Intrusion Detection System Examples: Protecting Your Network
In today’s interconnected world, cybersecurity threats are constantly evolving and becoming more sophisticated. Organizations of all sizes must implement robust security measures to protect their valuable data and systems from unauthorized access and malicious attacks. One crucial component of a comprehensive cybersecurity strategy is an Intrusion Detection System (IDS). An intrusion detection system acts as a security guard, monitoring network traffic and system activity for suspicious behavior, alerting administrators to potential breaches. This article will explore various examples of intrusion detection systems, their functionalities, and how they contribute to a stronger security posture.
Understanding Intrusion Detection Systems
Before diving into specific intrusion detection system examples, it’s essential to understand the core principles behind these systems. An IDS works by analyzing network traffic, system logs, and other data sources to identify patterns that may indicate malicious activity. It compares observed behavior against a database of known attack signatures and predefined rules to detect anomalies. When suspicious activity is detected, the IDS generates alerts, allowing security personnel to investigate and respond to potential threats.
Types of Intrusion Detection Systems
Intrusion detection systems can be broadly classified into several categories, each with its own strengths and weaknesses:
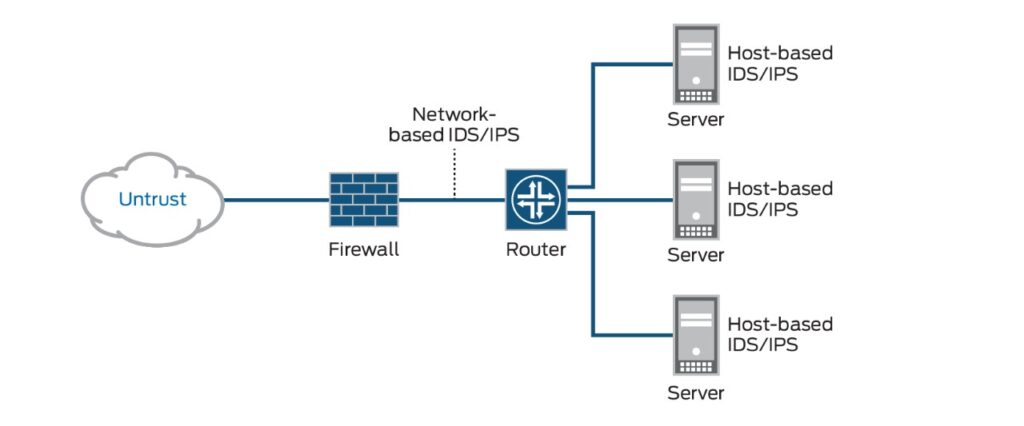
- Network Intrusion Detection Systems (NIDS): These systems monitor network traffic at strategic points within the network, such as at the perimeter or on critical network segments. They analyze network packets for malicious content or suspicious patterns.
- Host-based Intrusion Detection Systems (HIDS): HIDS are installed on individual hosts or servers and monitor system activity, such as file access, registry changes, and process execution. They can detect malicious activity that may not be visible to NIDS.
- Signature-based Intrusion Detection Systems: These systems rely on a database of known attack signatures to identify malicious activity. When a signature matches the observed behavior, an alert is generated.
- Anomaly-based Intrusion Detection Systems: These systems learn the normal behavior of a network or system and flag any deviations from this baseline as suspicious. They are effective at detecting zero-day attacks and other novel threats.
- Hybrid Intrusion Detection Systems: These systems combine the strengths of multiple IDS types to provide a more comprehensive security solution.
Examples of Intrusion Detection Systems in Action
Let’s examine some practical examples of intrusion detection systems and how they are used in real-world scenarios:
Example 1: Detecting a Port Scan
A common reconnaissance technique used by attackers is port scanning, where they attempt to identify open ports on a target system. A NIDS can be configured to detect port scan activity by monitoring network traffic for a large number of connection attempts to different ports on a single host within a short period. When a port scan is detected, the IDS generates an alert, allowing administrators to investigate the source of the scan and take appropriate action to block the attacker.
Example 2: Identifying Malware Infections
Malware infections can be detected by both NIDS and HIDS. A NIDS can identify malware by monitoring network traffic for communication with known command-and-control servers or by detecting suspicious file transfers. A HIDS can identify malware by monitoring system activity for the creation of suspicious files, registry changes, or the execution of malicious processes. [See also: Best Practices for Malware Removal] When malware is detected, the IDS generates an alert, allowing administrators to isolate the infected system and remove the malware.
Example 3: Detecting Insider Threats
Insider threats, where authorized users abuse their access privileges to steal or damage data, can be difficult to detect. A HIDS can be used to monitor user activity for suspicious behavior, such as accessing sensitive files outside of normal working hours or attempting to escalate privileges. Anomaly-based IDSs are particularly useful for detecting insider threats, as they can learn the normal behavior of individual users and flag any deviations as suspicious. When insider threat activity is detected, the IDS generates an alert, allowing security personnel to investigate the user’s actions.
Example 4: Preventing Data Exfiltration
Data exfiltration, the unauthorized transfer of data from an organization’s network, can be detected by NIDS. A NIDS can monitor network traffic for large file transfers to external destinations or for communication with known data exfiltration servers. It can also analyze the content of network traffic for sensitive data, such as credit card numbers or social security numbers. When data exfiltration is detected, the IDS generates an alert, allowing administrators to block the transfer and prevent further data loss.
Example 5: Identifying Web Application Attacks
Web applications are a common target for attackers. A NIDS can be used to detect web application attacks by monitoring HTTP traffic for malicious patterns, such as SQL injection attempts or cross-site scripting (XSS) attacks. Web application firewalls (WAFs) often incorporate IDS capabilities to provide real-time protection against web application attacks. When a web application attack is detected, the IDS generates an alert, allowing administrators to block the attack and protect the web application.
Popular Intrusion Detection System Solutions
Several commercial and open-source intrusion detection system solutions are available. Some popular examples of intrusion detection systems include:
- Snort: A free and open-source NIDS that is widely used for intrusion detection and prevention.
- Suricata: Another popular open-source NIDS that offers high performance and scalability.
- Bro (now Zeek): A powerful open-source network security monitoring platform that can be used for intrusion detection, network analysis, and security research.
- Cisco Intrusion Prevention System (IPS): A commercial NIDS that offers advanced threat detection and prevention capabilities.
- McAfee Network Security Platform (NSP): A commercial NIDS that provides comprehensive network security protection.
- IBM Security QRadar: A security information and event management (SIEM) platform that includes IDS capabilities.
Implementing an Intrusion Detection System
Implementing an intrusion detection system requires careful planning and execution. Here are some key steps to consider:
- Define your security objectives: What are you trying to protect and what threats are you most concerned about?
- Assess your network and system infrastructure: Where are the critical assets that need to be protected?
- Choose the right IDS solution: Select an IDS that meets your specific needs and budget.
- Configure the IDS: Configure the IDS to monitor the appropriate network traffic and system activity.
- Tune the IDS: Fine-tune the IDS to reduce false positives and ensure that it is detecting real threats.
- Monitor the IDS: Regularly monitor the IDS for alerts and investigate any suspicious activity.
- Maintain the IDS: Keep the IDS up-to-date with the latest signatures and software patches.
The Future of Intrusion Detection Systems
As cybersecurity threats continue to evolve, intrusion detection systems must also adapt to stay ahead of the attackers. Future trends in IDS include:
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML): AI and ML are being used to improve the accuracy and effectiveness of IDS by automatically learning normal behavior and detecting anomalies.
- Cloud-based IDS: Cloud-based IDS solutions are becoming increasingly popular, offering scalability, flexibility, and cost savings.
- Integration with Threat Intelligence: Integrating IDS with threat intelligence feeds provides real-time information about emerging threats, allowing for proactive security measures.
- Automated Response: IDS are increasingly being integrated with automated response systems, allowing for automatic remediation of security incidents.
Conclusion
Intrusion detection systems are an essential component of a comprehensive cybersecurity strategy. By monitoring network traffic and system activity for suspicious behavior, IDSs can help organizations detect and respond to potential breaches before they cause significant damage. This article has provided several examples of intrusion detection systems in action, highlighting their versatility and importance in protecting valuable data and systems. Choosing the right IDS and implementing it effectively can significantly enhance an organization’s security posture and reduce the risk of cyberattacks. Understanding the different types of intrusion detection system and how they function is crucial for any organization looking to improve its cybersecurity defenses. Investing in a robust intrusion detection system is a proactive step towards securing your digital assets. Regular updates and monitoring of your intrusion detection system are key to maintaining its effectiveness. These intrusion detection system examples should provide a solid foundation for understanding their value. The goal is to protect your network using the best possible intrusion detection system for your specific needs. Remember that an intrusion detection system is just one part of a larger security framework. Implementing a comprehensive security strategy that includes firewalls, antivirus software, and employee training is essential for protecting your organization from cyber threats. Selecting the right intrusion detection system requires careful consideration of your organization’s specific needs and resources. Properly configured, an intrusion detection system can significantly reduce the risk of successful cyberattacks. Effective use of an intrusion detection system requires ongoing monitoring and analysis of alerts. The best intrusion detection system is one that is tailored to your specific environment. Don’t underestimate the importance of an intrusion detection system in your overall security strategy. By understanding and implementing intrusion detection system technologies, you can significantly enhance your organization’s security posture.
