4G vs 5G: Unveiling the Key Differences and What They Mean for You
The world is increasingly connected, and the backbone of this connectivity is cellular technology. For years, 4G has been the standard, providing us with the speed and reliability we need for everyday tasks. However, a new generation is here: 5G. But what exactly is 5G, and what are the key differences between 4G and 5G? This article dives deep into the technical specifications, real-world implications, and future prospects of both technologies, offering a clear understanding for the average user.
Understanding 4G: The Foundation of Mobile Connectivity
4G, or Fourth Generation, is the successor to 3G. It was designed to provide significantly faster data speeds and improved network capacity compared to its predecessor. 4G networks use technologies like LTE (Long-Term Evolution) and WiMAX to achieve these higher speeds.
Key Features of 4G
- Faster Data Speeds: 4G offers significantly faster download and upload speeds compared to 3G. In ideal conditions, 4G LTE can reach speeds of up to 100 Mbps.
- Improved Network Capacity: 4G networks can handle more users and devices simultaneously without significant performance degradation.
- Lower Latency: Latency refers to the delay in data transmission. 4G offers lower latency compared to 3G, resulting in a more responsive user experience.
- Voice over LTE (VoLTE): VoLTE allows voice calls to be made over the 4G network, improving call quality and reducing the load on the older 2G and 3G networks.
4G has enabled a wide range of applications and services, including streaming high-definition video, online gaming, and mobile broadband access. It has become an essential part of our daily lives, connecting us to the internet and each other.
The Dawn of 5G: A New Era of Connectivity
5G, or Fifth Generation, is the latest generation of cellular technology. It promises to deliver even faster data speeds, lower latency, and greater network capacity compared to 4G. 5G networks utilize new technologies and spectrum bands to achieve these advancements.
Key Features of 5G
- Ultra-Fast Data Speeds: 5G offers significantly faster download and upload speeds compared to 4G. In ideal conditions, 5G can reach speeds of up to 10 Gbps, which is ten times faster than 4G LTE.
- Ultra-Low Latency: 5G boasts ultra-low latency, as low as 1 millisecond. This is crucial for applications that require real-time responsiveness, such as autonomous vehicles and augmented reality.
- Massive Network Capacity: 5G networks can support a massive number of devices simultaneously, making it ideal for the Internet of Things (IoT) and smart city applications.
- Network Slicing: 5G allows for network slicing, which means that the network can be divided into virtual slices, each optimized for a specific application or service.
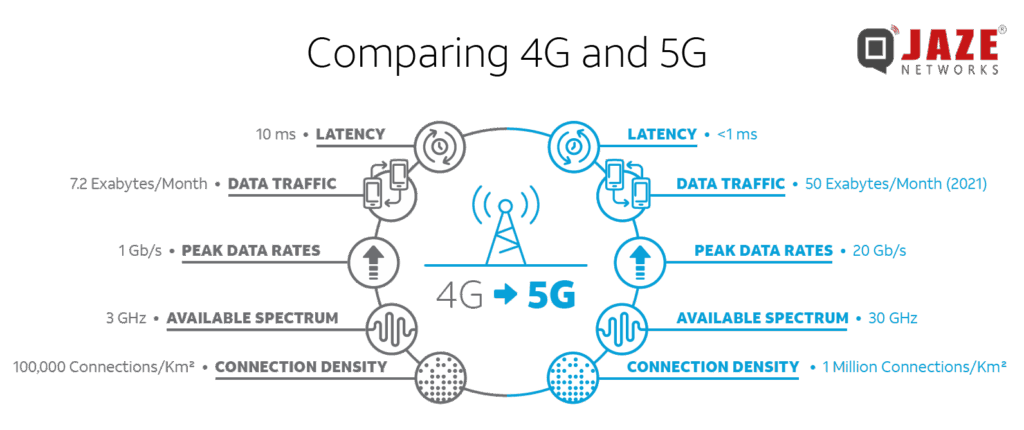
4G vs 5G: A Detailed Comparison
To fully understand the difference between 4G and 5G, let’s delve into a more detailed comparison of their key aspects:
Speed
This is perhaps the most noticeable difference between 4G and 5G. 5G offers significantly faster data speeds compared to 4G. While 4G LTE can reach speeds of up to 100 Mbps, 5G can reach speeds of up to 10 Gbps. This means that you can download movies in seconds, stream high-resolution video without buffering, and experience a more responsive online gaming experience with 5G.
Latency
Latency is another crucial difference between 4G and 5G. 5G offers ultra-low latency, as low as 1 millisecond, compared to 4G’s latency of around 50 milliseconds. This lower latency is essential for applications that require real-time responsiveness, such as autonomous vehicles, augmented reality, and remote surgery. Imagine controlling a robotic arm remotely with virtually no delay – that’s the power of 5G’s low latency.
Network Capacity
5G networks have a much higher capacity than 4G networks. This means that 5G can support a much larger number of devices simultaneously without significant performance degradation. This is particularly important for the Internet of Things (IoT), where billions of devices are expected to be connected to the internet in the coming years. [See also: IoT Security Best Practices] 5G can handle the massive data traffic generated by these devices, enabling smart cities, connected homes, and industrial automation.
Technology
The underlying technologies used by 4G and 5G are also quite different. 4G primarily uses LTE and WiMAX, while 5G utilizes new technologies such as millimeter wave (mmWave), massive MIMO (Multiple-Input Multiple-Output), and beamforming. mmWave allows 5G to operate on higher frequencies, enabling faster data speeds. Massive MIMO uses a large number of antennas to improve network capacity and coverage. Beamforming focuses the radio signal towards specific users, improving signal strength and efficiency. These technological advancements are what allow 5G to achieve its superior performance compared to 4G. Understanding these technological differences between 4G and 5G is key to appreciating the advancements that 5G brings.
Spectrum
Spectrum refers to the range of radio frequencies used for wireless communication. 4G primarily uses lower frequency bands, while 5G utilizes both lower and higher frequency bands, including mmWave. The use of higher frequency bands allows 5G to achieve faster data speeds, but it also presents challenges in terms of coverage and signal penetration. mmWave signals are easily blocked by buildings and other obstacles, requiring a denser network of base stations to provide adequate coverage. The deployment of 5G infrastructure is therefore more complex and expensive than that of 4G.
Use Cases
The differences between 4G and 5G also translate into different use cases. While 4G is well-suited for everyday tasks such as web browsing, email, and streaming video, 5G opens up a whole new range of possibilities. Some of the key use cases for 5G include:
- Autonomous Vehicles: 5G’s ultra-low latency and high reliability are crucial for autonomous vehicles, enabling them to communicate with each other and with infrastructure in real-time.
- Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR): 5G’s high bandwidth and low latency are essential for delivering immersive AR and VR experiences.
- Remote Surgery: 5G’s ultra-low latency allows surgeons to perform remote surgery with precision and minimal delay.
- Industrial Automation: 5G enables industrial automation by connecting machines, sensors, and robots in real-time, improving efficiency and productivity.
- Smart Cities: 5G provides the connectivity infrastructure for smart cities, enabling a wide range of applications such as smart lighting, traffic management, and public safety.
The Future of Mobile Connectivity: 5G and Beyond
5G is not just an incremental improvement over 4G; it represents a paradigm shift in mobile connectivity. It is poised to transform industries and enable new applications that were previously impossible. While 4G will continue to be relevant for many years to come, 5G is the future of mobile connectivity, and its impact will be felt across all aspects of our lives.
The rollout of 5G is still in its early stages, but it is rapidly expanding. As more and more 5G networks are deployed and more 5G-enabled devices become available, we can expect to see even more innovative applications and services emerge. The difference between 4G and 5G is not just about faster speeds; it’s about unlocking a new era of possibilities.
Is 5G Worth the Upgrade?
The question on many minds is whether upgrading to 5G is worth it. For some, the benefits of faster speeds and lower latency may be immediately apparent, particularly if they frequently use bandwidth-intensive applications like video streaming or online gaming. For others, the difference between 4G and 5G may not be as noticeable, especially if they primarily use their mobile devices for basic tasks like web browsing and email. However, as 5G networks become more widespread and more applications are optimized for 5G, the benefits of upgrading will become increasingly clear. Furthermore, the increased network capacity of 5G will lead to a more reliable and consistent mobile experience, even in crowded areas.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the difference between 4G and 5G is significant and far-reaching. 5G offers faster data speeds, lower latency, and greater network capacity compared to 4G. While 4G has served us well for many years, 5G is the future of mobile connectivity, enabling a wide range of new applications and services. As 5G networks continue to be deployed and more 5G-enabled devices become available, we can expect to see even more innovation and transformation in the years to come. The transition from 4G to 5G is not just about upgrading our devices; it’s about embracing a new era of connectivity and unlocking the potential of a truly connected world. Understanding the fundamental differences between 4G and 5G is crucial for navigating this technological shift and making informed decisions about our mobile connectivity needs.
