CTEM Security: A Comprehensive Guide to Cyber Threat Exposure Management
In today’s rapidly evolving threat landscape, organizations face an unprecedented number of cyber risks. Traditional security approaches often fall short in effectively managing and mitigating these exposures. Cyber Threat Exposure Management (CTEM) has emerged as a proactive and strategic framework designed to address this challenge. This article provides a comprehensive overview of CTEM security, exploring its principles, benefits, implementation strategies, and its crucial role in building a resilient cybersecurity posture. Understanding CTEM is vital for organizations looking to stay ahead of emerging threats and protect their critical assets.
Understanding Cyber Threat Exposure Management (CTEM)
Cyber Threat Exposure Management (CTEM) is a systematic approach to identifying, assessing, and mitigating an organization’s exposure to cyber threats. It goes beyond traditional vulnerability management by encompassing a broader range of risks, including misconfigurations, outdated software, exposed credentials, and human vulnerabilities. CTEM provides a holistic view of an organization’s security posture, enabling security teams to prioritize and remediate the most critical exposures effectively. CTEM is not just about fixing vulnerabilities; it’s about understanding the business context and potential impact of each exposure.
Key Principles of CTEM
- Visibility: Gaining comprehensive visibility into all assets, configurations, and potential vulnerabilities across the organization’s IT environment. This includes on-premises systems, cloud infrastructure, and remote endpoints.
- Prioritization: Focusing on the exposures that pose the greatest risk to the organization, based on factors such as exploitability, potential impact, and business criticality.
- Remediation: Implementing timely and effective remediation measures to address identified exposures, including patching, configuration changes, and security awareness training.
- Continuous Monitoring: Continuously monitoring the organization’s threat landscape and security posture to identify new exposures and track the effectiveness of remediation efforts.
- Automation: Leveraging automation tools and technologies to streamline CTEM processes, improve efficiency, and reduce the risk of human error.
Benefits of Implementing CTEM Security
Implementing a CTEM security program offers numerous benefits for organizations, including:
- Reduced Attack Surface: By proactively identifying and mitigating exposures, CTEM helps to reduce the organization’s attack surface, making it more difficult for attackers to gain access.
- Improved Risk Management: CTEM provides a clear understanding of the organization’s risk profile, enabling security teams to make informed decisions about resource allocation and risk mitigation strategies.
- Enhanced Compliance: CTEM helps organizations to meet regulatory requirements and industry standards by demonstrating a proactive approach to security risk management.
- Faster Incident Response: By continuously monitoring the threat landscape, CTEM enables organizations to detect and respond to security incidents more quickly and effectively.
- Increased Business Resilience: By reducing the likelihood and impact of cyberattacks, CTEM helps to improve the organization’s overall business resilience.
Implementing a CTEM Program: A Step-by-Step Guide
Implementing a successful CTEM program requires a structured and methodical approach. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help organizations get started:
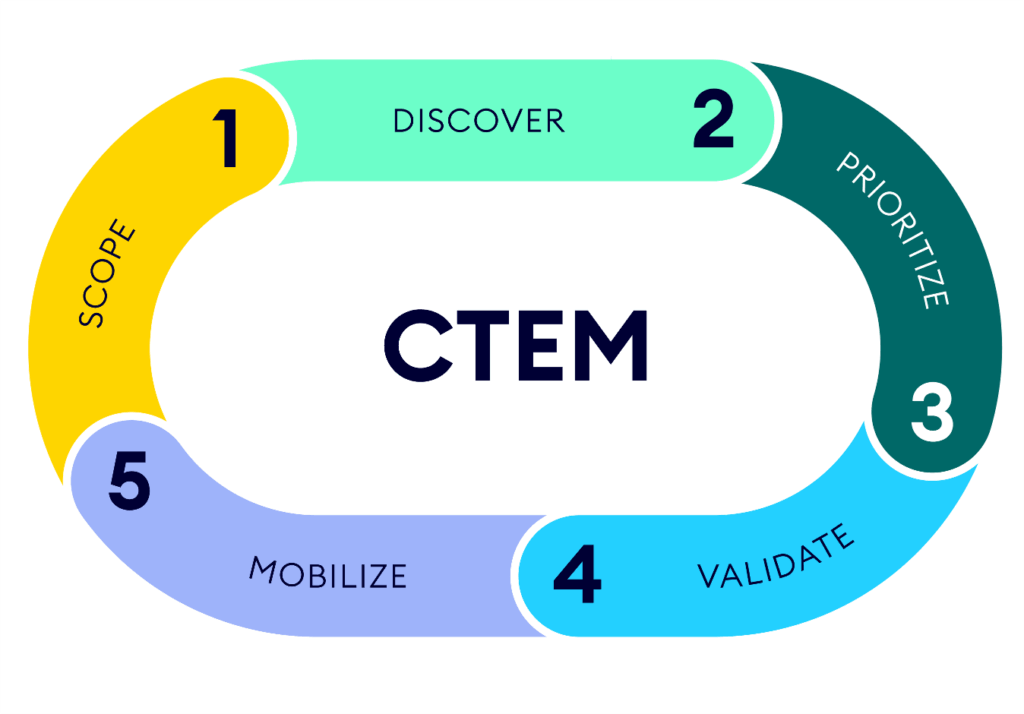
Step 1: Define Scope and Objectives
Clearly define the scope of the CTEM program, including the assets, systems, and processes that will be included. Establish specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) objectives for the program. For example, you might aim to reduce the number of critical vulnerabilities by a certain percentage within a specific timeframe. The scope of your CTEM security efforts should align with your business priorities.
Step 2: Assess Current Security Posture
Conduct a thorough assessment of the organization’s current security posture to identify existing vulnerabilities, misconfigurations, and other exposures. This may involve vulnerability scanning, penetration testing, and security audits. Understand your current state before planning future improvements to your CTEM security.
Step 3: Prioritize Exposures
Prioritize identified exposures based on factors such as exploitability, potential impact, and business criticality. Use a risk-based approach to focus on the exposures that pose the greatest threat to the organization. Consider using a common vulnerability scoring system (CVSS) to help prioritize vulnerabilities. Remember that effective CTEM security is about managing risk strategically.
Step 4: Develop Remediation Plans
Develop detailed remediation plans for each prioritized exposure, outlining the steps required to address the issue and the responsible parties. Ensure that remediation plans are aligned with the organization’s security policies and procedures. For example, this could include patching systems, updating configurations, or implementing new security controls. Remediation is a critical component of CTEM security.
Step 5: Implement Remediation Measures
Implement the remediation measures outlined in the remediation plans, ensuring that changes are properly tested and documented. Use change management processes to minimize the risk of disruption to business operations. Verify that the remediation measures have effectively addressed the identified exposures. This practical application is core to CTEM security.
Step 6: Continuously Monitor and Improve
Continuously monitor the organization’s threat landscape and security posture to identify new exposures and track the effectiveness of remediation efforts. Use security information and event management (SIEM) systems, threat intelligence feeds, and other tools to stay informed about emerging threats. Regularly review and update the CTEM program to ensure that it remains effective and aligned with the organization’s evolving needs. Continuous improvement is vital for maintaining a robust CTEM security posture.
Tools and Technologies for CTEM
A variety of tools and technologies can support CTEM efforts, including:
- Vulnerability Scanners: Automate the process of identifying vulnerabilities in systems and applications.
- Penetration Testing Tools: Simulate real-world attacks to identify weaknesses in the organization’s security defenses.
- Configuration Management Tools: Help to ensure that systems are configured securely and in compliance with security policies.
- Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) Systems: Collect and analyze security logs from various sources to detect suspicious activity and potential security incidents.
- Threat Intelligence Feeds: Provide up-to-date information about emerging threats and vulnerabilities.
- Attack Surface Management (ASM) Tools: Discover and monitor an organization’s external attack surface, identifying potential entry points for attackers.
CTEM vs. Traditional Vulnerability Management
While vulnerability management is an important component of CTEM, it is not the same thing. CTEM takes a broader and more proactive approach to managing cyber risk. Vulnerability management typically focuses on identifying and remediating known vulnerabilities in software and systems. CTEM, on the other hand, encompasses a wider range of exposures, including misconfigurations, exposed credentials, and human vulnerabilities. CTEM also emphasizes the importance of prioritization and risk-based decision-making. The shift towards CTEM security recognizes the limitations of traditional, reactive vulnerability management.
The Future of CTEM Security
As the threat landscape continues to evolve, CTEM will become increasingly important for organizations of all sizes. The rise of cloud computing, the Internet of Things (IoT), and remote work has expanded the attack surface and created new opportunities for attackers. CTEM provides a framework for managing these emerging risks and building a more resilient cybersecurity posture. The future of CTEM security will likely involve greater automation, integration with other security tools, and a stronger focus on threat intelligence. Organizations must embrace CTEM to effectively manage their cyber risk and protect their critical assets. [See also: Vulnerability Management Best Practices]
Conclusion
Cyber Threat Exposure Management (CTEM) is a critical framework for organizations seeking to proactively manage and mitigate their cyber risk. By implementing a CTEM program, organizations can reduce their attack surface, improve their risk management capabilities, enhance their compliance posture, and increase their overall business resilience. As the threat landscape continues to evolve, CTEM will become an increasingly essential component of a comprehensive cybersecurity strategy. Embracing CTEM security is no longer optional; it’s a necessity for staying ahead of emerging threats and protecting your organization’s future.
