What is a Continuity Plan: Ensuring Business Resilience
In today’s volatile business environment, organizations face a myriad of potential disruptions, ranging from natural disasters and cyberattacks to pandemics and economic downturns. A robust continuity plan is no longer a luxury but a necessity for survival and sustained success. This article will delve into what a continuity plan is, its key components, and why it’s crucial for every organization, regardless of size or industry.
Understanding the Essence of a Continuity Plan
A continuity plan, often referred to as a business continuity plan (BCP) or disaster recovery plan (DRP), is a comprehensive framework that outlines how an organization will continue operating during an unplanned disruption. It’s a proactive strategy designed to minimize downtime, protect critical assets, and ensure the resumption of essential functions as quickly as possible.
Think of it as an insurance policy for your business operations. While insurance protects against financial losses, a continuity plan safeguards your ability to deliver products or services, maintain customer relationships, and preserve your reputation in the face of adversity. It is about building resilience and adaptability into the very fabric of your organization.
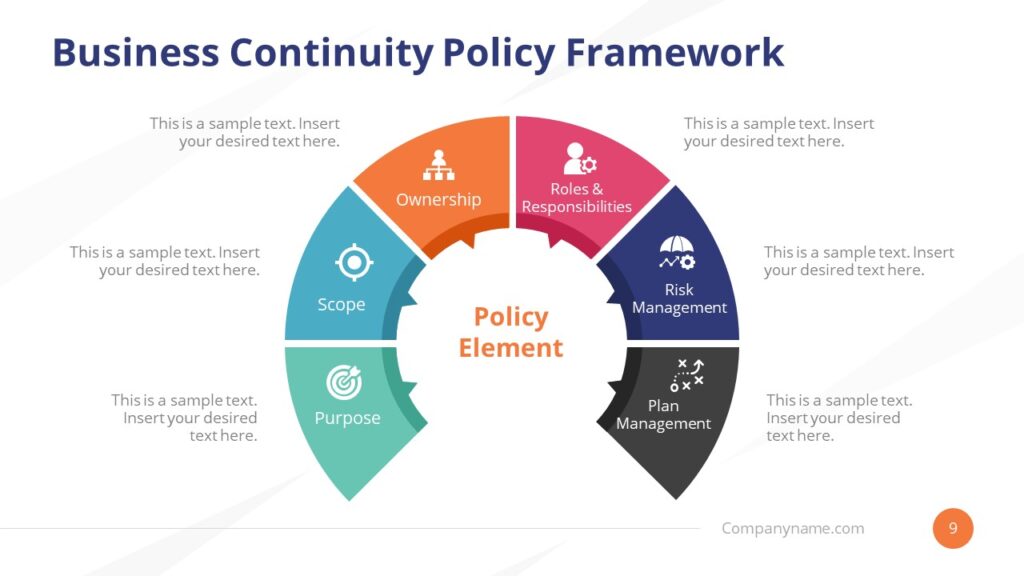
Key Components of an Effective Continuity Plan
A well-structured continuity plan typically includes several key components:
- Risk Assessment: Identifying potential threats and vulnerabilities that could disrupt business operations. This involves analyzing internal and external factors that could impact the organization’s ability to function. [See also: Conducting a Comprehensive Risk Assessment]
- Business Impact Analysis (BIA): Evaluating the potential impact of each identified risk on critical business functions. This helps prioritize recovery efforts and allocate resources effectively. The BIA determines which processes are most vital and the maximum tolerable downtime for each.
- Recovery Strategies: Developing specific plans and procedures for recovering critical business functions. This includes identifying alternative resources, establishing communication protocols, and defining roles and responsibilities.
- Data Backup and Recovery: Implementing strategies for backing up and restoring critical data. This is essential for ensuring data integrity and availability in the event of a disaster. Cloud-based solutions are increasingly popular for their scalability and accessibility.
- Communication Plan: Establishing clear communication channels for informing employees, customers, and stakeholders about the disruption and the organization’s response. This includes developing pre-scripted messages and identifying designated spokespersons.
- Testing and Training: Regularly testing the continuity plan to identify weaknesses and ensure that employees are familiar with their roles and responsibilities. This involves conducting simulations, tabletop exercises, and full-scale drills.
- Plan Maintenance: Keeping the continuity plan up-to-date by reviewing and revising it regularly to reflect changes in the business environment, technology, and organizational structure.
Why is a Continuity Plan Essential?
The benefits of having a robust continuity plan are numerous:
- Minimizes Downtime: A continuity plan helps organizations recover quickly from disruptions, minimizing downtime and lost revenue. Every minute of downtime can translate into significant financial losses and damage to reputation.
- Protects Critical Assets: A continuity plan helps protect critical assets, including data, equipment, and personnel. By having backup systems and alternative locations in place, organizations can safeguard their essential resources.
- Ensures Business Continuity: The primary goal of a continuity plan is to ensure that the business can continue operating, even in the face of adversity. This includes maintaining essential functions, meeting customer demands, and fulfilling contractual obligations.
- Enhances Reputation: A continuity plan demonstrates to customers, partners, and stakeholders that the organization is prepared for disruptions and committed to maintaining its operations. This can enhance the organization’s reputation and build trust.
- Meets Regulatory Requirements: Many industries and jurisdictions have regulatory requirements for business continuity planning. Having a continuity plan in place can help organizations comply with these requirements and avoid penalties.
- Provides a Competitive Advantage: In today’s competitive business environment, organizations with robust continuity plans have a distinct advantage. They are better positioned to weather disruptions and emerge stronger than their competitors.
Developing Your Continuity Plan: A Step-by-Step Guide
Creating a continuity plan can seem daunting, but by following a structured approach, organizations can develop a plan that meets their specific needs:
- Form a Planning Team: Assemble a team of representatives from different departments to ensure that all critical business functions are considered.
- Conduct a Risk Assessment: Identify potential threats and vulnerabilities that could disrupt business operations.
- Perform a Business Impact Analysis (BIA): Evaluate the potential impact of each identified risk on critical business functions.
- Develop Recovery Strategies: Create specific plans and procedures for recovering critical business functions.
- Document the Plan: Write a comprehensive continuity plan that includes all of the key components outlined above.
- Test the Plan: Regularly test the continuity plan to identify weaknesses and ensure that employees are familiar with their roles and responsibilities.
- Maintain the Plan: Keep the continuity plan up-to-date by reviewing and revising it regularly.
The Role of Technology in Continuity Planning
Technology plays a crucial role in continuity planning. Cloud computing, data backup and recovery solutions, and communication tools can help organizations quickly recover from disruptions and maintain their operations. [See also: The Impact of Cloud Computing on Disaster Recovery] For example, cloud-based services allow businesses to access their data and applications from anywhere in the world, even if their primary office is inaccessible. Automated backup systems ensure that data is regularly backed up and can be easily restored. And communication tools, such as instant messaging and video conferencing, enable employees to stay connected and collaborate during a disruption.
Real-World Examples of Continuity Plan Successes
Numerous organizations have successfully navigated disruptions thanks to well-executed continuity plans. Consider a hospital that was hit by a major power outage. Because it had a continuity plan in place that included backup generators and procedures for transferring patients to other facilities, the hospital was able to continue providing critical care without interruption. Another example is a financial services firm that experienced a cyberattack. Thanks to its data backup and recovery plan, the firm was able to quickly restore its systems and prevent significant financial losses. These examples highlight the importance of being prepared for the unexpected.
Continuity Plan vs. Disaster Recovery Plan
While the terms continuity plan and disaster recovery plan are often used interchangeably, there are subtle differences. A continuity plan focuses on maintaining business operations during a disruption, while a disaster recovery plan focuses on restoring IT systems and data after a disaster. In practice, these two plans are often integrated into a single comprehensive plan.
The Future of Continuity Planning
As the business environment becomes increasingly complex and unpredictable, continuity planning will become even more important. Organizations will need to adopt a more proactive and holistic approach to risk management, incorporating emerging technologies and best practices. This includes investing in cybersecurity, implementing robust data backup and recovery solutions, and developing comprehensive communication plans. The future of continuity planning will also involve greater collaboration between different departments and stakeholders, as well as a greater emphasis on employee training and awareness.
Conclusion: Investing in Business Resilience
In conclusion, a continuity plan is an essential investment for any organization that wants to ensure its long-term survival and success. By identifying potential threats, developing recovery strategies, and regularly testing the plan, organizations can minimize downtime, protect critical assets, and maintain their operations in the face of adversity. A well-executed continuity plan is not just a document; it’s a commitment to business resilience and a testament to an organization’s ability to adapt and thrive in a constantly changing world. Don’t wait for a crisis to strike – start developing your continuity plan today and safeguard your organization’s future.
