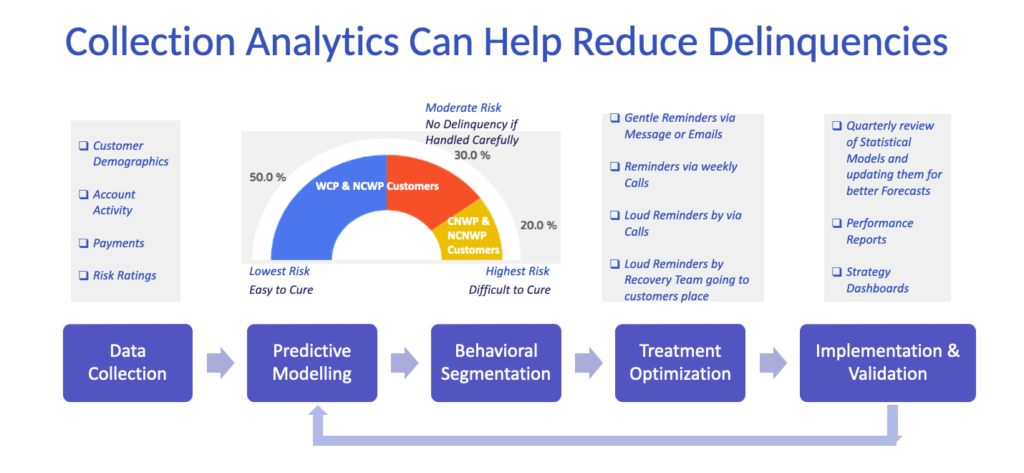
Evaluate the Lending Analytics: A Comprehensive Guide for Informed Decision-Making
In today’s dynamic financial landscape, the ability to evaluate the lending analytics effectively is paramount for lenders of all sizes. From credit unions to multinational banks, understanding and interpreting lending data is crucial for making sound decisions, mitigating risks, and maximizing profitability. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of evaluating lending analytics, providing a framework for understanding key metrics, identifying potential pitfalls, and ultimately, improving lending performance.
Understanding the Importance of Lending Analytics
Lending analytics refers to the process of collecting, analyzing, and interpreting data related to lending activities. This data encompasses a wide range of information, including loan applications, credit scores, repayment history, and market trends. By evaluating lending analytics, lenders can gain valuable insights into:
- Credit Risk Assessment: Accurately assess the creditworthiness of borrowers and identify potential risks associated with loan defaults.
- Loan Portfolio Performance: Monitor the performance of the loan portfolio, identify trends, and proactively address potential issues.
- Operational Efficiency: Streamline lending processes, reduce costs, and improve efficiency.
- Regulatory Compliance: Ensure compliance with relevant regulations and reporting requirements.
- Customer Segmentation: Identify different customer segments and tailor lending products and services to meet their specific needs.
Without effectively evaluating lending analytics, lenders are essentially operating in the dark, relying on gut feelings and outdated information. This can lead to poor lending decisions, increased risk, and ultimately, financial losses. [See also: Understanding Credit Scoring Models]
Key Metrics to Evaluate in Lending Analytics
Several key metrics are essential for evaluating lending analytics. These metrics provide a snapshot of the overall health and performance of the lending portfolio. Here are some of the most important ones:
Delinquency Rate
The delinquency rate measures the percentage of loans that are past due. It is a key indicator of credit risk and can signal potential problems with loan repayment. A high delinquency rate indicates that a significant portion of borrowers are struggling to make timely payments.
Charge-Off Rate
The charge-off rate measures the percentage of loans that are deemed uncollectible and written off. This metric provides a more definitive measure of credit losses than the delinquency rate. A high charge-off rate indicates that the lender is experiencing significant losses due to loan defaults.
Net Interest Margin (NIM)
The net interest margin (NIM) measures the difference between the interest income earned on loans and the interest expense paid on deposits and other funding sources. This metric is a key indicator of profitability and reflects the lender’s ability to generate income from its lending activities. When you evaluate the lending analytics, NIM provides a holistic view of financial performance.
Loan-to-Value (LTV) Ratio
The loan-to-value (LTV) ratio measures the amount of the loan relative to the value of the underlying asset, such as a home or a car. This metric is particularly important for secured loans. A high LTV ratio indicates that the lender has less collateral to recover in the event of a default.
Debt-to-Income (DTI) Ratio
The debt-to-income (DTI) ratio measures the borrower’s total debt payments relative to their income. This metric is a key indicator of the borrower’s ability to repay the loan. A high DTI ratio indicates that the borrower may be struggling to manage their debt obligations.
Credit Score Distribution
Understanding the distribution of credit scores within the loan portfolio is crucial for assessing overall credit risk. Analyzing the percentage of borrowers with different credit score ranges (e.g., excellent, good, fair, poor) can help lenders identify potential concentrations of risk. Evaluate the lending analytics regarding credit score distribution to refine lending strategies.
Steps to Effectively Evaluate Lending Analytics
Evaluating lending analytics is not a one-time task but rather an ongoing process that requires a structured approach. Here are the key steps to follow:
- Define Clear Objectives: Clearly define the objectives of the analysis. What questions are you trying to answer? What insights are you hoping to gain?
- Collect Relevant Data: Gather all relevant data from various sources, including loan origination systems, credit bureaus, and market research reports.
- Clean and Prepare the Data: Ensure the data is accurate, complete, and consistent. This may involve cleaning up errors, filling in missing values, and transforming the data into a usable format.
- Analyze the Data: Use appropriate statistical techniques and tools to analyze the data and identify trends, patterns, and anomalies.
- Interpret the Results: Interpret the results of the analysis in the context of the lender’s business objectives and risk appetite.
- Communicate the Findings: Communicate the findings to relevant stakeholders, including senior management, loan officers, and risk managers.
- Take Action: Based on the findings, take appropriate action to improve lending performance, mitigate risks, and enhance profitability.
- Monitor and Evaluate: Continuously monitor the performance of the lending portfolio and evaluate the effectiveness of the actions taken.
Tools and Technologies for Lending Analytics
A variety of tools and technologies are available to assist lenders in evaluating lending analytics. These tools range from basic spreadsheet software to sophisticated data analytics platforms. Some popular options include:
- Spreadsheet Software (e.g., Microsoft Excel, Google Sheets): Useful for basic data analysis and visualization.
- Statistical Software (e.g., SAS, SPSS, R): Provides advanced statistical capabilities for more complex analysis.
- Data Visualization Tools (e.g., Tableau, Power BI): Enables users to create interactive dashboards and visualizations to explore data and communicate insights.
- Machine Learning Platforms (e.g., TensorFlow, PyTorch): Can be used to develop predictive models for credit risk assessment and fraud detection.
- Specialized Lending Analytics Platforms: Offer a comprehensive suite of tools and features specifically designed for lending analytics.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid When Evaluating Lending Analytics
While evaluating lending analytics can provide valuable insights, it’s important to be aware of common pitfalls that can lead to inaccurate or misleading results. Some common pitfalls include:
- Data Quality Issues: Inaccurate or incomplete data can significantly compromise the accuracy of the analysis.
- Over-Reliance on Historical Data: Relying solely on historical data may not be sufficient to predict future performance, especially in a rapidly changing market.
- Ignoring External Factors: Failing to consider external factors, such as economic conditions and regulatory changes, can lead to inaccurate assessments.
- Lack of Statistical Expertise: Using inappropriate statistical techniques or misinterpreting the results can lead to flawed conclusions.
- Confirmation Bias: Seeking out data that confirms pre-existing beliefs and ignoring data that contradicts them can lead to biased analysis.
- Failing to Document Assumptions: Not documenting the assumptions made during the analysis can make it difficult to replicate or validate the results.
The Future of Lending Analytics
The field of lending analytics is constantly evolving, driven by advancements in technology and the increasing availability of data. Some key trends shaping the future of lending analytics include:
- Increased Use of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML): AI and ML are being used to automate various aspects of lending analytics, including credit risk assessment, fraud detection, and customer segmentation.
- Greater Emphasis on Real-Time Data: Lenders are increasingly relying on real-time data to make more timely and informed decisions.
- Integration of Alternative Data Sources: Lenders are exploring alternative data sources, such as social media activity and online behavior, to gain a more comprehensive view of borrowers.
- Enhanced Data Security and Privacy: Lenders are investing in robust data security and privacy measures to protect sensitive borrower information.
Conclusion
Evaluating lending analytics is essential for lenders seeking to improve their performance, mitigate risks, and enhance profitability. By understanding key metrics, following a structured approach, and leveraging appropriate tools and technologies, lenders can gain valuable insights into their lending activities and make more informed decisions. As the financial landscape continues to evolve, the ability to effectively evaluate the lending analytics will become even more critical for success. By continually refining their analytical capabilities, lenders can navigate the complexities of the market and achieve sustainable growth. The process to evaluate the lending analytics is a continuous one, requiring constant adaptation and improvement to stay ahead of the curve.
