Enterprise DNS: Securing and Optimizing Your Network Infrastructure
In today’s digital landscape, a robust and reliable Domain Name System (DNS) infrastructure is paramount for any enterprise. Enterprise DNS goes beyond the basic functionality of resolving domain names to IP addresses. It encompasses a comprehensive suite of features designed to enhance security, improve performance, and provide greater control over an organization’s network. This article explores the critical aspects of enterprise DNS, its benefits, challenges, and best practices for implementation and management.
Understanding the Importance of Enterprise DNS
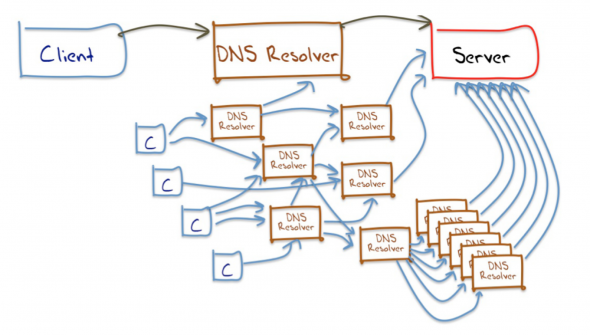
The DNS is often described as the internet’s phonebook, translating human-readable domain names into the numerical IP addresses that computers use to communicate. While this basic function is essential, enterprise DNS solutions offer a far more sophisticated set of capabilities. These include:
- Enhanced Security: Protecting against DNS-based attacks such as DNS spoofing, DNS hijacking, and DDoS attacks.
- Improved Performance: Optimizing DNS resolution times to reduce latency and improve application responsiveness.
- Increased Reliability: Ensuring high availability and redundancy to prevent DNS outages.
- Centralized Management: Providing a single point of control for managing DNS records and policies across the entire organization.
- Advanced Analytics: Offering insights into DNS traffic patterns to identify potential security threats and performance bottlenecks.
Key Features of Enterprise DNS Solutions
A comprehensive enterprise DNS solution typically includes the following features:
DNS Security Extensions (DNSSEC)
DNSSEC adds a layer of security to the DNS by digitally signing DNS records. This ensures that DNS responses are authentic and haven’t been tampered with, protecting against DNS spoofing and cache poisoning attacks. Implementing DNSSEC is a crucial step in securing your enterprise DNS infrastructure. [See also: DNS Security Best Practices]
DDoS Protection
Distributed Denial-of-Service (DDoS) attacks can overwhelm DNS servers, rendering them unavailable and disrupting critical services. Enterprise DNS solutions often include DDoS protection mechanisms to mitigate these attacks by filtering malicious traffic and ensuring that legitimate users can still access DNS services. Protecting against DDoS attacks is vital for maintaining the availability of your enterprise DNS infrastructure.
Global Server Load Balancing (GSLB)
GSLB distributes DNS traffic across multiple servers in different geographic locations. This improves performance by directing users to the closest server and enhances availability by providing redundancy in case of server failures. GSLB is a key component of a highly available and performant enterprise DNS infrastructure.
DNS Firewall
A DNS firewall acts as a security gateway, blocking access to malicious domains and preventing malware from communicating with command-and-control servers. This helps to protect against phishing attacks, malware infections, and other cyber threats. Implementing a DNS firewall is an important layer of defense for your enterprise DNS infrastructure.
Recursive DNS Servers
Recursive DNS servers perform the task of querying other DNS servers to resolve domain names on behalf of clients. Enterprise-grade recursive servers offer enhanced security features, such as rate limiting and response policy zones (RPZ), to protect against DNS-based attacks. Choosing robust recursive DNS servers is crucial for the security and performance of your enterprise DNS infrastructure. [See also: Choosing the Right DNS Server]
Anycast DNS
Anycast DNS uses the same IP address for multiple servers located in different geographic locations. This allows DNS queries to be routed to the nearest server, improving performance and providing redundancy. Anycast DNS is a popular choice for enterprise DNS deployments due to its scalability and resilience.
Benefits of Implementing Enterprise DNS
Implementing an enterprise DNS solution offers numerous benefits, including:
- Improved Security: Protecting against DNS-based attacks and preventing data breaches.
- Enhanced Performance: Reducing latency and improving application responsiveness.
- Increased Reliability: Ensuring high availability and preventing DNS outages.
- Simplified Management: Providing a centralized platform for managing DNS records and policies.
- Better Visibility: Gaining insights into DNS traffic patterns and identifying potential security threats.
- Compliance: Meeting regulatory requirements for data security and privacy.
Challenges of Implementing Enterprise DNS
While the benefits of enterprise DNS are significant, there are also some challenges to consider:
- Complexity: Configuring and managing a complex DNS infrastructure can be challenging.
- Cost: Enterprise-grade DNS solutions can be expensive.
- Integration: Integrating DNS with existing security and network infrastructure can be complex.
- Maintenance: Maintaining a secure and reliable DNS infrastructure requires ongoing effort.
Best Practices for Enterprise DNS Management
To ensure the success of your enterprise DNS implementation, follow these best practices:
- Implement DNSSEC: Digitally sign your DNS records to protect against DNS spoofing.
- Use a DNS Firewall: Block access to malicious domains to prevent malware infections.
- Monitor DNS Traffic: Analyze DNS traffic patterns to identify potential security threats.
- Implement Rate Limiting: Protect against DDoS attacks by limiting the number of DNS queries from a single source.
- Use Redundant DNS Servers: Ensure high availability by deploying multiple DNS servers.
- Regularly Update DNS Software: Patch vulnerabilities and stay up-to-date with the latest security features.
- Perform Regular Audits: Review your DNS configuration to identify potential security weaknesses.
- Educate Users: Train users to recognize and avoid phishing attacks that target DNS.
The Future of Enterprise DNS
The future of enterprise DNS is likely to be shaped by several key trends, including:
- Increased Automation: Automating DNS management tasks to reduce complexity and improve efficiency.
- Cloud-Based DNS: Migrating DNS infrastructure to the cloud to improve scalability and reduce costs.
- AI-Powered Security: Using artificial intelligence to detect and prevent DNS-based attacks.
- Integration with SASE: Integrating DNS security with Secure Access Service Edge (SASE) architectures.
Conclusion
Enterprise DNS is a critical component of any organization’s network infrastructure. By implementing a robust and secure DNS solution, enterprises can protect against DNS-based attacks, improve performance, and gain greater control over their network. While there are challenges to consider, the benefits of enterprise DNS far outweigh the risks. By following best practices for implementation and management, organizations can ensure that their DNS infrastructure is secure, reliable, and optimized for performance. As the threat landscape continues to evolve, enterprise DNS will become even more important for protecting against cyber threats and ensuring the availability of critical services. The implementation of a solid enterprise DNS strategy is not just a recommendation; it is a necessity for modern businesses navigating the complexities of the digital world. Ignoring the importance of a properly configured and managed enterprise DNS can leave organizations vulnerable to a wide range of attacks and performance issues. Therefore, investing in a comprehensive enterprise DNS solution is a strategic imperative for ensuring the security, reliability, and optimal performance of your network infrastructure.
