Connecting Computers on a Network: A Comprehensive Guide
In today’s interconnected world, connecting computers on a network is a fundamental skill, whether for home, office, or large-scale enterprise environments. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of the process, covering various methods, essential hardware, and crucial security considerations. Understanding how to connect computers on a network is essential for sharing resources, facilitating communication, and enhancing productivity. This article will walk you through the steps, from basic setups to more complex network configurations, ensuring you have the knowledge to establish a robust and secure network.
Understanding Network Basics
Before diving into the practical steps of connecting computers on a network, it’s crucial to grasp the foundational concepts. A network, at its core, is a collection of devices (typically computers, but also including printers, servers, and other peripherals) that are interconnected to share data and resources. These resources can include files, printers, internet access, and even specialized applications.
Types of Networks
- Local Area Network (LAN): A LAN connects devices within a limited area, such as a home, office, or school. LANs are typically characterized by high-speed data transfer rates and relatively low cost.
- Wide Area Network (WAN): A WAN spans a large geographical area, often connecting multiple LANs together. The internet is the most prominent example of a WAN.
- Wireless Local Area Network (WLAN): A WLAN uses wireless technology, such as Wi-Fi, to connect devices within a local area. This offers greater flexibility and mobility compared to traditional wired LANs.
Essential Hardware Components
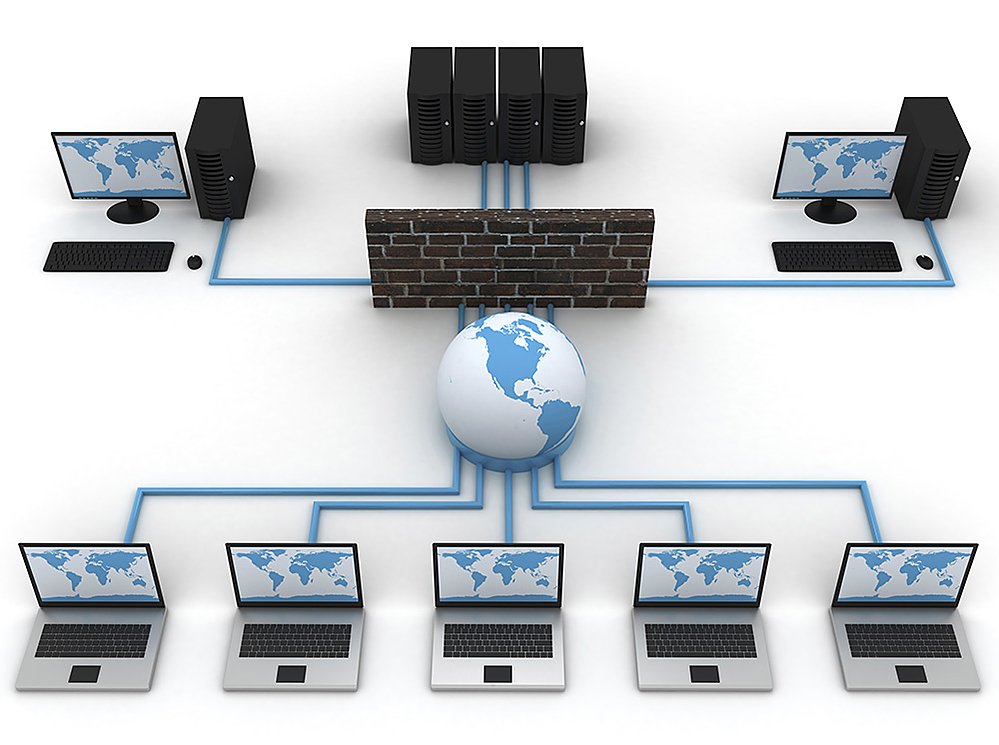
To connect computers on a network, several hardware components are required:
- Network Interface Card (NIC): Every computer needs a NIC to connect to the network. Modern computers usually have a built-in NIC, either wired (Ethernet) or wireless (Wi-Fi).
- Router: A router acts as a gateway, directing data traffic between your local network and the internet. It also assigns IP addresses to devices on your network.
- Switch: A switch connects multiple devices within a LAN, enabling them to communicate with each other. Switches are more efficient than hubs, as they direct traffic only to the intended recipient.
- Cables: For wired networks, Ethernet cables (typically Cat5e or Cat6) are used to connect devices to the router or switch.
Step-by-Step Guide to Connecting Computers on a Network
Now, let’s walk through the process of connecting computers on a network, focusing on both wired and wireless setups.
Wired Network Setup
- Connect the Router: Plug the router into a power outlet and connect it to your internet modem using an Ethernet cable.
- Connect the Switch (Optional): If you need to connect more devices than your router has ports, connect a switch to one of the router’s LAN ports.
- Connect Computers: Use Ethernet cables to connect each computer to the router or switch.
- Configure IP Addresses: Most routers will automatically assign IP addresses to connected devices using DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol). Ensure DHCP is enabled in your router settings. If you prefer static IP addresses, you’ll need to configure them manually on each computer.
- Test the Connection: Open a web browser on each computer and try accessing a website to verify internet connectivity. You can also use the ‘ping’ command in the command prompt to test connectivity between computers on the network.
Wireless Network Setup
- Configure the Router: Access your router’s configuration interface through a web browser. The default IP address and login credentials are usually found on the router’s label or in the user manual.
- Set Up Wi-Fi: Enable Wi-Fi on the router and configure the network name (SSID) and password (WPA2 or WPA3 encryption is recommended for security).
- Connect Computers: On each computer, select the Wi-Fi network from the available networks and enter the password.
- Test the Connection: Similar to the wired setup, test internet connectivity and connectivity between computers on the network.
Securing Your Network
Security is a critical aspect of connecting computers on a network. A poorly secured network is vulnerable to various threats, including unauthorized access, data breaches, and malware infections. Here are some essential security measures:
Firewall
A firewall acts as a barrier between your network and the outside world, blocking unauthorized access attempts. Most routers have built-in firewalls that should be enabled. Ensure your firewall is configured to block incoming connections from untrusted sources.
Strong Passwords
Use strong, unique passwords for your router’s administrative interface and your Wi-Fi network. Avoid using default passwords, as they are easily exploited by attackers. A strong password should be at least 12 characters long and include a mix of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and symbols.
Network Encryption
For wireless networks, use WPA2 or WPA3 encryption to protect your data from eavesdropping. WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy) is an older encryption standard that is no longer considered secure.
Regular Updates
Keep your router’s firmware and your computers’ operating systems and software up to date. Software updates often include security patches that address known vulnerabilities. Regularly check for updates and install them promptly.
Guest Network
If you frequently have guests who need internet access, consider setting up a guest network. A guest network provides internet access without granting access to your main network, protecting your sensitive data.
Troubleshooting Common Network Issues
Even with careful planning and setup, network issues can arise. Here are some common problems and their solutions:
No Internet Connection
- Check Cables: Ensure all cables are securely connected to the router, modem, and computers.
- Restart Devices: Restart the router, modem, and computers. This often resolves temporary glitches.
- Check IP Address: Verify that your computer has a valid IP address. If not, try releasing and renewing the IP address.
- Contact ISP: If the problem persists, contact your internet service provider (ISP) to check for outages or other issues.
Slow Network Speed
- Check Wi-Fi Signal Strength: Ensure your computer has a strong Wi-Fi signal. Weak signal strength can significantly impact network speed.
- Limit Bandwidth Usage: Close unnecessary applications that may be consuming bandwidth.
- Upgrade Hardware: If your hardware is outdated, consider upgrading to newer devices that support faster network speeds.
- Run a Speed Test: Use an online speed test tool to measure your network speed and compare it to your ISP’s advertised speed.
Connectivity Issues Between Computers
- Check Firewall Settings: Ensure your firewall is not blocking communication between computers on the network.
- Verify Network Discovery: Enable network discovery in your operating system settings to allow computers to see each other on the network.
- Check Workgroup/Domain: Ensure all computers are on the same workgroup or domain.
Advanced Networking Concepts
For more advanced users, understanding these concepts can further optimize your network:
Network Address Translation (NAT)
NAT allows multiple devices on a private network to share a single public IP address. This is essential for connecting to the internet, as most home and small business networks only have one public IP address assigned by their ISP.
Port Forwarding
Port forwarding allows specific traffic from the internet to be directed to a specific device on your network. This is often used for hosting game servers or accessing internal resources from outside the network.
Virtual Private Network (VPN)
A VPN creates a secure, encrypted connection between your computer and a remote server. This protects your data from eavesdropping and allows you to bypass geographical restrictions. [See also: VPN Security Protocols Explained]
Quality of Service (QoS)
QoS allows you to prioritize certain types of network traffic, ensuring that critical applications (such as video conferencing or online gaming) receive sufficient bandwidth. This can improve the performance of these applications, especially during periods of high network usage.
Conclusion
Connecting computers on a network is a crucial skill in today’s digital landscape. By following the steps outlined in this guide, you can establish a robust and secure network for your home or office. Remember to prioritize security and regularly troubleshoot any issues that may arise. With a solid understanding of networking principles, you can effectively share resources, facilitate communication, and enhance productivity. Whether you’re setting up a simple home network or a complex business infrastructure, the fundamentals of connecting computers on a network remain the same. Continually learning and adapting to new technologies will ensure your network remains efficient and secure for years to come. The ability to connect computers on a network effectively is a valuable asset in our increasingly connected world. This guide should provide a solid foundation for anyone looking to build or maintain a network, regardless of their technical expertise. Remember to always prioritize security when connecting computers on a network. The benefits of a well-connected and secure network are numerous, ranging from increased productivity to enhanced collaboration. The process of connecting computers on a network may seem daunting at first, but with careful planning and execution, it can be a rewarding experience. By understanding the principles and following the best practices outlined in this guide, you can ensure a smooth and successful network setup. The world of connecting computers on a network is constantly evolving, so staying informed about the latest technologies and trends is essential for maintaining a cutting-edge network. From wired connections to wireless solutions, the options for connecting computers on a network are vast and varied. Choose the solution that best meets your needs and budget, and always remember to prioritize security and performance. The future of connecting computers on a network is bright, with new technologies and innovations constantly emerging. By staying informed and embracing these advancements, you can ensure that your network remains efficient, secure, and ready to meet the challenges of tomorrow.
