BYOD Access Control: Securing Your Network in a Bring Your Own Device World
The Bring Your Own Device (BYOD) trend has revolutionized the modern workplace, offering employees flexibility and convenience. However, it also presents significant security challenges for IT departments. Managing access to sensitive data and resources from a diverse range of personal devices requires a robust BYOD access control strategy. This article delves into the intricacies of BYOD access control, exploring its benefits, challenges, and best practices for implementation.
Understanding BYOD and Its Security Implications
BYOD refers to the practice of allowing employees to use their personal devices, such as smartphones, tablets, and laptops, for work-related purposes. This trend has gained popularity due to its potential to increase productivity, reduce costs, and improve employee satisfaction. However, the use of personal devices introduces several security risks that must be addressed.
The Risks Associated with BYOD
- Malware and Viruses: Personal devices are often less secure than company-issued devices, making them more vulnerable to malware and viruses.
- Data Breaches: If a personal device is lost or stolen, sensitive company data could be compromised.
- Unauthorized Access: Employees may inadvertently grant unauthorized access to company resources through unsecured apps or networks.
- Lack of Control: IT departments have limited control over the security settings and software updates on personal devices.
- Compliance Issues: BYOD can complicate compliance with industry regulations such as HIPAA and GDPR.
What is BYOD Access Control?
BYOD access control is the process of managing and securing access to company resources from personal devices. It involves implementing policies, procedures, and technologies to ensure that only authorized users and devices can access sensitive data and applications. Effective BYOD access control is crucial for mitigating the security risks associated with BYOD.
Key Components of BYOD Access Control
- Device Enrollment: Registering personal devices with the company’s IT system.
- Device Authentication: Verifying the identity of users and devices before granting access.
- Policy Enforcement: Implementing security policies to ensure that devices meet minimum security standards.
- Access Management: Controlling which resources users and devices can access.
- Data Encryption: Protecting sensitive data by encrypting it both in transit and at rest.
- Mobile Device Management (MDM): Using software to manage and secure mobile devices.
- Mobile Application Management (MAM): Managing and securing mobile applications.
- Network Access Control (NAC): Controlling access to the network based on device security posture.
Benefits of Implementing BYOD Access Control
Implementing a robust BYOD access control strategy offers several benefits, including:
- Enhanced Security: Protecting sensitive data and resources from unauthorized access.
- Improved Compliance: Meeting industry regulations and compliance requirements.
- Reduced Risk: Minimizing the risk of data breaches and security incidents.
- Increased Productivity: Enabling employees to work from anywhere, at any time, on their preferred devices.
- Cost Savings: Reducing the need for company-issued devices.
- Better Visibility: Gaining greater visibility into the devices and applications being used on the network.
- Simplified Management: Streamlining the management of mobile devices and applications.
Challenges of Implementing BYOD Access Control
While BYOD access control offers numerous benefits, it also presents several challenges:
- Device Diversity: Supporting a wide range of devices with different operating systems and security capabilities.
- User Privacy: Balancing security with employee privacy concerns.
- Complexity: Implementing and managing BYOD access control can be complex and time-consuming.
- Cost: Implementing BYOD access control solutions can be expensive.
- User Adoption: Encouraging employees to adopt and adhere to security policies.
- Integration: Integrating BYOD access control solutions with existing IT infrastructure.
- Security Threats: Staying ahead of evolving security threats.
Best Practices for BYOD Access Control
To effectively implement BYOD access control, organizations should follow these best practices:
Develop a Comprehensive BYOD Policy
A well-defined BYOD policy is essential for outlining the rules and guidelines for using personal devices for work-related purposes. The policy should address issues such as device enrollment, security requirements, acceptable use, and data ownership. [See also: Creating a Robust BYOD Policy]
Implement Strong Authentication Methods
Strong authentication methods, such as multi-factor authentication (MFA), should be used to verify the identity of users and devices before granting access to company resources. MFA adds an extra layer of security by requiring users to provide multiple forms of identification. This helps prevent unauthorized access even if a password is compromised.
Use Mobile Device Management (MDM) Software
MDM software provides a centralized platform for managing and securing mobile devices. MDM solutions can be used to enforce security policies, remotely wipe devices, and track device location. They also allow IT departments to manage applications and data on personal devices.
Implement Mobile Application Management (MAM)
MAM focuses on managing and securing the applications used on personal devices. MAM solutions allow IT departments to control which applications can be installed on devices, enforce security policies for specific applications, and remotely wipe application data. This is especially useful for organizations concerned about data leakage through unapproved applications.
Use Network Access Control (NAC)
NAC solutions control access to the network based on the security posture of devices. NAC can be used to ensure that devices meet minimum security requirements, such as having up-to-date antivirus software, before granting access to the network. This helps prevent infected devices from spreading malware throughout the network.
Encrypt Sensitive Data
Data encryption is essential for protecting sensitive data both in transit and at rest. Encryption scrambles data so that it is unreadable to unauthorized users. Organizations should encrypt data stored on personal devices and data transmitted over the network. [See also: Data Encryption Best Practices]
Regularly Monitor and Audit Devices
IT departments should regularly monitor and audit devices to ensure that they are complying with security policies. This includes monitoring device activity, tracking security incidents, and conducting regular security audits. Monitoring and auditing can help identify and address potential security vulnerabilities.
Provide Security Awareness Training
Employees should be provided with security awareness training to educate them about the risks associated with BYOD and how to protect their devices and company data. Training should cover topics such as password security, phishing awareness, and malware prevention. A well-informed workforce is a crucial component of a strong BYOD access control strategy.
Implement Data Loss Prevention (DLP)
DLP solutions help prevent sensitive data from leaving the organization’s control. DLP can monitor data in transit, data at rest, and data in use to detect and prevent data breaches. DLP can be used to block sensitive data from being copied, printed, or emailed from personal devices.
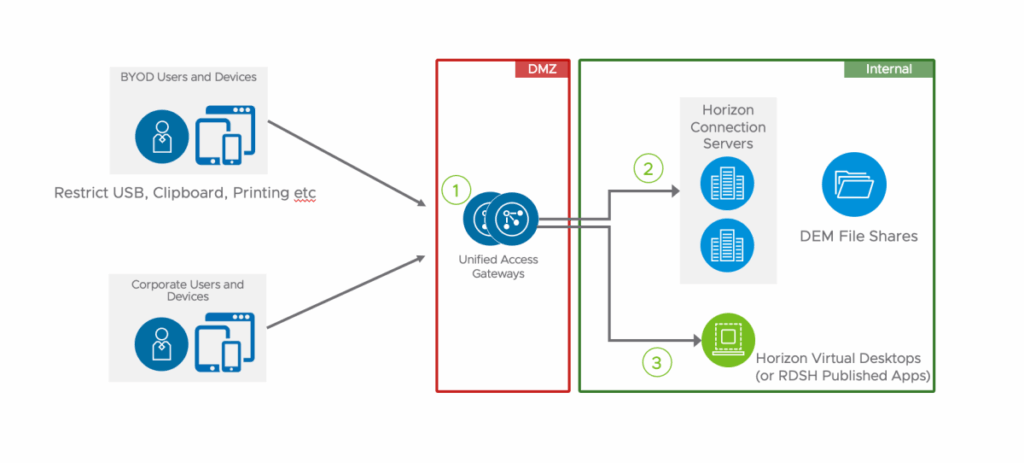
Use Virtual Desktop Infrastructure (VDI)
VDI allows users to access a virtual desktop environment from their personal devices. This provides a secure way to access company resources without storing sensitive data on the device itself. VDI can also simplify management and reduce the risk of data breaches.
Choosing the Right BYOD Access Control Solution
Selecting the right BYOD access control solution is crucial for ensuring the security and productivity of your organization. When evaluating solutions, consider the following factors:
- Scalability: The solution should be able to scale to meet the needs of your organization as it grows.
- Compatibility: The solution should be compatible with a wide range of devices and operating systems.
- Integration: The solution should integrate seamlessly with your existing IT infrastructure.
- Ease of Use: The solution should be easy to use and manage.
- Security Features: The solution should offer a comprehensive set of security features.
- Cost: The solution should be cost-effective and provide a good return on investment.
- Vendor Reputation: Choose a vendor with a strong reputation and a proven track record.
The Future of BYOD Access Control
The future of BYOD access control is likely to be shaped by several key trends, including:
- Increased Automation: Automation will play a greater role in managing and securing mobile devices.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI will be used to detect and prevent security threats.
- Zero Trust Security: Zero trust security models will become more prevalent.
- Cloud-Based Solutions: Cloud-based BYOD access control solutions will become more popular.
- Enhanced User Experience: BYOD access control solutions will focus on providing a seamless and user-friendly experience.
Conclusion
BYOD access control is essential for securing your network in a Bring Your Own Device world. By implementing a robust BYOD access control strategy, organizations can mitigate the security risks associated with BYOD while still enabling employees to work from their preferred devices. By following the best practices outlined in this article, organizations can create a secure and productive BYOD environment.
The key to successful BYOD access control lies in a layered approach, combining strong policies, robust technologies, and ongoing user education. As the BYOD landscape continues to evolve, organizations must adapt their BYOD access control strategies to stay ahead of emerging security threats. Ensuring the security of your data and network requires a proactive and comprehensive approach to BYOD access control.
