Essential Code Review Criteria: A Comprehensive Guide for Developers
In the fast-paced world of software development, delivering high-quality code is paramount. One of the most effective methods for achieving this is through rigorous code review. But what makes a code review truly effective? The answer lies in establishing clear and comprehensive code review criteria. This guide delves into the essential code review criteria that developers should consider to ensure their code is robust, maintainable, and secure. By implementing these code review criteria, teams can significantly improve the overall quality of their software and reduce the risk of costly errors. Let’s explore the key aspects of effective code review criteria.
Why Code Review Criteria Matter
Code review is more than just a quick glance at lines of code. It’s a structured process of evaluating code against a predefined set of standards and best practices. Having well-defined code review criteria ensures that all reviewers are on the same page and know what to look for. This consistency leads to more thorough and effective reviews. Without clear criteria, reviews can become subjective and inconsistent, potentially missing critical issues. Furthermore, clearly defined code review criteria help to onboard new team members and promote a shared understanding of code quality expectations.
Key Code Review Criteria
The following sections outline the essential code review criteria that should be considered during every code review:
Functionality
Does the code perform as intended? This is the most fundamental aspect of any code review. Reviewers should verify that the code meets the specified requirements and that it handles all expected inputs and outputs correctly. Consider edge cases and boundary conditions to ensure the code is robust and reliable. Testing the functionality thoroughly is crucial to identify any potential bugs or unexpected behavior.
- Does the code fulfill the intended purpose?
- Are there any edge cases or boundary conditions that are not handled correctly?
- Are there any potential bugs or errors?
- Does the code produce the expected output?
Readability
Code is read far more often than it is written. Therefore, readability is a crucial aspect of maintainability. Code should be clear, concise, and easy to understand. Use meaningful variable and function names, consistent indentation, and comments to explain complex logic. Adhering to a consistent coding style guide enhances readability and makes it easier for other developers to understand and modify the code. [See also: Coding Style Guides Best Practices]
- Is the code easy to understand?
- Are variable and function names meaningful?
- Is the code properly indented?
- Are there sufficient comments to explain complex logic?
Maintainability
Code should be designed in a way that makes it easy to modify and extend in the future. This involves using modular design principles, avoiding code duplication, and adhering to SOLID principles. Well-maintained code reduces the risk of introducing bugs during future modifications and makes it easier to add new features. Consider the long-term implications of the code and whether it will be easy to maintain as the project evolves. Proper code review criteria will emphasize this.
- Is the code modular and easy to modify?
- Is there any code duplication?
- Does the code adhere to SOLID principles?
- Is the code well-structured and organized?
Performance
Code should be efficient and performant. Avoid unnecessary loops, inefficient algorithms, and excessive memory usage. Profile the code to identify performance bottlenecks and optimize them. Consider the impact of the code on the overall system performance and ensure that it does not introduce any performance regressions. Evaluating performance is an important code review consideration.
- Is the code efficient and performant?
- Are there any unnecessary loops or inefficient algorithms?
- Is memory usage optimized?
- Are there any potential performance bottlenecks?
Security
Security is a critical concern in modern software development. Code should be reviewed for potential security vulnerabilities, such as SQL injection, cross-site scripting (XSS), and buffer overflows. Use secure coding practices and validate all inputs to prevent attacks. Consider the potential security implications of the code and ensure that it does not introduce any new vulnerabilities. Security should be a high priority in your code review criteria. [See also: Secure Coding Practices Checklist]
- Are there any potential security vulnerabilities?
- Is input validation performed?
- Are secure coding practices followed?
- Does the code protect against common attacks?
Testability
Code should be designed in a way that makes it easy to test. This involves using dependency injection, writing unit tests, and ensuring that the code is well-isolated. Testable code is easier to verify and reduces the risk of introducing bugs. Consider the testability of the code and ensure that it can be easily tested using automated testing tools. The code review criteria should include consideration for testability.
- Is the code easy to test?
- Are unit tests written?
- Is the code well-isolated?
- Can the code be easily tested using automated testing tools?
Error Handling
Proper error handling is essential for robust and reliable software. Code should handle errors gracefully and provide informative error messages. Avoid swallowing exceptions or ignoring errors. Consider the potential error conditions that could occur and ensure that the code handles them appropriately. This is a crucial component of the code review criteria. [See also: Best Practices for Exception Handling]
- Does the code handle errors gracefully?
- Are informative error messages provided?
- Are exceptions properly handled?
- Are potential error conditions considered?
Complexity
Complex code is difficult to understand, maintain, and test. Aim for simplicity and avoid unnecessary complexity. Break down complex tasks into smaller, more manageable functions. Use design patterns to simplify code and improve readability. Consider the complexity of the code and strive to reduce it whenever possible. Simplicity is a key consideration for good code review criteria.
- Is the code unnecessarily complex?
- Can complex tasks be broken down into smaller functions?
- Are design patterns used to simplify code?
- Is the code as simple as possible?
Adherence to Standards
Code should adhere to established coding standards and best practices. This ensures consistency and makes it easier for developers to work together. Follow the coding style guide, use consistent naming conventions, and adhere to established design patterns. Consider the standards and best practices that are applicable to the project and ensure that the code adheres to them. The code review criteria should always reference the relevant coding standards.
- Does the code adhere to coding standards?
- Are naming conventions followed?
- Are established design patterns used?
- Does the code follow best practices?
Implementing Code Review Criteria
Implementing code review criteria effectively requires a structured approach. Here are some tips for implementing code review criteria in your development process:
- Define Clear Criteria: Start by defining a clear and comprehensive set of code review criteria that are tailored to your project’s specific needs.
- Document the Criteria: Document the code review criteria in a central location that is easily accessible to all developers.
- Train Reviewers: Train reviewers on the code review criteria and provide them with the tools and resources they need to perform effective reviews.
- Use Code Review Tools: Use code review tools to automate the review process and track progress.
- Provide Feedback: Provide constructive feedback to developers and encourage them to improve their code based on the code review criteria.
- Continuously Improve: Continuously review and improve the code review criteria based on feedback and experience.
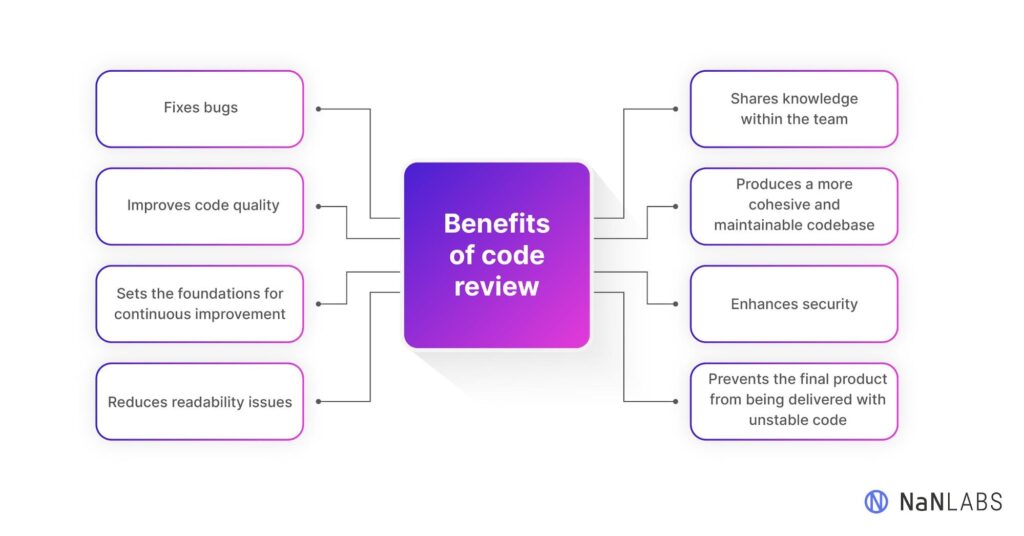
The Benefits of Effective Code Review
Implementing effective code review criteria offers numerous benefits, including:
- Improved Code Quality: Code review helps to identify and fix bugs early in the development process, resulting in higher quality code.
- Reduced Risk: Code review helps to identify and mitigate potential security vulnerabilities, reducing the risk of attacks.
- Increased Maintainability: Code review ensures that code is well-structured and easy to maintain, reducing the cost of future modifications.
- Knowledge Sharing: Code review promotes knowledge sharing among developers, helping them to learn from each other and improve their skills.
- Consistency: Code review ensures that code adheres to established coding standards and best practices, resulting in more consistent code.
Conclusion
Establishing and adhering to comprehensive code review criteria is essential for delivering high-quality, maintainable, and secure software. By focusing on functionality, readability, maintainability, performance, security, testability, error handling, complexity, and adherence to standards, developers can significantly improve the overall quality of their code and reduce the risk of costly errors. Investing in a robust code review process is an investment in the long-term success of your software project.
