new technologies, changing business needs, and increasing data volumes. Some of the key trends shaping the future of MDM include:
- Cloud-Based MDM: Cloud-based MDM solutions are becoming increasingly popular, offering scalability, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness.
- AI and Machine Learning: AI and machine learning are being used to automate data cleansing, data matching, and data governance processes.
- Real-Time MDM: Real-time MDM enables organizations to make decisions based on up-to-the-minute data.
- Data Fabric: Data fabric architectures are emerging as a way to integrate and manage data across disparate systems and environments, including on-premises, cloud, and hybrid environments.
- Graph Databases: Graph databases are being used to model and manage complex relationships between master data entities.
Conclusion
Master data management (MDM) definition is a critical discipline for organizations that want to leverage the full potential of their data. By ensuring the accuracy, consistency, and completeness of master data, MDM enables organizations to make better decisions, improve operational efficiency, enhance customer experience, and reduce costs. While implementing an MDM strategy can be challenging, the benefits are well worth the effort. As the data landscape continues to evolve, MDM will become even more important for organizations that want to stay ahead of the curve.
Understanding the master data management definition is paramount for any organization seeking to harness the power of its data. By embracing MDM principles and best practices, businesses can unlock valuable insights, optimize operations, and achieve a sustainable competitive advantage.
[See also: Data Governance Best Practices] [See also: Data Quality Management]
