Application Security Testing (AST): A Comprehensive Guide
In today’s digital landscape, where applications are the backbone of businesses, ensuring their security is paramount. Application Security Testing (AST) is a critical process that helps identify and mitigate vulnerabilities in software applications. This comprehensive guide will delve into the world of application security testing, exploring its various types, benefits, and best practices. Whether you’re a seasoned security professional or just starting your journey in cybersecurity, understanding AST is essential for building secure and resilient applications.
What is Application Security Testing?
Application Security Testing (AST) is the process of evaluating software applications to identify security vulnerabilities and weaknesses. This testing is performed to ensure that applications are protected from unauthorized access, data breaches, and other security threats. AST involves a range of techniques and tools designed to analyze application code, architecture, and behavior to uncover potential risks.
The goal of application security testing is to find and fix security flaws before they can be exploited by malicious actors. This proactive approach to security helps organizations reduce the risk of cyberattacks, protect sensitive data, and maintain compliance with industry regulations.
Why is Application Security Testing Important?
The importance of application security testing cannot be overstated. Here are several key reasons why it’s a crucial aspect of software development and deployment:
- Protection Against Cyberattacks: AST helps identify and fix vulnerabilities that could be exploited by attackers, preventing data breaches and other security incidents.
- Data Protection: By securing applications, AST ensures the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of sensitive data.
- Compliance with Regulations: Many industries are subject to regulations that require organizations to implement security measures, including application security testing.
- Cost Savings: Identifying and fixing vulnerabilities early in the development lifecycle is much more cost-effective than addressing them after deployment.
- Reputation Management: A security breach can damage an organization’s reputation and erode customer trust. AST helps prevent such incidents and maintain a positive public image.
Types of Application Security Testing
There are several types of application security testing, each with its own strengths and weaknesses. Here’s an overview of the most common types:
Static Application Security Testing (SAST)
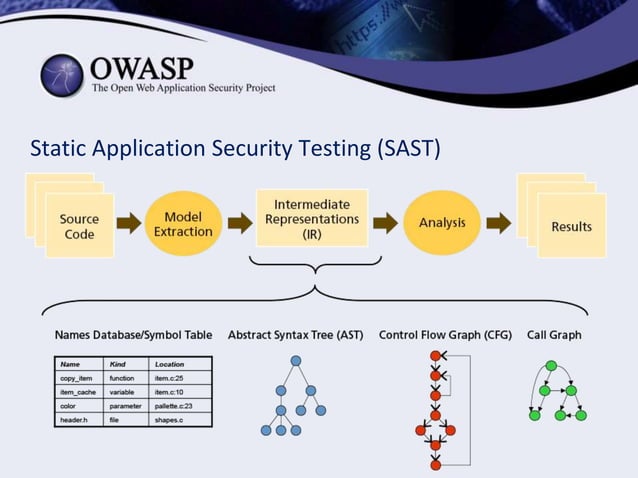
Static Application Security Testing (SAST), also known as “white box testing,” analyzes the source code of an application to identify vulnerabilities. SAST tools examine the code for patterns that are known to be associated with security flaws, such as buffer overflows, SQL injection vulnerabilities, and cross-site scripting (XSS) vulnerabilities. SAST is performed early in the development lifecycle and can help developers identify and fix vulnerabilities before they are introduced into the production environment.
Dynamic Application Security Testing (DAST)
Dynamic Application Security Testing (DAST), also known as “black box testing,” analyzes the application while it is running. DAST tools simulate real-world attacks to identify vulnerabilities in the application’s runtime environment. DAST is typically performed later in the development lifecycle, after the application has been deployed to a test environment. DAST can help identify vulnerabilities that are not detectable by SAST, such as authentication flaws, session management issues, and configuration errors.
Interactive Application Security Testing (IAST)
Interactive Application Security Testing (IAST) combines elements of SAST and DAST. IAST tools analyze the application’s code and runtime behavior simultaneously. IAST provides real-time feedback to developers as they are writing code, helping them identify and fix vulnerabilities quickly. IAST is typically performed during the development and testing phases of the software development lifecycle.
Mobile Application Security Testing (MAST)
Mobile Application Security Testing (MAST) is a specialized type of application security testing that focuses on mobile applications. MAST tools analyze mobile applications for vulnerabilities that are specific to mobile platforms, such as iOS and Android. MAST can help identify vulnerabilities in the application’s code, configuration, and data storage.
Software Composition Analysis (SCA)
Software Composition Analysis (SCA) is a type of application security testing that focuses on identifying vulnerabilities in third-party components and libraries used in an application. SCA tools analyze the application’s dependencies to identify known vulnerabilities, license compliance issues, and other risks associated with using third-party code. [See also: Open Source Security Best Practices]
Benefits of Application Security Testing
Implementing application security testing offers numerous benefits to organizations, including:
- Reduced Risk of Cyberattacks: By identifying and fixing vulnerabilities, AST helps reduce the risk of cyberattacks and data breaches.
- Improved Data Protection: AST ensures the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of sensitive data.
- Compliance with Regulations: AST helps organizations comply with industry regulations and standards.
- Cost Savings: Identifying and fixing vulnerabilities early in the development lifecycle is much more cost-effective than addressing them after deployment.
- Enhanced Reputation: AST helps prevent security breaches that can damage an organization’s reputation.
- Faster Time to Market: By automating application security testing, organizations can accelerate the development and deployment of secure applications.
Best Practices for Application Security Testing
To maximize the effectiveness of application security testing, organizations should follow these best practices:
- Integrate AST into the SDLC: Incorporate application security testing into the software development lifecycle (SDLC) to identify and fix vulnerabilities early in the process.
- Use a Combination of AST Tools: Use a combination of SAST, DAST, IAST, MAST, and SCA tools to provide comprehensive coverage of the application’s security.
- Automate Testing: Automate application security testing to improve efficiency and reduce the risk of human error.
- Prioritize Vulnerabilities: Prioritize vulnerabilities based on their severity and impact to focus on the most critical issues first.
- Provide Training: Provide training to developers and security professionals on application security testing techniques and best practices.
- Regularly Update Tools and Processes: Regularly update application security testing tools and processes to stay ahead of emerging threats and vulnerabilities.
- Establish Clear Roles and Responsibilities: Define clear roles and responsibilities for application security testing to ensure that everyone knows their part in the process.
- Foster a Security Culture: Create a security culture within the organization to promote awareness and accountability for application security.
Implementing Application Security Testing
Implementing application security testing involves several key steps:
- Assess Your Application Portfolio: Identify the applications that are most critical to your business and prioritize them for application security testing.
- Select the Right AST Tools: Choose application security testing tools that are appropriate for your application portfolio and development environment.
- Integrate AST into Your SDLC: Integrate application security testing into your software development lifecycle (SDLC) to automate the testing process.
- Configure Your AST Tools: Configure your application security testing tools to scan for the vulnerabilities that are most relevant to your application portfolio.
- Analyze the Results: Analyze the results of your application security testing scans to identify and prioritize vulnerabilities.
- Remediate Vulnerabilities: Remediate the vulnerabilities that are identified by your application security testing scans.
- Monitor Your Applications: Monitor your applications for new vulnerabilities on an ongoing basis.
The Future of Application Security Testing
The future of application security testing is likely to be shaped by several key trends:
- Increased Automation: Application security testing will become increasingly automated, with AI and machine learning playing a greater role in identifying and remediating vulnerabilities.
- Shift Left Security: Security will continue to shift left in the SDLC, with developers taking more responsibility for application security. [See also: DevSecOps: Integrating Security into DevOps]
- Cloud-Native Security: Application security testing will need to adapt to the challenges of cloud-native applications, such as microservices and containers.
- API Security: As APIs become increasingly important, application security testing will need to focus on securing APIs and preventing API-related vulnerabilities.
- Emphasis on Risk-Based Testing: Organizations will increasingly focus on risk-based application security testing, prioritizing vulnerabilities based on their potential impact on the business.
Conclusion
Application Security Testing (AST) is a vital component of any organization’s cybersecurity strategy. By understanding the different types of AST, implementing best practices, and staying ahead of emerging trends, organizations can build secure and resilient applications that protect their data, reputation, and bottom line. Investing in application security testing is an investment in the long-term success and security of your organization. Embracing AST is no longer optional; it’s a necessity in today’s threat landscape.
