Botnets in Cyber Security: Understanding, Detecting, and Preventing Attacks
In the ever-evolving landscape of cyber security, one of the most persistent and potent threats is the botnet. A botnet, short for robot network, is a network of computers infected with malicious software (malware) that allows a hacker to control them remotely without the owners’ knowledge. These compromised machines, often referred to as ‘bots’ or ‘zombies,’ can be used to launch a wide range of cyber attacks, making botnets a significant concern for individuals, businesses, and governments alike.
This article delves into the intricate world of botnets, exploring their architecture, common uses, methods of detection, and strategies for prevention. We will examine the impact of botnets on cyber security and provide practical advice on how to protect yourself and your organization from these insidious threats.
What is a Botnet?
A botnet is essentially a collection of internet-connected devices, which can include computers, servers, mobile devices, and IoT (Internet of Things) devices, that have been infected with malware. The malware allows a cybercriminal, known as the ‘bot herder’ or ‘attacker,’ to control these devices remotely and coordinate malicious activities. The owners of the infected devices are typically unaware that their machines have been compromised, making botnets particularly difficult to detect and dismantle.
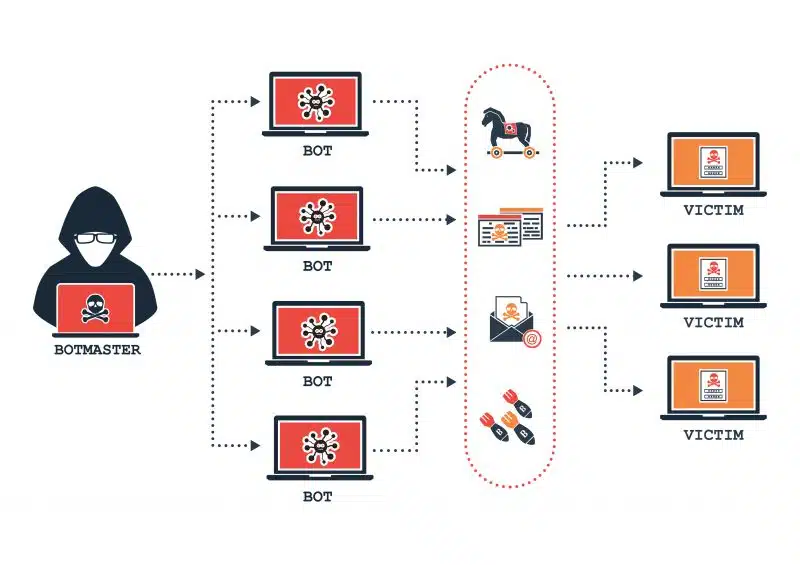
Botnet Architecture
The architecture of a botnet typically consists of the following components:
- Bots (Zombies): The infected devices within the network. These bots carry out the commands issued by the bot herder.
- Command and Control (C&C) Server: The central server(s) used by the bot herder to communicate with and control the bots. The C&C server is the nerve center of the botnet.
- Bot Herder (Attacker): The individual or group controlling the botnet. They use the C&C server to issue commands and orchestrate attacks.
How Botnets are Created
Botnets are typically created through various methods, including:
- Malware Infections: Victims unknowingly download and install malware, often through phishing emails, malicious websites, or infected software.
- Exploiting Vulnerabilities: Attackers exploit security vulnerabilities in software or operating systems to gain access to devices and install malware.
- Drive-by Downloads: Users visit compromised websites that automatically download and install malware onto their devices.
- IoT Device Hacking: Default credentials or unpatched vulnerabilities in IoT devices are exploited to turn them into bots.
Common Uses of Botnets
Botnets are versatile tools in the hands of cybercriminals and can be used for a variety of malicious purposes, including:
- Distributed Denial-of-Service (DDoS) Attacks: Overwhelming a target server or network with a flood of traffic, rendering it unavailable to legitimate users. This is one of the most common and disruptive uses of a botnet.
- Spam Distribution: Sending large volumes of spam emails to promote products, services, or phishing scams.
- Click Fraud: Generating fraudulent clicks on online advertisements to inflate revenue for the attacker.
- Data Theft: Stealing sensitive data, such as login credentials, financial information, or personal data, from infected devices.
- Cryptocurrency Mining (Cryptojacking): Using the processing power of infected devices to mine cryptocurrencies without the owners’ consent.
- Malware Distribution: Spreading malware to other devices within the network or beyond.
Detecting Botnets
Detecting botnets can be challenging, as infected devices often operate discreetly in the background. However, there are several indicators that may suggest a device is part of a botnet:
- Slow Performance: Noticeably slower computer performance, especially when performing simple tasks.
- Increased Network Activity: Unusual or excessive network activity, even when the device is not actively being used.
- Unexpected Pop-ups or Ads: A sudden increase in pop-up ads or unwanted browser extensions.
- Disabled Security Software: Antivirus software or firewalls that have been disabled without your knowledge.
- Unexplained System Crashes: Frequent system crashes or freezes.
Tools for Botnet Detection
Several tools and techniques can be used to detect botnets, including:
- Network Monitoring Tools: These tools monitor network traffic for suspicious patterns, such as unusual communication with known C&C servers.
- Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS): These systems detect malicious activity on a network by analyzing network traffic and system logs.
- Antivirus Software: Updated antivirus software can detect and remove malware associated with botnets.
- Behavioral Analysis: Analyzing the behavior of network devices to identify anomalies that may indicate botnet activity.
Preventing Botnet Infections
Preventing botnet infections is crucial to protecting your devices and data. Here are some essential steps you can take:
- Keep Software Updated: Regularly update your operating system, software applications, and antivirus software to patch security vulnerabilities.
- Use Strong Passwords: Use strong, unique passwords for all your accounts and devices. Avoid using the same password for multiple accounts.
- Be Cautious of Phishing Emails: Be wary of suspicious emails, especially those asking you to click on links or download attachments.
- Avoid Suspicious Websites: Only visit reputable websites and avoid clicking on suspicious links.
- Install a Firewall: Use a firewall to block unauthorized access to your network and devices.
- Secure IoT Devices: Change the default passwords on your IoT devices and keep their firmware updated.
- Use a Reputable Antivirus Program: Install and maintain a reputable antivirus program and keep it updated.
The Impact of Botnets on Cyber Security
Botnets pose a significant threat to cyber security due to their ability to launch large-scale attacks and remain undetected for extended periods. The impact of botnets can be far-reaching, affecting individuals, businesses, and critical infrastructure.
- Financial Losses: Botnets can cause significant financial losses through data theft, fraud, and disruption of services.
- Reputational Damage: Businesses that are victims of botnet attacks may suffer reputational damage and loss of customer trust.
- Disruption of Services: DDoS attacks launched by botnets can disrupt essential services, such as online banking, e-commerce, and government websites.
- Privacy Violations: Botnets can be used to steal personal data, leading to privacy violations and identity theft.
Real-World Examples of Botnets
Several high-profile botnet attacks have made headlines in recent years, demonstrating the scale and impact of these threats. Some notable examples include:
- Mirai Botnet: The Mirai botnet, which emerged in 2016, infected hundreds of thousands of IoT devices and launched massive DDoS attacks that disrupted major websites and online services.
- Emotet Botnet: Emotet is a sophisticated malware strain that has been used to distribute other malware and steal data from infected systems. It has been active since 2014 and continues to pose a significant threat.
- Zeus Botnet: Zeus is a well-known banking Trojan that has been used to steal login credentials and financial information from millions of users worldwide.
The Future of Botnets
As technology evolves, so do the tactics used by botnet operators. The rise of IoT devices, the increasing sophistication of malware, and the growing availability of botnet-for-hire services are all factors that contribute to the ongoing threat of botnets. [See also: Emerging Cyber Security Threats]
In the future, we can expect to see botnets becoming more sophisticated, more difficult to detect, and more targeted in their attacks. Defending against these threats will require a multi-layered approach that includes proactive security measures, advanced threat detection techniques, and international cooperation.
Conclusion
Botnets are a persistent and evolving threat in the cyber security landscape. Understanding how botnets work, how to detect them, and how to prevent infections is essential for protecting yourself and your organization from these malicious networks. By implementing the security measures outlined in this article, you can significantly reduce your risk of becoming a victim of a botnet attack. Staying informed and vigilant is key to navigating the complex world of cyber security and mitigating the risks posed by botnets.
