Computing at the Edge: Revolutionizing Data Processing and Beyond
In today’s hyper-connected world, data is being generated at an unprecedented rate. From smart devices to industrial sensors, the sheer volume of information presents both opportunities and challenges. Traditional cloud computing, while powerful, often struggles to keep pace with the demands of real-time processing and low latency applications. This is where computing at the edge comes into play, offering a decentralized approach that brings computation and data storage closer to the source. This article explores the concept of computing at the edge, its benefits, applications, and its transformative impact across various industries.
Understanding Edge Computing
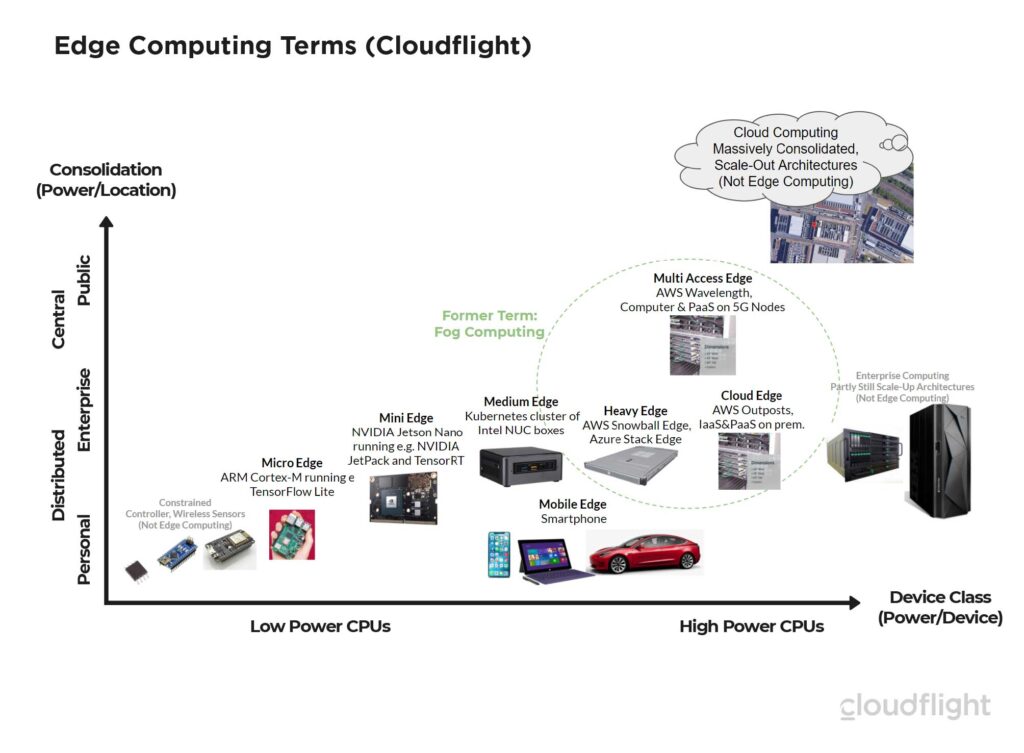
Computing at the edge, often simply called edge computing, is a distributed computing paradigm that brings data storage and computation closer to the location where it is needed, to improve response times and save bandwidth. Instead of relying solely on centralized data centers or cloud services, edge computing places processing power near the ‘edge’ of the network, where devices generate data. This reduces latency, enhances security, and enables real-time decision-making.
Key Components of an Edge Computing Architecture
- Edge Devices: These are the devices that generate data, such as sensors, cameras, and IoT devices.
- Edge Servers: These servers are located closer to the edge devices and perform data processing and analysis.
- Network Infrastructure: The network infrastructure connects the edge devices and edge servers, enabling data transmission and communication.
- Cloud Platform: The cloud platform provides centralized management, storage, and advanced analytics capabilities.
Benefits of Computing at the Edge
Computing at the edge offers a multitude of benefits, making it an increasingly attractive option for businesses and organizations across various sectors.
Reduced Latency
One of the most significant advantages of computing at the edge is reduced latency. By processing data closer to the source, it minimizes the time required for data to travel to a central server and back. This is crucial for applications that require real-time responses, such as autonomous vehicles, industrial automation, and augmented reality.
Enhanced Bandwidth Efficiency
Computing at the edge reduces the amount of data that needs to be transmitted over the network, thereby improving bandwidth efficiency. By processing data locally, only relevant information is sent to the cloud, reducing network congestion and costs.
Improved Security and Privacy
Edge computing enhances security and privacy by keeping sensitive data closer to the source. This reduces the risk of data breaches and unauthorized access. Furthermore, edge devices can implement security measures such as encryption and access control to protect data at the edge.
Increased Reliability and Resilience
Computing at the edge increases reliability and resilience by allowing applications to continue functioning even when the network connection to the cloud is disrupted. Edge devices can operate autonomously, processing data and making decisions locally, ensuring uninterrupted service.
Cost Savings
By reducing bandwidth consumption and reliance on centralized infrastructure, computing at the edge can lead to significant cost savings. Organizations can optimize their IT infrastructure and reduce expenses associated with data transmission and storage.
Applications of Computing at the Edge
The applications of computing at the edge are diverse and span across numerous industries. Here are a few notable examples:
Smart Manufacturing
In smart manufacturing, edge computing enables real-time monitoring and control of production processes. Sensors and IoT devices collect data from machines and equipment, which is then processed locally by edge servers. This allows for predictive maintenance, quality control, and optimized resource utilization. [See also: Predictive Maintenance Strategies]
Autonomous Vehicles
Autonomous vehicles rely heavily on computing at the edge to process sensor data and make real-time driving decisions. Edge computing enables vehicles to react quickly to changing road conditions and avoid accidents. The low latency processing is critical for safety and reliability. [See also: The Future of Autonomous Driving]
Healthcare
In healthcare, edge computing enables remote patient monitoring and telemedicine applications. Wearable devices and sensors collect patient data, which is then processed locally by edge devices. This allows healthcare providers to monitor patients’ health in real-time and provide timely interventions. [See also: Telemedicine and Remote Patient Monitoring]
Retail
In the retail industry, edge computing enhances the customer experience and optimizes operations. Edge devices can analyze customer behavior, personalize offers, and manage inventory in real-time. This leads to improved customer satisfaction and increased sales. [See also: Enhancing Retail with Technology]
Smart Cities
Smart cities leverage edge computing to manage various urban services, such as traffic management, waste management, and public safety. Edge devices collect data from sensors and cameras, which is then processed locally to optimize resource allocation and improve the quality of life for citizens. [See also: Building Smarter Cities]
Challenges of Implementing Computing at the Edge
While computing at the edge offers numerous benefits, there are also challenges associated with its implementation.
Security Concerns
Securing edge devices and data is a major challenge. Edge devices are often deployed in remote and unsecured locations, making them vulnerable to cyberattacks. Robust security measures, such as encryption and access control, are essential to protect data at the edge.
Management Complexity
Managing a distributed edge computing infrastructure can be complex and challenging. Organizations need to have the tools and expertise to monitor, manage, and maintain a large number of edge devices and servers. Centralized management platforms can help simplify the management process.
Connectivity Issues
Reliable connectivity is essential for edge computing to function effectively. However, in some locations, connectivity may be limited or unreliable. Organizations need to ensure that they have robust connectivity solutions in place to support their edge computing deployments.
Scalability Challenges
Scaling an edge computing infrastructure can be challenging. Organizations need to plan for future growth and ensure that their edge computing infrastructure can handle increasing data volumes and processing demands. Cloud-based management platforms can help with scalability.
The Future of Computing at the Edge
Computing at the edge is poised for significant growth in the coming years. As the number of connected devices continues to increase, the demand for real-time processing and low latency applications will drive further adoption of edge computing. The convergence of edge computing with other technologies, such as artificial intelligence and 5G, will unlock new possibilities and transform industries.
Edge AI
Edge AI combines the power of artificial intelligence with the capabilities of computing at the edge. This enables real-time AI processing at the edge, allowing devices to make intelligent decisions without relying on the cloud. Edge AI is transforming applications such as autonomous vehicles, robotics, and industrial automation. [See also: The Rise of Edge AI]
5G and Edge Computing
5G technology is a key enabler of edge computing. The high bandwidth and low latency of 5G networks make it ideal for supporting edge computing applications. 5G enables edge devices to communicate with each other and with the cloud more efficiently, opening up new opportunities for innovation. [See also: 5G and Its Impact on Technology]
Conclusion
Computing at the edge is revolutionizing data processing and transforming industries by bringing computation and data storage closer to the source. Its benefits, including reduced latency, enhanced bandwidth efficiency, improved security, and increased reliability, make it an attractive option for businesses and organizations across various sectors. While there are challenges associated with its implementation, the future of computing at the edge is bright, with the convergence of edge computing with other technologies like AI and 5G unlocking new possibilities and driving further innovation. As the demand for real-time processing and low latency applications continues to grow, computing at the edge will play an increasingly important role in shaping the future of technology. The ability to process data locally, make quick decisions, and operate independently makes computing at the edge a critical component of modern infrastructure. Embracing computing at the edge is no longer a futuristic concept, but a strategic imperative for organizations seeking to stay competitive and thrive in the digital age. This distributed approach ensures businesses can harness the full potential of their data, driving efficiency, innovation, and growth. The shift towards computing at the edge marks a significant step forward in how we manage and utilize data, paving the way for a more connected and intelligent world. Therefore, understanding and adopting computing at the edge is crucial for anyone looking to leverage the power of data in real-time. The transformative potential of computing at the edge is undeniable, promising a future where data-driven decisions are made faster, more efficiently, and closer to the point of action. This paradigm shift is not just about technology; it’s about empowering businesses and individuals to make better, more informed decisions in a rapidly evolving world. The growth and adoption of computing at the edge are set to continue, making it a vital area of focus for organizations and technologists alike.
