IDS Definition: Understanding Intrusion Detection Systems
In today’s interconnected world, cybersecurity is paramount. Protecting networks and systems from malicious activities requires a multi-layered approach, and one crucial component is the Intrusion Detection System, often referred to as an IDS. But what exactly is an IDS definition, and how does it work? This article will delve into the intricacies of IDS, exploring its purpose, types, functionalities, and importance in modern cybersecurity landscapes.
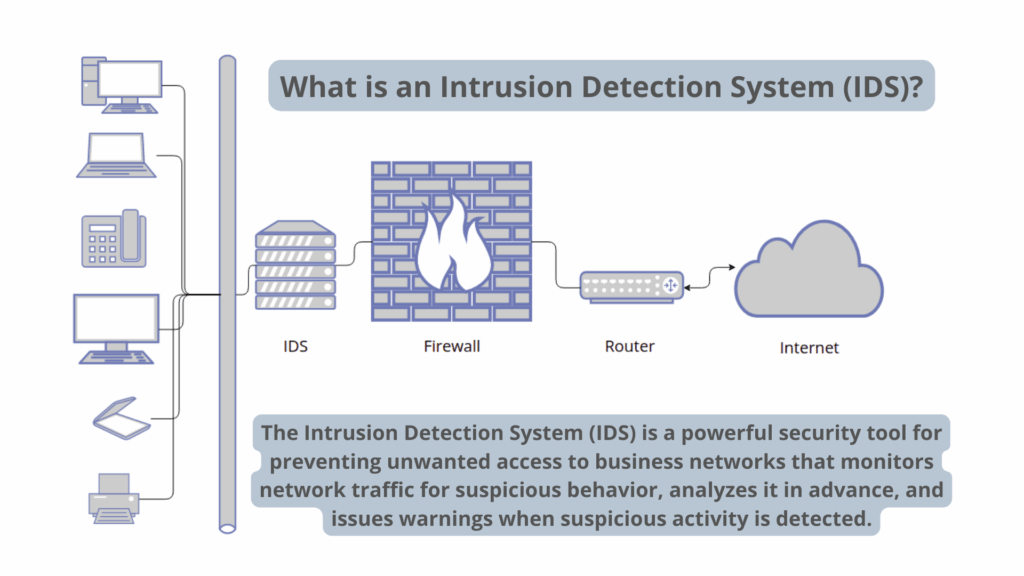
What is an Intrusion Detection System (IDS)?
An IDS is a security system that monitors network traffic and system activities for malicious activity or policy violations. It analyzes this activity, looking for suspicious patterns or known attack signatures. Think of it as a burglar alarm for your digital infrastructure. Instead of detecting physical intrusions, an IDS detects unauthorized or malicious activities within a network or on a host system.
The primary purpose of an IDS is to identify and alert administrators to potential security threats. Unlike Intrusion Prevention Systems (IPS), which actively block or prevent intrusions, an IDS primarily focuses on detection and reporting. However, the information provided by an IDS is invaluable for incident response and preventing future attacks. [See also: Understanding the Difference Between IDS and IPS]
Types of Intrusion Detection Systems
IDS solutions come in various forms, each designed to monitor different aspects of a network or system. Understanding these different types is crucial for selecting the right IDS for your specific needs:
Network Intrusion Detection System (NIDS)
A NIDS monitors network traffic for suspicious activity. It analyzes packets traversing the network, comparing them against a database of known attack signatures. NIDS are typically deployed at strategic points within the network, such as at the perimeter or within critical network segments. They are particularly effective at detecting attacks that target network vulnerabilities or attempt to exploit network protocols.
Host-based Intrusion Detection System (HIDS)
A HIDS resides on a specific host or endpoint and monitors activity on that particular system. It analyzes system logs, file integrity, and other host-based data to detect malicious activity. HIDS are valuable for detecting attacks that originate from within the network or target specific systems. They can also detect unauthorized modifications to system files or configurations.
Signature-based Intrusion Detection System
Signature-based IDS, also known as knowledge-based IDS, relies on a database of known attack signatures. When the IDS detects traffic or activity that matches a signature in its database, it triggers an alert. This type of IDS is effective at detecting known attacks, but it may not be able to detect new or unknown threats (zero-day exploits).
Anomaly-based Intrusion Detection System
Anomaly-based IDS, also known as behavior-based IDS, establishes a baseline of normal network or system behavior. It then monitors activity and flags any deviations from this baseline as potentially malicious. This type of IDS is capable of detecting unknown attacks, but it may also generate false positives if the baseline is not properly configured or if legitimate activity deviates from the norm.
Hybrid Intrusion Detection System
A hybrid IDS combines the strengths of multiple IDS types. For example, it may combine signature-based detection with anomaly-based detection to provide a more comprehensive security solution. Hybrid IDS are often more effective than single-type IDS, but they can also be more complex to configure and manage.
How an Intrusion Detection System Works
The functionality of an IDS can be broken down into several key steps:
- Data Collection: The IDS collects data from various sources, such as network traffic, system logs, and file integrity monitoring.
- Data Analysis: The IDS analyzes the collected data, looking for suspicious patterns or known attack signatures. This analysis may involve signature matching, anomaly detection, or other techniques.
- Alert Generation: When the IDS detects a potential security threat, it generates an alert. This alert typically includes information about the type of threat, the source and destination of the activity, and the severity of the threat.
- Reporting: The IDS reports alerts and other security information to administrators. This information can be used to investigate incidents, respond to threats, and improve security posture.
Benefits of Using an Intrusion Detection System
Implementing an IDS provides numerous benefits for organizations of all sizes:
- Early Threat Detection: IDS can detect malicious activity before it causes significant damage.
- Improved Security Posture: By identifying vulnerabilities and weaknesses, IDS helps organizations improve their overall security posture.
- Compliance: Many regulations and standards require organizations to implement security controls, including intrusion detection systems.
- Incident Response: The information provided by an IDS is invaluable for incident response and forensics.
- Deterrence: The presence of an IDS can deter attackers from targeting a network or system.
Challenges of Using an Intrusion Detection System
While IDS offers significant benefits, it’s important to be aware of the challenges associated with their implementation and management:
- False Positives: Anomaly-based IDS can generate false positives, which can be time-consuming to investigate.
- False Negatives: Signature-based IDS may not detect new or unknown attacks.
- Performance Impact: IDS can consume significant resources, potentially impacting network or system performance.
- Configuration Complexity: Configuring and managing an IDS can be complex, requiring specialized expertise.
- Evasion Techniques: Attackers may use evasion techniques to bypass IDS detection.
Best Practices for Implementing and Managing an Intrusion Detection System
To maximize the effectiveness of an IDS, it’s important to follow these best practices:
- Choose the Right IDS: Select an IDS that meets your specific needs and requirements. Consider the size and complexity of your network, the types of threats you are most concerned about, and your budget.
- Properly Configure the IDS: Configure the IDS to accurately detect malicious activity while minimizing false positives. This may involve tuning signatures, adjusting thresholds, and creating custom rules.
- Regularly Update the IDS: Keep the IDS up-to-date with the latest signatures and software updates. This will ensure that the IDS is able to detect the latest threats.
- Monitor Alerts: Monitor alerts generated by the IDS and investigate any suspicious activity.
- Integrate with Other Security Tools: Integrate the IDS with other security tools, such as firewalls and SIEM systems, to provide a more comprehensive security solution.
- Train Staff: Train staff on how to use and manage the IDS.
The Future of Intrusion Detection Systems
The landscape of cybersecurity is constantly evolving, and IDS technology is adapting to meet new challenges. Future trends in IDS include:
- Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning: AI and ML are being used to improve the accuracy and effectiveness of IDS by automating threat detection and response.
- Cloud-based IDS: Cloud-based IDS solutions are becoming increasingly popular, offering scalability, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness.
- Integration with Threat Intelligence: IDS are being integrated with threat intelligence feeds to provide real-time information about emerging threats.
- Behavioral Analytics: Behavioral analytics are being used to detect anomalous behavior that may indicate a security threat.
Conclusion
Understanding the IDS definition is crucial for building a robust cybersecurity strategy. Intrusion Detection Systems play a vital role in detecting and responding to security threats. By understanding the different types of IDS, how they work, and the best practices for implementing and managing them, organizations can significantly improve their security posture and protect themselves from cyberattacks. As technology evolves, so too must the strategies and tools we use to defend against cyber threats. The future of IDS is bright, with advancements in AI, cloud technology, and threat intelligence promising to make these systems even more effective in the fight against cybercrime.
