Decoding the Man-in-the-Middle (MITM) Attack: A Comprehensive Guide
In today’s interconnected world, cybersecurity threats are constantly evolving, demanding heightened vigilance and proactive defense mechanisms. Among these threats, the Man-in-the-Middle (MITM) attack stands out as a particularly insidious and challenging form of cybercrime. This article aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of MITM attacks, exploring their mechanics, potential consequences, and effective mitigation strategies. Understanding the intricacies of a man in the middle attack is crucial for individuals and organizations alike to safeguard their sensitive data and maintain a secure online environment. We’ll break down how a MITM attack works, the different types, and most importantly, how to protect yourself. This is not just about technical jargon; it’s about understanding a real threat to your digital security.
What is a Man-in-the-Middle Attack?
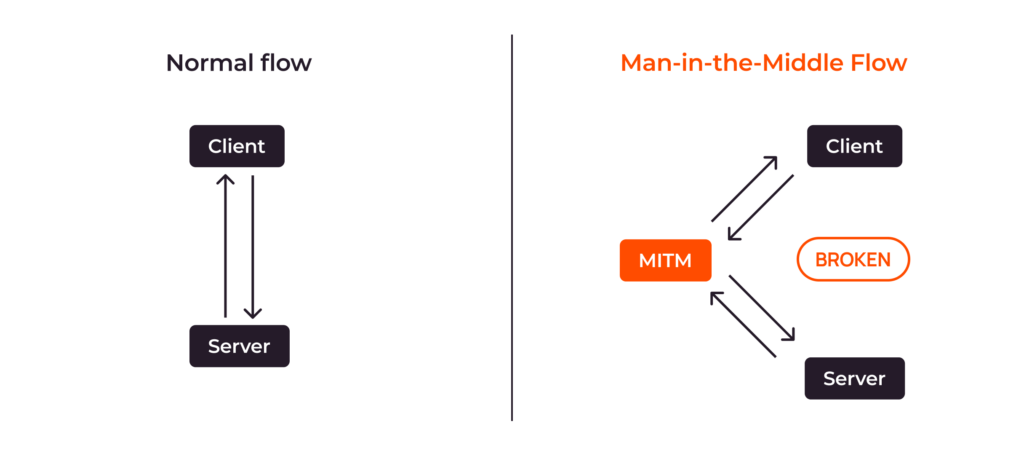
A Man-in-the-Middle (MITM) attack is a type of cyberattack where an attacker intercepts communication between two parties, secretly relaying and potentially altering the information exchanged. The attacker positions themselves between the sender and receiver, making them believe they are communicating directly with each other. In reality, all data passes through the attacker’s control, allowing them to eavesdrop, steal sensitive information, or even manipulate the communication for malicious purposes. A successful MITM attack is often undetectable to the victim, making it particularly dangerous.
Think of it like this: you’re trying to have a private conversation with a friend, but someone is secretly listening in and even changing what you say to each other. That’s essentially what a man in the middle attack does in the digital realm.
How MITM Attacks Work
The process of a MITM attack typically involves several key stages:
- Interception: The attacker gains access to the communication channel between the two parties. This can be achieved through various methods, such as exploiting vulnerabilities in network security, using rogue Wi-Fi hotspots, or employing malware.
- Interception and Decryption: Once the traffic is intercepted, the attacker may need to decrypt the data if it’s encrypted. Weak encryption protocols or the lack of proper SSL/TLS implementation make this step easier for the attacker.
- Data Manipulation (Optional): The attacker can choose to simply eavesdrop on the communication, stealing sensitive information like passwords, credit card details, or personal data. Alternatively, they can modify the data being transmitted, injecting malicious code, altering financial transactions, or spreading misinformation.
- Forwarding: The attacker then forwards the intercepted and potentially modified data to the intended recipient, making it appear as if the communication is legitimate.
Types of MITM Attacks
MITM attacks can manifest in various forms, each leveraging different techniques to intercept and manipulate communication. Some common types include:
Wi-Fi Eavesdropping
Attackers set up fake Wi-Fi hotspots that mimic legitimate networks, enticing users to connect. Once connected, all traffic passing through the hotspot is under the attacker’s control. This is a common entry point for a man in the middle attack.
IP Spoofing
Attackers forge IP addresses to impersonate trusted sources, redirecting traffic to malicious servers under their control. This allows them to intercept and manipulate data intended for the legitimate destination.
ARP Spoofing
Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) spoofing involves sending falsified ARP messages over a local area network. This can link the attacker’s MAC address with the IP address of a legitimate device or server on the network, causing traffic intended for that device to be misdirected to the attacker.
DNS Spoofing
Domain Name System (DNS) spoofing involves altering DNS records to redirect users to malicious websites that resemble legitimate ones. This is often used to steal login credentials or distribute malware. Imagine typing in your bank’s website address, but being secretly redirected to a fake website that looks identical. This is a classic example of how DNS spoofing can facilitate a MITM attack.
SSL Stripping
SSL stripping downgrades secure HTTPS connections to unencrypted HTTP, allowing attackers to intercept sensitive data transmitted between the user and the web server. This type of man in the middle attack exploits vulnerabilities in how websites handle secure connections.
HTTPS Spoofing
HTTPS Spoofing involves creating a fake website that mimics a legitimate HTTPS website, complete with a valid-looking SSL certificate. Users may be tricked into entering sensitive information on the fake website, believing it is secure. This is a sophisticated form of MITM attack that requires careful execution.
Examples of Man-in-the-Middle Attacks
To further illustrate the nature of MITM attacks, consider these real-world examples:
- Public Wi-Fi at Cafes: Connecting to unsecured public Wi-Fi networks without a VPN makes you vulnerable to MITM attacks. Attackers can easily intercept your traffic and steal login credentials or personal information.
- Compromised Routers: Attackers can compromise routers to redirect traffic to malicious servers, allowing them to intercept and manipulate data. This can affect all devices connected to the compromised router.
- Malware Infections: Malware can be used to install a man in the middle proxy on a user’s device, intercepting all network traffic.
- Attacks on Financial Institutions: Attackers may use MITM attacks to steal financial information, such as credit card numbers and bank account details, by intercepting transactions between users and financial institutions.
Consequences of MITM Attacks
The consequences of a successful MITM attack can be severe, both for individuals and organizations:
- Data Theft: Sensitive information, such as passwords, credit card details, personal data, and trade secrets, can be stolen and used for malicious purposes.
- Financial Loss: Attackers can intercept financial transactions and steal funds, leading to significant financial losses for victims.
- Identity Theft: Stolen personal information can be used to commit identity theft, opening fraudulent accounts, and damaging the victim’s credit rating.
- Reputational Damage: Organizations that suffer a MITM attack can experience significant reputational damage, leading to loss of customer trust and business opportunities.
- Malware Distribution: Attackers can inject malicious code into websites or software, spreading malware to unsuspecting users.
How to Prevent MITM Attacks
Protecting yourself and your organization from MITM attacks requires a multi-layered approach, encompassing technical safeguards, user education, and proactive monitoring:
Use Strong Encryption
Ensure that all communication channels use strong encryption protocols, such as TLS 1.3 or higher. Avoid using outdated or weak encryption protocols, as they are more vulnerable to attacks.
Use a VPN
A Virtual Private Network (VPN) encrypts your internet traffic and routes it through a secure server, protecting it from eavesdropping. This is particularly important when using public Wi-Fi networks. Using a VPN is a simple yet effective way to prevent a man in the middle attack.
Verify Website Security Certificates
Before entering any sensitive information on a website, verify that it has a valid SSL certificate. Look for the padlock icon in the address bar and ensure that the website’s address starts with “https://”. Be wary of websites with invalid or expired certificates.
Be Cautious of Public Wi-Fi
Avoid using unsecured public Wi-Fi networks for sensitive transactions. If you must use public Wi-Fi, use a VPN to encrypt your traffic. Never enter passwords or other sensitive information on websites that are not secured with HTTPS.
Implement Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
MFA adds an extra layer of security by requiring users to provide multiple forms of authentication, such as a password and a code sent to their mobile device. This makes it more difficult for attackers to gain access to accounts, even if they have stolen the password.
Keep Software Up-to-Date
Regularly update your operating system, web browser, and other software to patch security vulnerabilities. Attackers often exploit known vulnerabilities in outdated software to launch MITM attacks.
Educate Users
Educate users about the risks of MITM attacks and how to identify suspicious activity. Train them to be cautious of phishing emails, fake websites, and unsecured Wi-Fi networks. A well-informed user is a strong defense against a man in the middle attack.
Monitor Network Traffic
Implement network monitoring tools to detect suspicious activity, such as unusual traffic patterns or unauthorized access attempts. This can help you identify and respond to MITM attacks in real-time.
Use DNSSEC
DNSSEC (Domain Name System Security Extensions) adds a layer of security to the DNS system, preventing DNS spoofing attacks. By implementing DNSSEC, you can ensure that users are directed to the correct website and not to a malicious imposter.
Employ Intrusion Detection and Prevention Systems (IDPS)
IDPS can help detect and prevent MITM attacks by monitoring network traffic for malicious activity and automatically blocking or alerting administrators to potential threats.
Conclusion
Man-in-the-Middle (MITM) attacks pose a significant threat to online security, allowing attackers to intercept and manipulate communication between unsuspecting parties. By understanding the mechanics of these attacks and implementing effective prevention strategies, individuals and organizations can significantly reduce their risk of falling victim. Staying informed, practicing safe online habits, and employing robust security measures are essential for protecting yourself in today’s increasingly interconnected world. Remember, vigilance is key in the ongoing battle against cyber threats like the man in the middle attack. [See also: Understanding Network Security] [See also: Best VPN Services for 2024] [See also: How to Identify Phishing Emails]
