Decoding the Gartner Magic Quadrant for Data Analytics Platforms: A Comprehensive Guide
The Gartner Magic Quadrant for Data Analytics Platforms is a widely recognized and respected research report that evaluates vendors in the data analytics space. It provides a visual snapshot of the market, assessing vendors based on their ability to execute and completeness of vision. Understanding this quadrant is crucial for businesses looking to invest in or optimize their data analytics capabilities. This guide will delve into the intricacies of the Gartner Magic Quadrant for Data Analytics, explaining its methodology, key players, and what it means for organizations seeking to leverage data analytics for competitive advantage.
Understanding the Gartner Magic Quadrant Methodology
The Gartner Magic Quadrant isn’t just a ranking; it’s a complex analysis based on rigorous research and objective criteria. Gartner analysts evaluate vendors based on two primary axes:
- Ability to Execute: This assesses a vendor’s overall viability, market responsiveness, marketing execution, sales execution, operations, and customer experience. It reflects how effectively the vendor is delivering on its promises and meeting the needs of its customers.
- Completeness of Vision: This evaluates a vendor’s understanding of market trends, innovation, marketing strategy, sales strategy, offering (product) strategy, geographic strategy, and business model. It indicates how well the vendor is positioned to capitalize on future opportunities and address evolving customer requirements.
Based on these assessments, vendors are placed into one of four quadrants:
- Leaders: These vendors demonstrate a strong ability to execute and completeness of vision. They have a significant market presence, a proven track record, and a clear understanding of the future direction of the data analytics market.
- Challengers: These vendors have a strong ability to execute but may lack the completeness of vision of the Leaders. They often have a large customer base and a solid product offering but may not be as innovative or forward-thinking as the Leaders.
- Visionaries: These vendors have a strong completeness of vision but may lack the ability to execute as effectively as the Leaders. They often have innovative products and a compelling vision for the future but may struggle to scale their operations or gain market share.
- Niche Players: These vendors focus on a specific segment of the data analytics market or have a limited geographic presence. They may have a strong understanding of their niche but lack the resources or capabilities to compete more broadly.
Key Players in the Gartner Magic Quadrant for Data Analytics Platforms
The specific vendors included in the Gartner Magic Quadrant for Data Analytics vary from year to year, reflecting the dynamic nature of the market. However, some vendors consistently appear in the report, often occupying the Leaders quadrant. These include:
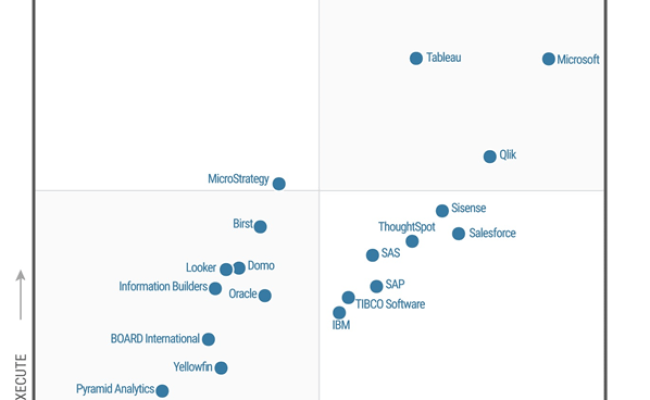
- Microsoft (Power BI): Microsoft’s Power BI is a leading data analytics platform known for its ease of use, comprehensive features, and integration with other Microsoft products.
- Tableau (Salesforce): Tableau, now part of Salesforce, is another popular data analytics platform known for its visual analytics capabilities and user-friendly interface.
- Qlik: Qlik offers a range of data analytics solutions, including Qlik Sense, which is known for its associative engine and ability to uncover hidden insights.
- ThoughtSpot: ThoughtSpot is a search-driven data analytics platform that allows users to ask questions in natural language and get instant answers.
- Amazon Web Services (AWS): AWS offers a suite of data analytics services, including Amazon QuickSight, a cloud-based BI service that integrates with other AWS services.
- Google (Looker): Looker, now part of Google Cloud, is a modern data analytics platform that emphasizes data governance and collaboration.
It’s important to note that the Gartner Magic Quadrant is just one source of information. Organizations should conduct their own due diligence and consider their specific needs and requirements when evaluating data analytics platforms.
What the Gartner Magic Quadrant Means for Your Organization
The Gartner Magic Quadrant for Data Analytics can be a valuable tool for organizations seeking to improve their data analytics capabilities. Here are some ways to leverage the report:
- Identify Potential Vendors: The quadrant can help you identify vendors that are well-positioned to meet your needs. Consider vendors in the Leaders quadrant for established solutions or vendors in the Visionaries quadrant for innovative approaches.
- Evaluate Vendor Strengths and Weaknesses: The report provides detailed assessments of each vendor’s strengths and weaknesses, allowing you to compare different platforms and identify the best fit for your organization.
- Understand Market Trends: The quadrant provides insights into the latest trends in the data analytics market, helping you stay ahead of the curve and make informed decisions about your technology investments.
- Benchmark Your Current Solution: Compare your current data analytics platform to the vendors in the quadrant to identify areas for improvement and potential gaps in your capabilities.
- Negotiate Better Pricing: Use the information in the report to negotiate better pricing and terms with vendors.
Beyond the Quadrant: Key Considerations for Choosing a Data Analytics Platform
While the Gartner Magic Quadrant is a helpful resource, it’s important to consider other factors when choosing a data analytics platform. These include:
- Your Specific Business Needs: What are your key business challenges? What types of data do you need to analyze? What insights are you hoping to gain?
- Your Technical Requirements: What are your infrastructure requirements? Do you need a cloud-based solution or an on-premise solution? What level of technical expertise do you have in-house?
- Your Budget: How much are you willing to spend on a data analytics platform? Consider both the initial cost and the ongoing maintenance and support costs.
- Ease of Use: How easy is the platform to use? Will your users be able to quickly learn and adopt the platform?
- Scalability: Can the platform scale to meet your growing data needs?
- Integration Capabilities: Does the platform integrate with your existing systems and data sources?
- Security: Does the platform provide adequate security to protect your sensitive data?
- Support and Training: Does the vendor offer adequate support and training to help you get the most out of the platform?
The Future of Data Analytics Platforms
The data analytics market is constantly evolving, with new technologies and trends emerging all the time. Some key trends to watch include:
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML): AI and ML are increasingly being integrated into data analytics platforms to automate tasks, improve accuracy, and uncover hidden insights.
- Augmented Analytics: Augmented analytics uses AI and ML to automate the process of data analysis, making it easier for non-technical users to gain insights from data.
- Cloud-Based Analytics: Cloud-based data analytics platforms are becoming increasingly popular due to their scalability, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness.
- Embedded Analytics: Embedded analytics allows organizations to embed data analytics capabilities directly into their applications and workflows.
- Data Storytelling: Data storytelling is the art of communicating data insights in a clear, concise, and engaging way.
Conclusion
The Gartner Magic Quadrant for Data Analytics Platforms is a valuable resource for organizations seeking to improve their data analytics capabilities. By understanding the methodology, key players, and trends in the market, you can make informed decisions about your technology investments and leverage data analytics to gain a competitive advantage. Remember to consider your specific business needs and technical requirements when choosing a data analytics platform and don’t rely solely on the Gartner Magic Quadrant. Conduct thorough research, evaluate different options, and choose the platform that best fits your organization’s unique needs.
[See also: Choosing the Right Data Analytics Tool for Your Business]
[See also: The Importance of Data Governance in Data Analytics]
[See also: How to Build a Data-Driven Culture in Your Organization]
