Data Mesh vs Data Lake vs Data Fabric: A Comprehensive Comparison
In the ever-evolving landscape of data management, organizations are constantly seeking efficient and effective strategies to harness the power of their data. Three prominent approaches have emerged: data mesh, data lake, and data fabric. Each offers a unique solution to the challenges of data storage, access, and governance. Understanding the nuances of each approach is crucial for making informed decisions about which strategy best aligns with an organization’s specific needs and goals. This article provides a comprehensive comparison of data mesh, data lake, and data fabric, exploring their key characteristics, benefits, drawbacks, and use cases.
Understanding Data Lakes
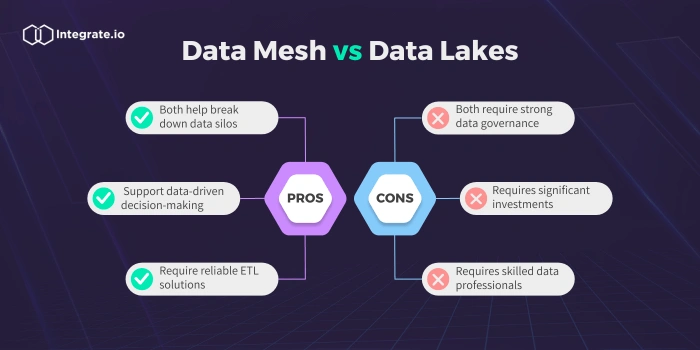
A data lake is a centralized repository that stores vast amounts of raw data in its native format. This can include structured, semi-structured, and unstructured data. The primary advantage of a data lake is its flexibility. Data can be ingested without pre-defined schemas, allowing for a wide range of analytical possibilities. However, this flexibility also introduces challenges related to data governance and quality.
Key Characteristics of a Data Lake
- Centralized Repository: All data is stored in a single location.
- Schema-on-Read: Data schemas are applied when the data is accessed, not when it’s ingested.
- Raw Data Storage: Data is stored in its original format.
- Scalability: Designed to handle large volumes of data.
Benefits of Using a Data Lake
- Flexibility: Supports diverse data types and use cases.
- Cost-Effective: Can reduce storage costs by storing data in its raw format.
- Agility: Allows for rapid experimentation and prototyping.
Drawbacks of Using a Data Lake
- Data Swamp Risk: Without proper governance, a data lake can become a disorganized and unusable “data swamp.”
- Complexity: Managing a data lake requires specialized skills and tools.
- Security Concerns: Ensuring data security and compliance can be challenging.
Exploring Data Mesh
Data mesh is a decentralized approach to data management that emphasizes domain ownership and self-service data infrastructure. Unlike the centralized nature of data lakes, a data mesh distributes data ownership and responsibility to individual business domains. This empowers teams to manage their data as a product, ensuring its quality, discoverability, and accessibility. The data mesh architecture promotes agility and scalability by allowing domains to independently evolve their data solutions.
Key Characteristics of a Data Mesh
- Decentralized Ownership: Data is owned and managed by individual business domains.
- Data as a Product: Data is treated as a valuable product with defined quality standards and service level agreements (SLAs).
- Self-Service Data Infrastructure: Domains have access to a shared infrastructure that enables them to manage their data independently.
- Federated Governance: A set of global standards and policies ensures interoperability and compliance across domains.
Benefits of Using a Data Mesh
- Improved Agility: Domains can quickly adapt to changing business needs.
- Increased Scalability: The decentralized architecture allows for greater scalability.
- Enhanced Data Quality: Domain ownership promotes accountability for data quality.
- Better Alignment with Business Needs: Data solutions are tailored to the specific requirements of each domain.
Drawbacks of Using a Data Mesh
- Organizational Complexity: Implementing a data mesh requires significant organizational change.
- Technical Challenges: Building a self-service data infrastructure can be complex.
- Governance Overhead: Establishing and enforcing federated governance policies requires careful planning and execution.
Delving into Data Fabric
A data fabric is an architectural approach that provides a unified and consistent view of data across a distributed environment. It leverages various technologies, such as metadata management, data virtualization, and data integration, to connect disparate data sources and provide seamless access to data. A data fabric aims to simplify data access and governance, regardless of where the data resides. The core concept of a data fabric is to create a layer of abstraction that shields users from the underlying complexity of the data landscape.
Key Characteristics of a Data Fabric
- Unified Data Access: Provides a single point of access to data across multiple sources.
- Metadata Management: Leverages metadata to understand and manage data assets.
- Data Virtualization: Creates a virtual layer that abstracts the physical location of data.
- Intelligent Data Integration: Uses AI and machine learning to automate data integration tasks.
Benefits of Using a Data Fabric
- Simplified Data Access: Users can easily find and access the data they need.
- Improved Data Governance: Provides a consistent framework for data governance.
- Enhanced Data Integration: Simplifies the integration of disparate data sources.
- Increased Data Agility: Enables faster access to insights and improved decision-making.
Drawbacks of Using a Data Fabric
- Complexity of Implementation: Implementing a data fabric can be technically challenging.
- Cost: The technologies required for a data fabric can be expensive.
- Vendor Lock-in: Relying on a specific vendor’s data fabric platform can lead to vendor lock-in.
Data Mesh vs Data Lake vs Data Fabric: A Detailed Comparison Table
To further illustrate the differences between data mesh, data lake, and data fabric, consider the following comparison table:
| Feature | Data Lake | Data Mesh | Data Fabric |
|---|---|---|---|
| Data Ownership | Centralized | Decentralized (Domain-Oriented) | Distributed (Governed Centrally) |
| Data Governance | Centralized (Often a Challenge) | Federated | Centralized & Automated |
| Data Architecture | Centralized Repository | Decentralized Network of Data Products | Abstracted Layer Over Disparate Sources |
| Schema | Schema-on-Read | Domain-Specific | Virtualized Schema |
| Use Cases | Exploratory Analytics, Data Discovery | Agile Analytics, Domain-Specific Insights | Unified Data Access, Data Integration |
| Complexity | High (Governance & Management) | High (Organizational & Technical) | High (Technical Implementation) |
When to Choose Which Approach
The choice between data mesh, data lake, and data fabric depends on an organization’s specific needs and priorities.
- Choose a Data Lake if: You need a centralized repository for storing large volumes of raw data, and you have the resources to manage data governance and quality. A data lake is suitable for organizations that prioritize flexibility and exploratory analytics.
- Choose a Data Mesh if: You want to empower business domains to own and manage their data, and you are willing to invest in organizational change and self-service data infrastructure. The data mesh approach is best suited for organizations that prioritize agility, scalability, and data quality.
- Choose a Data Fabric if: You need to provide a unified and consistent view of data across a distributed environment, and you are willing to invest in technologies that simplify data access and integration. A data fabric is ideal for organizations that prioritize data governance, data integration, and ease of access.
Real-World Examples
To illustrate the practical application of each approach, consider the following examples:
- Data Lake Example: A large e-commerce company uses a data lake to store customer data, product data, and transaction data. They use this data to perform exploratory analytics and identify trends in customer behavior.
- Data Mesh Example: A global financial services firm adopts a data mesh to enable individual business units to manage their own data products. This allows them to quickly respond to changing market conditions and develop innovative financial products.
- Data Fabric Example: A healthcare provider implements a data fabric to provide a unified view of patient data across multiple systems. This enables them to improve patient care and reduce healthcare costs.
[See also: Data Lake Best Practices] [See also: Data Governance Frameworks] [See also: Cloud Data Integration]
Conclusion
Data mesh, data lake, and data fabric each offer distinct advantages and disadvantages. The optimal choice depends on an organization’s specific requirements and priorities. Understanding the key characteristics of each approach is essential for making informed decisions and successfully leveraging data to drive business value. As data continues to grow in volume and complexity, adopting the right data management strategy is crucial for staying competitive and achieving business success. The data mesh offers a decentralized approach, the data lake provides a centralized repository, and the data fabric delivers a unified view across disparate sources. Carefully evaluating these options will pave the way for a robust and effective data strategy.
