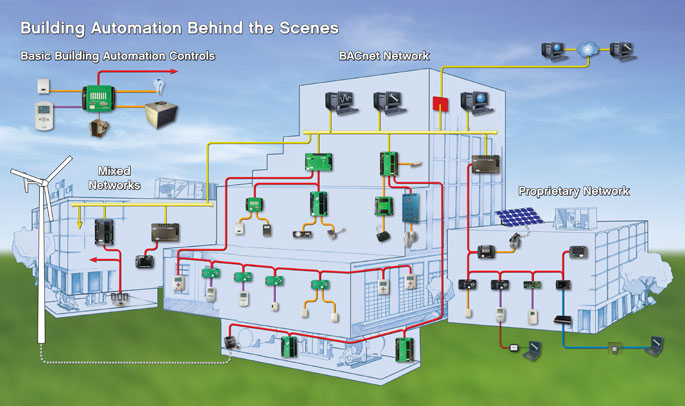
Building Automation and Control Systems: Optimizing Efficiency and Sustainability
In today’s world, where energy efficiency and sustainable practices are paramount, building automation and control systems (BACS) have emerged as essential components of modern infrastructure. These systems are not merely technological advancements; they represent a fundamental shift in how we manage and interact with our built environment. From sprawling commercial complexes to compact residential dwellings, building automation and control systems are revolutionizing the way buildings operate, offering unprecedented levels of control, efficiency, and sustainability. This article delves into the intricacies of building automation and control systems, exploring their functionalities, benefits, challenges, and future trends.
Understanding Building Automation and Control Systems
At its core, a building automation and control system is an integrated network of hardware and software designed to monitor, control, and optimize various building functions. These functions typically include:
- Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning (HVAC): Regulating temperature, airflow, and humidity to maintain optimal comfort levels.
- Lighting: Controlling lighting systems to maximize energy efficiency and create comfortable environments.
- Security: Monitoring and controlling access to the building, detecting intrusions, and managing surveillance systems.
- Fire Safety: Detecting and responding to fire emergencies, including smoke detection, sprinkler systems, and alarm management.
- Energy Management: Monitoring and optimizing energy consumption across all building systems.
The components of a building automation and control system typically include sensors, controllers, actuators, and a central management system. Sensors collect data on various parameters, such as temperature, humidity, and occupancy. Controllers process this data and make decisions based on pre-programmed algorithms or real-time conditions. Actuators then carry out these decisions by adjusting HVAC systems, lighting levels, or other building functions. The central management system provides a user interface for monitoring and controlling the entire system.
Benefits of Implementing Building Automation and Control Systems
The adoption of building automation and control systems offers a multitude of benefits, impacting operational efficiency, energy consumption, and occupant comfort. These benefits include:
Enhanced Energy Efficiency
One of the most significant advantages of building automation and control systems is their ability to optimize energy consumption. By continuously monitoring and adjusting building systems based on real-time conditions, these systems can significantly reduce energy waste. For example, HVAC systems can be adjusted based on occupancy levels, lighting can be dimmed or turned off in unoccupied areas, and energy-intensive equipment can be scheduled to operate during off-peak hours. [See also: Smart HVAC Systems for Commercial Buildings]
Improved Occupant Comfort
Building automation and control systems can create more comfortable and productive environments for occupants. By maintaining optimal temperature, humidity, and lighting levels, these systems can enhance employee well-being, reduce absenteeism, and improve overall job satisfaction. Furthermore, personalized control options can allow occupants to adjust their immediate environment to suit their individual preferences.
Reduced Operational Costs
While the initial investment in a building automation and control system may seem substantial, the long-term operational cost savings can be significant. By reducing energy consumption, minimizing maintenance requirements, and optimizing equipment performance, these systems can generate a substantial return on investment over their lifespan. Moreover, predictive maintenance capabilities can help prevent costly equipment failures and downtime.
Enhanced Security
Building automation and control systems can integrate with security systems to provide enhanced protection for buildings and their occupants. Access control systems can restrict entry to authorized personnel, surveillance systems can monitor activity throughout the building, and alarm systems can alert authorities to potential threats. Furthermore, these systems can be integrated with fire safety systems to ensure a rapid and coordinated response to fire emergencies.
Sustainable Building Practices
The implementation of building automation and control systems aligns with sustainable building practices and can contribute to achieving green building certifications, such as LEED (Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design). By reducing energy consumption, minimizing waste, and promoting responsible resource management, these systems can help buildings meet environmental performance standards and reduce their carbon footprint. [See also: Green Building Technologies and Sustainability]
Challenges in Implementing Building Automation and Control Systems
Despite the numerous benefits, the implementation of building automation and control systems can present several challenges. These challenges include:
High Initial Investment
The initial cost of purchasing and installing a building automation and control system can be a significant barrier for some building owners. The cost can vary depending on the size and complexity of the building, the specific features and functionalities required, and the level of integration with existing building systems. However, it’s important to consider the long-term cost savings and return on investment when evaluating the initial investment.
Integration Complexity
Integrating a building automation and control system with existing building systems can be a complex and challenging process. Different systems may use different communication protocols and data formats, requiring specialized expertise to ensure seamless integration. Furthermore, legacy systems may need to be upgraded or replaced to ensure compatibility with the new system.
Cybersecurity Risks
As building automation and control systems become increasingly connected to the internet, they become more vulnerable to cybersecurity threats. Hackers can potentially gain access to the system and manipulate building functions, disrupt operations, or steal sensitive data. Therefore, it is crucial to implement robust cybersecurity measures, such as firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and regular security audits, to protect the system from cyberattacks. [See also: Cybersecurity for Smart Buildings]
Lack of Expertise
The successful implementation and operation of a building automation and control system require specialized expertise in areas such as control systems engineering, network communication, and cybersecurity. Many building owners may lack the in-house expertise to manage these systems effectively, requiring them to rely on external consultants or service providers. This can add to the overall cost of the system and create a dependency on external resources.
Future Trends in Building Automation and Control Systems
The field of building automation and control systems is constantly evolving, driven by technological advancements and changing market demands. Some of the key trends shaping the future of this industry include:
Internet of Things (IoT) Integration
The integration of building automation and control systems with the Internet of Things (IoT) is enabling new levels of connectivity and intelligence. IoT devices, such as smart sensors, actuators, and wearables, can collect and transmit data to the system, providing a more comprehensive view of building operations. This data can be used to optimize building performance, improve occupant comfort, and enhance security.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML)
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) are being increasingly used to analyze data collected by building automation and control systems and to make intelligent decisions. AI and ML algorithms can identify patterns and anomalies in building operations, predict equipment failures, and optimize energy consumption. This can lead to significant improvements in building performance and efficiency.
Cloud-Based Solutions
Cloud-based building automation and control systems are becoming increasingly popular due to their scalability, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness. Cloud-based solutions allow building owners to access and manage their systems remotely from any location. They also offer improved data storage, security, and backup capabilities. [See also: Cloud Computing for Building Management]
Wireless Communication Technologies
Wireless communication technologies, such as Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, and Zigbee, are making it easier and more cost-effective to deploy building automation and control systems. Wireless sensors and actuators can be easily installed without the need for extensive wiring, reducing installation costs and minimizing disruption to building operations.
Conclusion
Building automation and control systems are transforming the way we manage and interact with our built environment. By optimizing energy consumption, improving occupant comfort, enhancing security, and promoting sustainable practices, these systems are contributing to a more efficient, comfortable, and sustainable future. While there are challenges associated with their implementation, the benefits far outweigh the costs. As technology continues to evolve, building automation and control systems will become even more sophisticated and integrated, playing an increasingly important role in shaping the future of the built environment.
