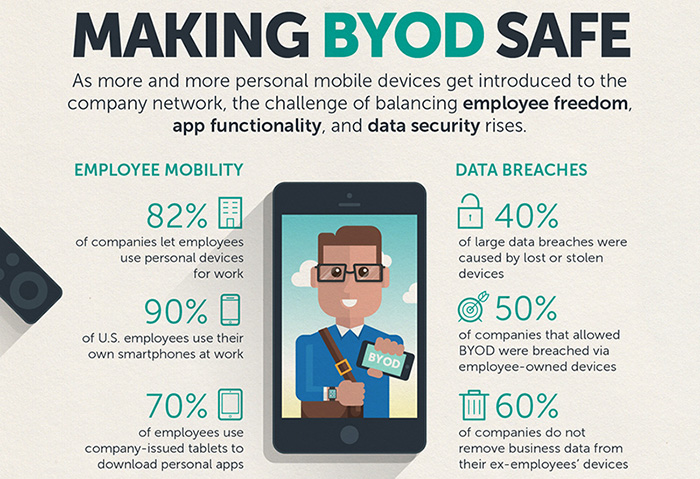
BYOD Application: Navigating the Benefits and Challenges of Bring Your Own Device
In today’s rapidly evolving digital landscape, the Bring Your Own Device (BYOD) application model has become increasingly prevalent across various industries. This approach allows employees to use their personal devices, such as smartphones, tablets, and laptops, for work-related tasks. While offering numerous advantages, including cost savings and increased productivity, the implementation of a BYOD application also presents significant challenges related to security, privacy, and IT management. This article delves into the multifaceted aspects of BYOD application, exploring its benefits, drawbacks, and best practices for successful implementation.
Understanding the BYOD Application Landscape
The BYOD application concept emerged as a response to the growing consumerization of IT. Employees are increasingly comfortable and proficient with their personal devices, and they often prefer using them over company-issued equipment. This preference stems from familiarity, customization options, and the ability to use a single device for both personal and professional activities. A well-designed BYOD application strategy can capitalize on these preferences, leading to a more engaged and productive workforce.
The Rise of BYOD Application
Several factors have contributed to the rise of BYOD application. Firstly, the proliferation of mobile devices and high-speed internet access has made it easier for employees to work remotely and access company resources from anywhere. Secondly, the increasing sophistication of mobile device management (MDM) and mobile application management (MAM) solutions has provided organizations with the tools to securely manage and control employee-owned devices. Finally, the potential cost savings associated with BYOD application – by reducing the need to purchase and maintain company-issued devices – have made it an attractive option for many businesses.
Benefits of Implementing a BYOD Application
The advantages of adopting a BYOD application approach are compelling and can significantly impact an organization’s efficiency and bottom line.
- Cost Savings: One of the most significant benefits is the reduction in hardware costs. Companies no longer need to purchase and maintain devices for every employee. Employees bear the cost of their devices, and the organization can focus its resources on other critical areas.
- Increased Productivity: Employees are generally more comfortable and familiar with their personal devices, leading to increased productivity. They can work from anywhere, at any time, and access company resources seamlessly.
- Improved Employee Satisfaction: Allowing employees to use their preferred devices can boost morale and job satisfaction. It gives them a sense of ownership and control over their work environment.
- Reduced IT Burden: By shifting the responsibility of device maintenance to employees, the IT department can focus on more strategic initiatives. However, this requires robust MDM and MAM solutions to ensure security and compliance.
- Access to Latest Technology: Employees often upgrade their devices more frequently than companies would typically replace their equipment, ensuring access to the latest technology and features.
Challenges and Risks Associated with BYOD Application
While the benefits of BYOD application are substantial, organizations must also be aware of the potential challenges and risks involved.
- Security Risks: One of the most significant concerns is the increased security risk. Personal devices are often less secure than company-issued devices, making them vulnerable to malware, viruses, and data breaches.
- Data Privacy: Ensuring the privacy of company data on personal devices is crucial. Organizations must implement policies and technologies to prevent unauthorized access, data leakage, and compliance violations.
- IT Management Complexity: Managing a diverse range of devices and operating systems can be challenging for the IT department. Compatibility issues, software updates, and troubleshooting can consume significant resources.
- Compliance Issues: Organizations must comply with various regulations, such as GDPR and HIPAA, when handling sensitive data on personal devices. A well-defined BYOD application policy is essential to ensure compliance.
- Support Costs: While BYOD application aims to reduce IT burden, providing support for a wide range of devices can still incur costs. Clear guidelines and self-service resources are necessary to minimize support requests.
Best Practices for Implementing a Successful BYOD Application
To mitigate the risks and maximize the benefits of BYOD application, organizations should follow these best practices:
- Develop a Comprehensive BYOD Application Policy: A clear and comprehensive policy is the foundation of a successful BYOD application program. The policy should outline the rules, responsibilities, and expectations for employees using personal devices for work.
- Implement Mobile Device Management (MDM) Solutions: MDM solutions provide the tools to remotely manage and secure mobile devices. They enable organizations to enforce security policies, remotely wipe devices, and track device usage.
- Utilize Mobile Application Management (MAM) Solutions: MAM solutions focus on managing and securing specific applications on personal devices. They allow organizations to control access to sensitive data and prevent data leakage.
- Enforce Strong Security Measures: Implement strong passwords, encryption, and multi-factor authentication to protect data on personal devices. Regularly update security software and patches to address vulnerabilities.
- Provide Employee Training: Educate employees about the risks associated with BYOD application and how to protect their devices and company data. Training should cover topics such as password security, phishing awareness, and data privacy.
- Establish Clear Support Guidelines: Define the level of support that the IT department will provide for personal devices. Create self-service resources and FAQs to address common issues.
- Regularly Review and Update the BYOD Application Policy: The BYOD application landscape is constantly evolving. Organizations should regularly review and update their policies to address new threats and technologies.
- Consider Containerization: Containerization creates a separate, secure environment on the personal device for work-related applications and data, isolating it from personal data and applications.
- Implement Data Loss Prevention (DLP) Tools: DLP tools can help prevent sensitive data from leaving the organization’s control, even on personal devices.
BYOD Application Policy Essentials
A robust BYOD application policy should include several key elements to ensure clarity and compliance:
- Device Eligibility: Specify which types of devices are eligible for the BYOD application program.
- Security Requirements: Outline the security measures that employees must implement on their devices, such as passwords, encryption, and antivirus software.
- Acceptable Use Policy: Define the acceptable use of personal devices for work-related activities.
- Data Ownership: Clarify the ownership of data stored on personal devices.
- Privacy Policy: Explain how the organization will protect the privacy of employees’ personal data.
- Support Guidelines: Detail the level of support that the IT department will provide for personal devices.
- Termination Clause: Outline the procedures for removing company data from personal devices when an employee leaves the organization.
The Future of BYOD Application
The BYOD application model is expected to continue to evolve as technology advances and the workforce becomes increasingly mobile. Emerging trends, such as the Internet of Things (IoT) and artificial intelligence (AI), will likely have a significant impact on the future of BYOD application. Organizations will need to adapt their policies and technologies to address these new challenges and opportunities.
One potential trend is the rise of “choose your own device” (CYOD) programs, where employees can select from a pre-approved list of devices provided by the company. This approach offers a compromise between BYOD and company-issued devices, providing employees with more choice while maintaining a higher level of security and control.
Another trend is the increasing integration of BYOD application with cloud-based services. Cloud computing provides a flexible and scalable platform for accessing and managing company resources from personal devices. Organizations can leverage cloud-based MDM and MAM solutions to simplify BYOD application management and enhance security.
Conclusion
The BYOD application model offers significant benefits for organizations seeking to reduce costs, increase productivity, and improve employee satisfaction. However, successful implementation requires careful planning, a comprehensive policy, and robust security measures. By following the best practices outlined in this article, organizations can navigate the challenges of BYOD application and unlock its full potential. A well-managed BYOD application program not only empowers employees but also enhances the overall security and efficiency of the organization. Understanding the nuances of BYOD application, from its inception to its future trends, is crucial for any organization aiming to stay competitive in today’s dynamic business environment. Furthermore, the continuous evolution of [See also: Mobile Security Best Practices] and [See also: Enterprise Mobility Management] necessitates a proactive approach to BYOD application, ensuring that policies and technologies remain aligned with the latest advancements and security threats.
