Man-in-the-Middle (MITM) Attack: Understanding, Prevention, and Real-World Examples
In the digital age, where data is the new currency, cybersecurity threats are constantly evolving. Among these threats, the man-in-the-middle (MITM) attack stands out as a particularly insidious and dangerous form of cybercrime. This attack involves an adversary intercepting and potentially altering communications between two parties who believe they are communicating directly with each other. This article delves into the intricacies of MITM attacks, exploring how they work, the various forms they take, and, most importantly, how to protect yourself and your organization from becoming victims. Understanding the nuances of a man-in-the-middle attack is crucial for anyone operating in the digital realm.
What is a Man-in-the-Middle (MITM) Attack?
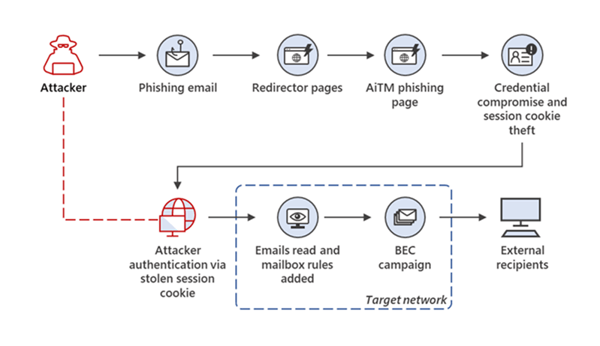
A man-in-the-middle (MITM) attack is a type of cyberattack where a malicious actor intercepts communications between two parties without their knowledge. The attacker positions themselves between the victim and the intended recipient, essentially eavesdropping on and potentially manipulating the data being exchanged. The goal of a MITM attack is typically to steal sensitive information, such as login credentials, financial details, or personal data. Because the victim believes they are communicating directly with a legitimate entity, they are often unaware that their information is being compromised.
How a MITM Attack Works
The mechanics of a MITM attack can be broken down into a few key steps:
- Interception: The attacker intercepts the communication between the victim and the intended recipient. This can be achieved through various methods, such as Wi-Fi eavesdropping, ARP spoofing, or DNS spoofing.
- Decryption (if necessary): If the communication is encrypted, the attacker may attempt to decrypt it. This can involve using stolen encryption keys or employing techniques like SSL stripping.
- Manipulation (optional): The attacker may choose to alter the data being exchanged. This could involve injecting malicious code, modifying financial transactions, or simply gathering information.
- Re-transmission: The attacker re-transmits the communication to the intended recipient, often without raising suspicion. The victim remains unaware that their data has been compromised.
Types of MITM Attacks
MITM attacks come in various forms, each with its own unique characteristics and methods of execution. Some of the most common types include:
Wi-Fi Eavesdropping
This type of attack involves the attacker setting up a fake Wi-Fi hotspot that appears legitimate. When users connect to this hotspot, the attacker can intercept their internet traffic and steal sensitive information. Coffee shops, airports, and other public places are common locations for these attacks. This is a classic example of a man-in-the-middle attack.
ARP Spoofing
ARP spoofing (Address Resolution Protocol spoofing) involves sending fake ARP messages over a local area network. This allows the attacker to associate their MAC address with the IP address of another device on the network, effectively intercepting traffic intended for that device.
DNS Spoofing
DNS spoofing (Domain Name System spoofing) involves manipulating DNS records to redirect users to a fake website. When a user attempts to access a legitimate website, they are instead directed to a malicious site controlled by the attacker. This site can then be used to steal login credentials or other sensitive information. This allows for a sophisticated man-in-the-middle attack.
SSL Stripping
SSL stripping is a technique used to downgrade a secure HTTPS connection to an insecure HTTP connection. This allows the attacker to intercept and view the data being exchanged in plain text. This is a particularly dangerous man-in-the-middle attack when dealing with sensitive information.
Email Hijacking
Email hijacking involves gaining unauthorized access to a user’s email account and using it to intercept or manipulate email communications. The attacker can then use this access to steal sensitive information, send phishing emails, or impersonate the victim. Securing your email is paramount to preventing a man-in-the-middle attack.
Real-World Examples of MITM Attacks
MITM attacks have been used in numerous high-profile cyberattacks throughout history. Here are a few notable examples:
- DigiNotar Hack (2011): A Dutch certificate authority, DigiNotar, was hacked, allowing attackers to issue fraudulent SSL certificates for various websites, including Google, Yahoo, and Microsoft. This allowed the attackers to intercept communications between users and these websites.
- Superfish Lenovo Scandal (2015): Lenovo pre-installed adware called Superfish on its laptops, which acted as a man-in-the-middle to intercept and analyze encrypted web traffic. This created a significant security vulnerability for users.
- Operation Aurora (2009-2010): This series of cyberattacks targeted major technology and defense companies, including Google, Adobe, and Lockheed Martin. While not exclusively MITM attacks, they involved intercepting and exfiltrating sensitive data from these organizations.
How to Prevent MITM Attacks
Protecting yourself and your organization from MITM attacks requires a multi-faceted approach. Here are some key preventative measures:
Use Strong Encryption
Encryption is one of the most effective ways to protect your data from interception. Ensure that you are using HTTPS (SSL/TLS) when transmitting sensitive information online. Look for the padlock icon in your browser’s address bar to verify that a website is using encryption. End-to-end encryption is also useful, especially for messaging applications.
Be Wary of Public Wi-Fi
Avoid using public Wi-Fi networks for sensitive transactions, such as online banking or shopping. If you must use public Wi-Fi, use a virtual private network (VPN) to encrypt your internet traffic and protect it from eavesdropping. A VPN creates a secure tunnel for your data, making it much harder for attackers to intercept.
Use a VPN
As mentioned above, a VPN can provide an extra layer of security when using public Wi-Fi or any untrusted network. A VPN encrypts your internet traffic and routes it through a secure server, masking your IP address and location. This makes it more difficult for attackers to intercept your data or track your online activity.
Verify Website Certificates
Before entering any sensitive information on a website, verify the website’s SSL certificate. Check that the certificate is valid and has been issued by a trusted certificate authority. Look for the padlock icon in your browser’s address bar and click on it to view the certificate details.
Keep Software Updated
Keep your operating system, web browser, and other software updated with the latest security patches. Software updates often include fixes for vulnerabilities that could be exploited by attackers. Enabling automatic updates is a good way to ensure that your software is always up to date.
Use Strong Passwords and Two-Factor Authentication
Use strong, unique passwords for all of your online accounts. Avoid using the same password for multiple accounts, and consider using a password manager to generate and store your passwords securely. Enable two-factor authentication (2FA) whenever possible. 2FA adds an extra layer of security by requiring you to enter a code from your phone or another device in addition to your password. This makes it much harder for attackers to gain access to your accounts, even if they have your password.
Educate Yourself and Your Employees
Educate yourself and your employees about the risks of MITM attacks and other cybersecurity threats. Teach them how to recognize phishing emails, suspicious links, and other red flags. Regular security awareness training can help to reduce the risk of falling victim to a MITM attack or other cybercrime.
Monitor Network Traffic
Organizations should implement network monitoring tools to detect suspicious activity on their networks. These tools can help to identify potential MITM attacks by analyzing network traffic patterns and identifying anomalies. Early detection is critical for mitigating the impact of a MITM attack.
Implement Intrusion Detection and Prevention Systems
Intrusion detection systems (IDS) and intrusion prevention systems (IPS) can help to detect and prevent MITM attacks by monitoring network traffic for malicious activity. These systems can be configured to automatically block or quarantine suspicious traffic, preventing attackers from gaining access to sensitive data.
The Future of MITM Attacks
As technology continues to evolve, so too will the tactics used in MITM attacks. With the rise of IoT devices and the increasing reliance on cloud computing, there are more potential attack vectors than ever before. Staying informed about the latest threats and implementing robust security measures is essential for protecting yourself and your organization from becoming victims of MITM attacks.
In conclusion, understanding the nature of a man-in-the-middle attack, its various forms, and effective prevention strategies is crucial for maintaining online security. By staying vigilant and implementing the measures outlined above, you can significantly reduce your risk of falling victim to this dangerous form of cybercrime. [See also: Protecting Your Data Online] [See also: Cybersecurity Best Practices for Small Businesses]
