IAM Strategy: Securing Your Digital Identity Landscape
In today’s interconnected digital world, a robust IAM strategy is no longer optional; it’s a fundamental necessity. Identity and Access Management (IAM) governs how users are identified, authenticated, and authorized to access resources within an organization. A well-defined IAM strategy mitigates risks, streamlines operations, and enhances overall security posture. This article delves into the key components of an effective IAM strategy, exploring its benefits and providing practical guidance for implementation.
Understanding the Core of IAM Strategy
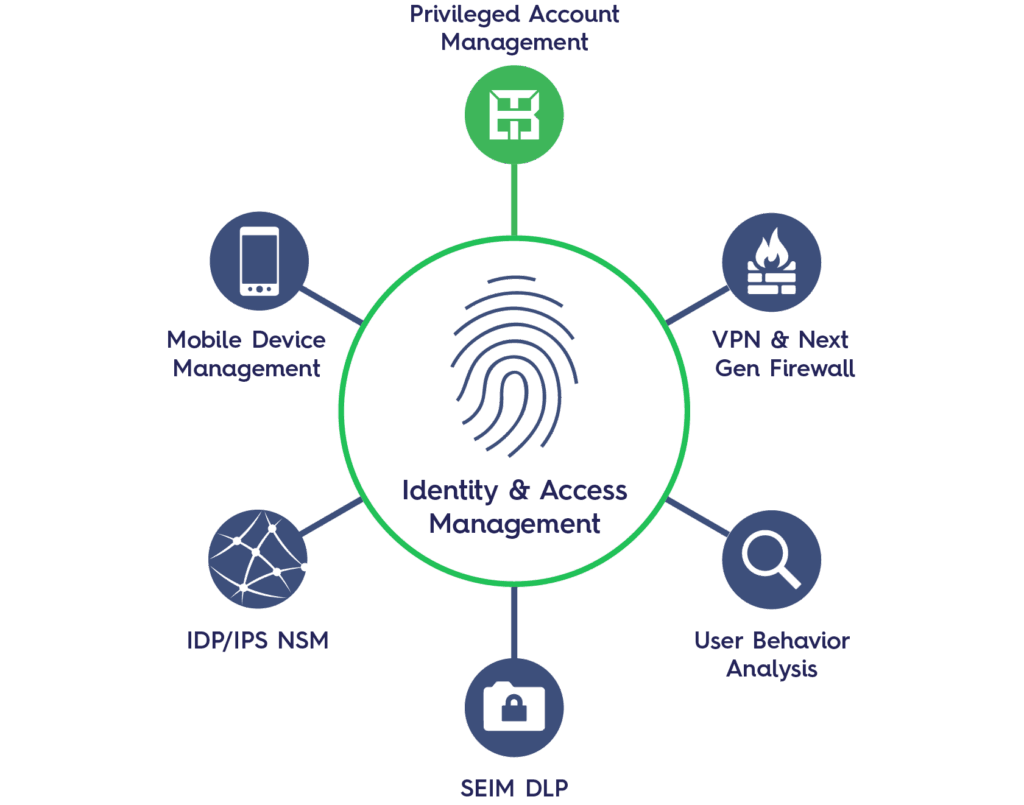
At its core, an IAM strategy is a comprehensive plan that outlines how an organization will manage digital identities and control access to its resources. It encompasses policies, processes, and technologies designed to ensure that only authorized individuals can access sensitive data and systems. This includes employees, contractors, partners, and even customers. The goal is to create a secure and efficient environment where access is granted based on roles, responsibilities, and the principle of least privilege.
Key Components of a Successful IAM Strategy
An effective IAM strategy is built on several key components. These components work together to provide a holistic approach to identity and access management:
- Identity Governance: Defines the policies and procedures for managing user identities throughout their lifecycle, from onboarding to offboarding.
- Access Management: Controls who has access to what resources, ensuring that users only have the privileges necessary to perform their job functions.
- Authentication: Verifies the identity of users before granting access to resources, often through methods like passwords, multi-factor authentication (MFA), and biometrics.
- Authorization: Determines what actions a user is allowed to perform once they have been authenticated.
- Privileged Access Management (PAM): Focuses on securing privileged accounts, such as administrator accounts, which have elevated access rights.
- Identity Analytics: Provides insights into user behavior and access patterns, helping to detect and prevent security threats.
The Benefits of a Strong IAM Strategy
Implementing a strong IAM strategy offers numerous benefits, including:
- Enhanced Security: Reduces the risk of unauthorized access, data breaches, and other security incidents.
- Improved Compliance: Helps organizations meet regulatory requirements, such as GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI DSS.
- Streamlined Operations: Automates identity and access management processes, freeing up IT staff to focus on other priorities.
- Reduced Costs: Minimizes the costs associated with manual identity management and security breaches.
- Enhanced User Experience: Provides users with a seamless and secure access experience.
- Increased Agility: Enables organizations to quickly adapt to changing business needs and new technologies.
Developing Your IAM Strategy: A Step-by-Step Guide
Developing an effective IAM strategy requires careful planning and execution. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you get started:
Step 1: Assess Your Current State
Begin by assessing your current identity and access management capabilities. Identify your existing systems, processes, and technologies. Evaluate your security risks and compliance requirements. Understand your business needs and goals. This assessment will provide a baseline for measuring your progress.
Step 2: Define Your Goals and Objectives
Clearly define your goals and objectives for your IAM strategy. What do you want to achieve? Do you want to improve security, streamline operations, or enhance user experience? Be specific and measurable. For example, you might aim to reduce the number of security incidents by 20% or decrease the time it takes to onboard new employees by 50%.
Step 3: Select the Right Technologies
Choose the right technologies to support your IAM strategy. There are many different IAM solutions available, each with its own strengths and weaknesses. Consider your specific needs and requirements when making your selection. Look for solutions that are scalable, flexible, and easy to integrate with your existing systems. Consider cloud-based IAM solutions for added agility and cost savings. [See also: Cloud Identity Management Best Practices]
Step 4: Develop Your IAM Policies and Procedures
Develop comprehensive IAM policies and procedures that outline how you will manage identities and control access to your resources. These policies should cover topics such as user provisioning, access requests, password management, and privileged access management. Ensure that your policies are clear, concise, and easy to understand. Communicate your policies to all employees and stakeholders.
Step 5: Implement Your IAM Strategy
Implement your IAM strategy in a phased approach. Start with a pilot project to test your policies and procedures. Gradually roll out your IAM solution to the rest of your organization. Provide training and support to your users. Monitor your progress and make adjustments as needed.
Step 6: Monitor and Maintain Your IAM Strategy
Continuously monitor and maintain your IAM strategy. Regularly review your policies and procedures to ensure that they are still effective. Stay up-to-date on the latest security threats and compliance requirements. Implement security updates and patches promptly. Conduct regular audits to identify and address any vulnerabilities. An ongoing IAM strategy is crucial in a landscape of ever-changing threats. [See also: Importance of Regular Security Audits]
Common IAM Challenges and How to Overcome Them
Implementing an IAM strategy can be challenging. Here are some common challenges and how to overcome them:
- Complexity: IAM can be complex, especially in large organizations with diverse systems and applications. Simplify your IAM architecture by consolidating systems and standardizing processes.
- Lack of Resources: Implementing and managing IAM requires skilled resources. Invest in training and development for your IT staff. Consider outsourcing some IAM functions to a managed services provider.
- User Resistance: Users may resist changes to their access privileges or authentication methods. Communicate the benefits of IAM to your users. Provide training and support to help them adapt to the new processes.
- Integration Issues: Integrating IAM with existing systems can be challenging. Choose IAM solutions that are easy to integrate with your existing infrastructure. Work with experienced integrators to ensure a smooth implementation.
The Future of IAM
The future of IAM strategy is evolving rapidly. Emerging trends include:
- Zero Trust Architecture: A security model that assumes that no user or device should be trusted by default.
- Passwordless Authentication: Authentication methods that do not require passwords, such as biometrics and security keys.
- Decentralized Identity: A model where users control their own digital identities.
- AI-Powered IAM: Using artificial intelligence to automate IAM tasks and improve security.
Conclusion
A well-defined IAM strategy is essential for securing your digital identity landscape. By understanding the key components of IAM, implementing best practices, and staying up-to-date on the latest trends, you can protect your organization from security threats, streamline operations, and enhance user experience. Investing in a robust IAM strategy is an investment in the long-term security and success of your business. An effective IAM strategy is not a one-time project; it’s an ongoing process that requires continuous monitoring and improvement. By prioritizing IAM strategy, organizations can build a more secure and resilient digital environment. The careful consideration of your specific needs and a commitment to continuous improvement are key to a successful IAM strategy. Ignoring the importance of a comprehensive IAM strategy can leave an organization vulnerable to significant risks. Make IAM strategy a priority today to safeguard your future. [See also: IAM and Zero Trust – A Synergistic Approach]
