Define Master Data Management: A Comprehensive Guide
In today’s data-driven world, organizations are constantly seeking ways to improve efficiency, reduce costs, and gain a competitive edge. One crucial aspect of achieving these goals is effective master data management (MDM). But what does it really mean to define master data management, and why is it so important? This comprehensive guide will explore the concept of MDM, its benefits, key components, implementation strategies, and future trends.
Understanding Master Data
Before we can truly define master data management, it’s essential to understand what master data actually is. Master data refers to the critical business information that is shared across multiple systems and departments within an organization. This data typically includes information about customers, products, suppliers, locations, and employees. Think of it as the ‘single source of truth’ for these core entities.
Unlike transactional data, which changes frequently and reflects individual business events, master data is relatively static and provides a consistent view of these core entities. For example, a customer’s name, address, and contact information are all considered master data.
What is Master Data Management (MDM)?
Now that we understand master data, let’s define master data management more formally. MDM is a technology-enabled discipline that aims to create and maintain a consistent, accurate, and complete view of an organization’s master data. It involves a set of processes, policies, rules, and technologies that ensure data quality, consistency, and governance across all systems and applications.
Essentially, MDM provides a single, authoritative source of truth for critical business information. This, in turn, allows organizations to make better decisions, improve operational efficiency, and enhance customer experiences.
To define master data management more simply, consider it the practice of ensuring that key business data is accurate, consistent, and readily available across the organization. It’s about creating a ‘golden record’ for each master data entity.
Why is MDM Important?
The importance of MDM stems from the numerous benefits it offers to organizations. Here are some key reasons why MDM is crucial:
- Improved Data Quality: MDM helps to identify and correct data errors, inconsistencies, and duplicates, leading to higher data quality.
- Enhanced Decision-Making: With a single, accurate view of master data, organizations can make more informed and data-driven decisions.
- Increased Operational Efficiency: MDM streamlines business processes by providing consistent and reliable data across all systems.
- Reduced Costs: By eliminating data silos and improving data quality, MDM can help organizations reduce costs associated with data errors and inefficiencies.
- Improved Customer Experience: MDM enables organizations to deliver personalized and consistent customer experiences across all channels.
- Compliance and Regulatory Requirements: MDM helps organizations comply with data privacy regulations and industry standards.
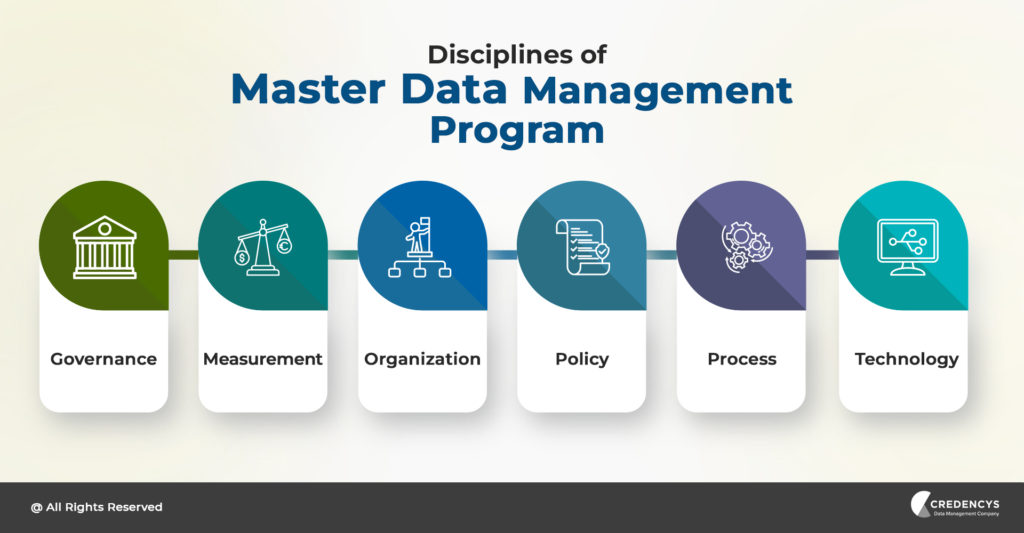
Key Components of MDM
To effectively define master data management, it’s important to understand its key components. These components work together to ensure data quality, consistency, and governance.
Data Governance
Data governance establishes the policies, procedures, and responsibilities for managing master data. It defines who is responsible for creating, maintaining, and accessing master data, and ensures that data quality standards are met. Strong data governance is the foundation of a successful MDM program.
Data Modeling
Data modeling involves defining the structure and relationships of master data entities. This includes identifying the attributes, data types, and validation rules for each entity. A well-defined data model is essential for ensuring data consistency and accuracy.
Data Integration
Data integration involves connecting different systems and applications to share master data. This can be achieved through various integration techniques, such as ETL (Extract, Transform, Load), data virtualization, and APIs (Application Programming Interfaces). Effective data integration is crucial for creating a single, unified view of master data.
Data Quality Management
Data quality management includes processes for cleansing, standardizing, and enriching master data. This involves identifying and correcting data errors, inconsistencies, and duplicates. Data quality tools can automate many of these tasks, ensuring that master data is accurate and reliable.
Master Data Repository
The master data repository is a central location for storing and managing master data. This repository can be a dedicated MDM system or a component of a larger data management platform. It provides a single source of truth for master data, ensuring that all systems and applications have access to the same information.
MDM Implementation Strategies
Implementing an MDM program can be a complex undertaking. Here are some common implementation strategies:
- Centralized MDM: In this approach, all master data is managed in a central repository. This provides a single, authoritative source of truth and ensures data consistency across the organization.
- Decentralized MDM: In this approach, master data is managed in multiple systems or departments. This allows for greater flexibility and control, but it can also lead to data inconsistencies.
- Hybrid MDM: This approach combines elements of both centralized and decentralized MDM. It allows organizations to balance the need for data consistency with the need for flexibility and control.
The best implementation strategy will depend on the specific needs and requirements of the organization. It’s important to carefully evaluate the different options and choose the approach that best aligns with your business goals.
Challenges of Implementing MDM
While MDM offers numerous benefits, it also presents several challenges. These challenges include:
- Data Complexity: Organizations often have a wide variety of data sources and formats, making it difficult to integrate and manage master data.
- Data Governance: Establishing effective data governance policies and procedures can be challenging, especially in large, complex organizations.
- Organizational Culture: MDM requires a shift in organizational culture, with a greater emphasis on data quality and governance.
- Technology Selection: Choosing the right MDM technology can be a complex process, as there are many different vendors and solutions available.
- Budget Constraints: Implementing an MDM program can be expensive, especially if it involves significant infrastructure upgrades or software purchases.
Overcoming these challenges requires careful planning, strong leadership, and a commitment to data quality and governance.
Future Trends in MDM
The field of MDM is constantly evolving, with new technologies and approaches emerging all the time. Here are some key trends to watch:
- Cloud-Based MDM: More organizations are adopting cloud-based MDM solutions, which offer greater scalability, flexibility, and cost savings.
- AI and Machine Learning: AI and machine learning are being used to automate many MDM tasks, such as data cleansing, matching, and enrichment.
- Data Fabric: The data fabric approach provides a unified view of data across multiple systems and locations, making it easier to manage master data.
- Graph Databases: Graph databases are being used to model complex relationships between master data entities, providing a more holistic view of the data.
These trends are making MDM more accessible, affordable, and effective than ever before. As organizations continue to generate more data, the importance of MDM will only continue to grow.
Examples of Master Data Management in Action
To further illustrate the concept, let’s look at some real-world examples of how master data management is used:
- Retail: A retailer uses MDM to manage product data, ensuring that product information is consistent across all channels, including online stores, brick-and-mortar stores, and mobile apps. This allows customers to easily find the products they’re looking for and make informed purchasing decisions.
- Healthcare: A hospital uses MDM to manage patient data, ensuring that patient information is accurate and up-to-date. This helps to improve patient care and reduce medical errors.
- Financial Services: A bank uses MDM to manage customer data, ensuring that customer information is consistent across all departments and systems. This helps to improve customer service and prevent fraud.
- Manufacturing: A manufacturer uses MDM to manage supplier data, ensuring that supplier information is accurate and reliable. This helps to improve supply chain efficiency and reduce costs.
These examples demonstrate the wide range of applications for MDM across different industries.
Conclusion
In conclusion, to define master data management is to understand it as a critical discipline for organizations seeking to improve data quality, enhance decision-making, and increase operational efficiency. By creating and maintaining a consistent, accurate, and complete view of master data, organizations can unlock valuable insights, streamline business processes, and deliver better customer experiences. While implementing MDM can be challenging, the benefits far outweigh the costs. As data volumes continue to grow, MDM will become increasingly important for organizations of all sizes.
[See also: Data Governance Best Practices]
[See also: Choosing the Right MDM Solution]
[See also: The Future of Data Management]
